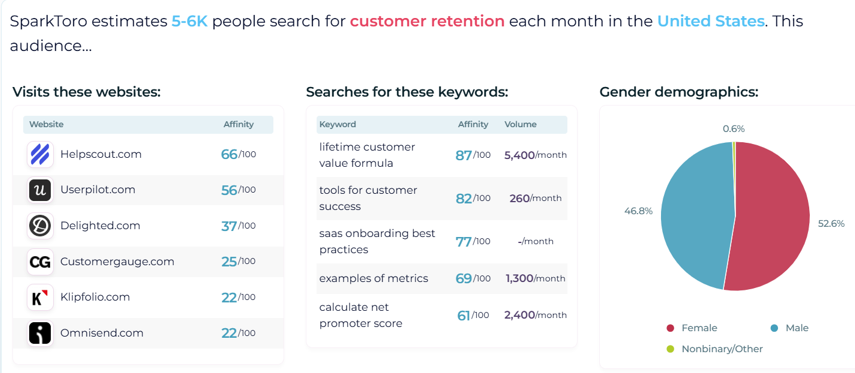
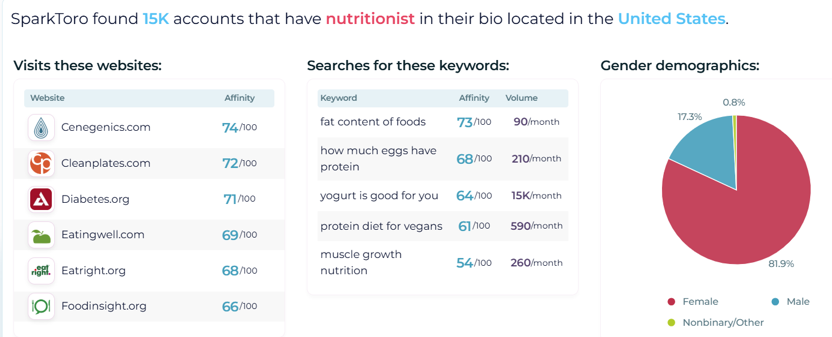
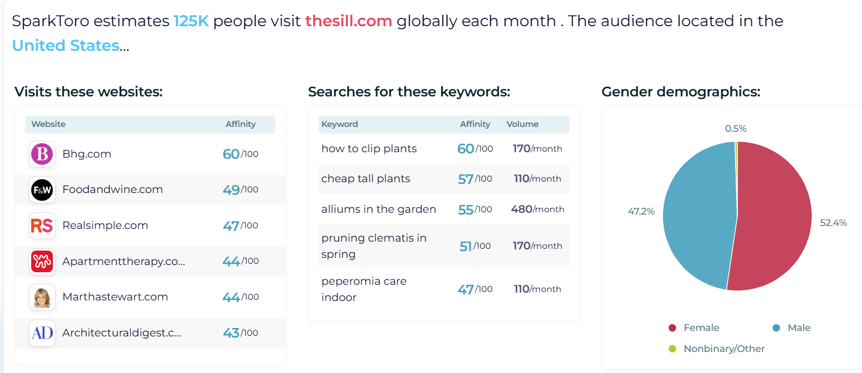
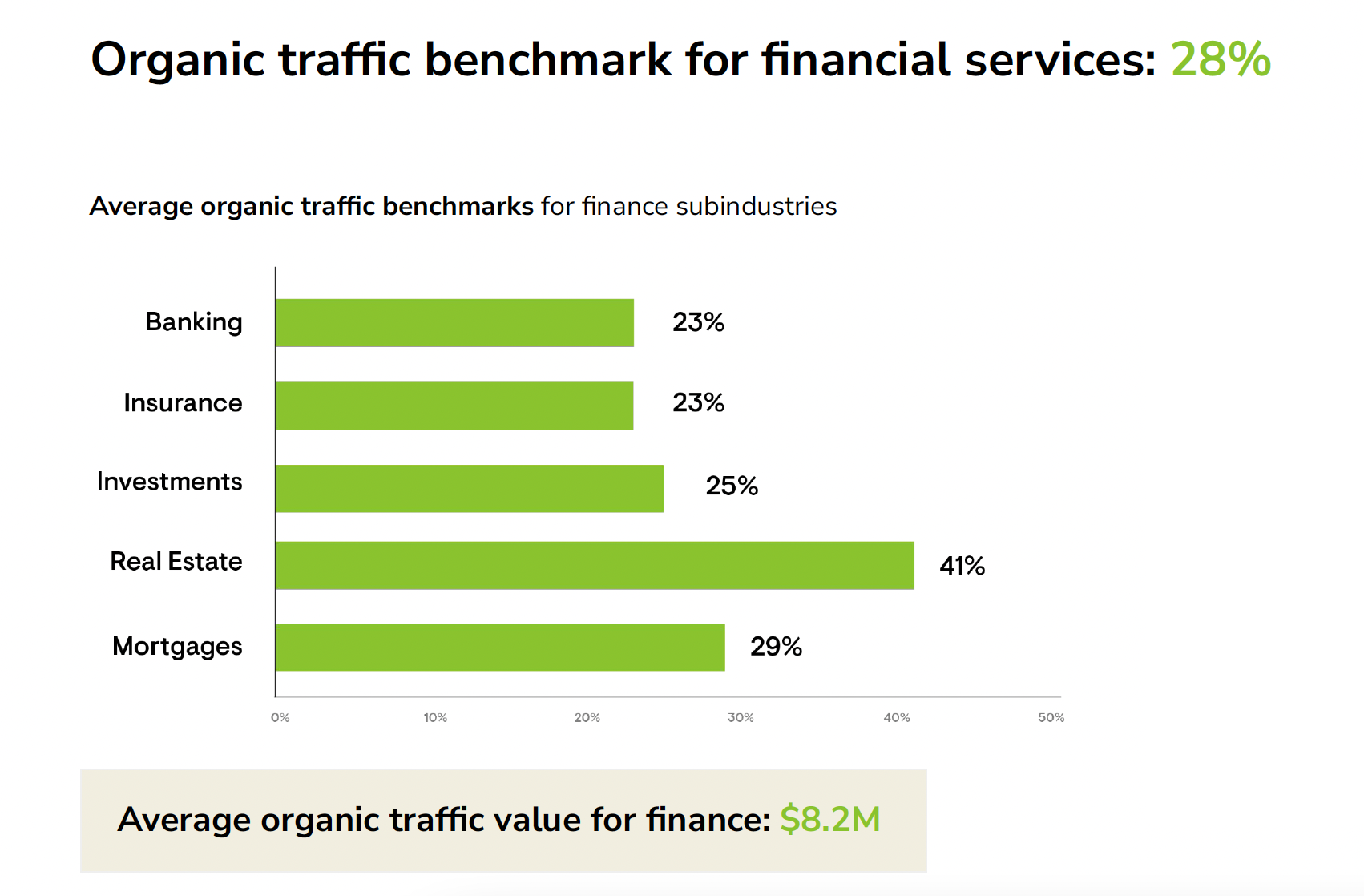
As a search engine optimization specialist, you already know the importance of content that answers query intent. But what happens when an internet user doesn’t know what information they need?
Google took it upon itself to solve this with the release of Google Discover, first seen in 2018.
Known as Google Feed until 2018, Discover uses data the search engine has gathered about you to create a personalized content feed that proactively delivers relevant content.
Available exclusively on mobile devices, it goes beyond responding to queries by anticipating user behavior and delivering content it thinks you will find interesting and valuable.
Taking user activity into account to deliver results, it presents a new and powerful way to drive web traffic.
Google Discover can include a variety of different types of content, including news, articles, videos, advertisements, and special rich results like live sports scores. It appears on Google’s homepage and is highly personalized to each user.
As machine learning and artificial intelligence continue advancing, this new form of discovery looks likely to become more common – and accurate.
In this piece, we’ll take a deeper look at this technology and show you ways you can put it to work for you.
How Does Google Discover Work?
Google makes content eligible to appear in Discover once it has been indexed, and Google has determined it doesn’t violate its content policies.
Similar to the AI-driven video recommendations made by platforms like TikTok and Facebook, Google Discover uses an algorithm to create a custom feed.
Using information collected from user data, Discover has moved the search engine toward “query-less search,” in which the understanding of the individual user replaces the understanding of a singular query.
The user is the central focus with Discover.
Google Discover automatically shows personalized content based on a user’s:
- Search history.
- Browser history.
- App activity.
- Location (dependent on your Google account setup and privacy settings).
Google Discover uses your information to identify and display topics Google believes will be relevant for you, known as “interests.”
What’s Interesting?
To gain a deeper understanding of Google Discover interests, I looked at over 700 Google Discover interests (provided by members of the SEO community).
While this is an extraordinarily small sample size compared to all potential interests, there were a few notable observations.
Interests Related To Sports & Entertainment Were The Most Prevalent
While my Discover feed primarily focuses on who former Bachelor Peter Weber is dating, I imagine others’ feeds are full of the latest sports updates.
It’s Largely Focused On Hobbies & Activities
Whatever you do in your pastime – whether it be baking or beekeeping – you’re likely to see content on your favorite after-work activities.
Brands Also Had A Strong Presence
Almost every submission included specific brands or local businesses.
While Discover aims to suggest new content to users, it still remembers your go-to stores and restaurants.
SEO Has Its Own Category
We love SEO so much that it got its own category.
Thanks to all the SEO folks who filled out my Google Form.
Below is a visual of all submitted user interests, organized by category (i.e., finance, education, etc.) and type of entity (i.e., brand, product, person, etc.).
 Screenshot from author, February 2023
Screenshot from author, February 2023User Input
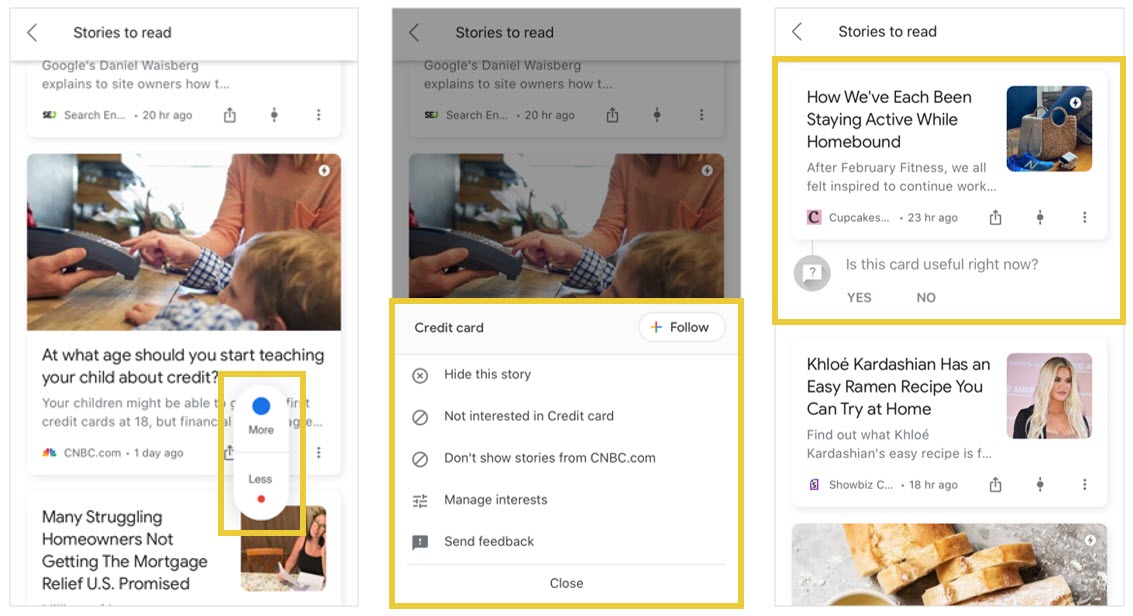
Users can also provide direct feedback to further customize their feed by following or unfollowing topics, selecting “show more” or “show less,” and choosing not to see content from certain publishers.
Occasionally, Google will directly prompt the user for feedback.
 Screenshot from author, February 2023
Screenshot from author, February 2023Is it Possible To Optimize For Google Discover?
Yes, it is possible to optimize for Google Discover. Google Discover is a personalized recommendation engine that aims to deliver relevant and engaging content to users based on their interests and browsing history.
To optimize for Google Discover, it’s important to focus on creating high-quality and engaging content that resonates with your target audience.
The key difference between traditional search engine optimization and optimizing for Google Discover is a shift in focus from the query to the user.
While traditional SEO aims to target specific queries and provide the most relevant results, Google Discover focuses on delivering content that match users’ interests without explicit search queries.
There are a number of steps publishers can take to increase their visibility in Discover.
Those include:
Importance Of Expertise, Experience, Authority, And Trust (E-E-A-T)
Google Discover strives to recommend content that is not only interesting but also trustworthy, reliable, and credible.
The elements of E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trustworthiness) play a pivotal role in determining the suitability of content for recommendations. You didn’t expect Google to recommend just any content, did you?
When creating content for Google Discover, it’s important to be selective and prioritize topics that align with your expertise or the expertise and experience of your content creators.
Focus on providing valuable and relevant information on those subjects to build authority in your niche over time, which yields better long-term results compared to broad topics that don’t closely align with your brand and expertise.
Once you’ve identified suitable topics, take the following steps to improve your E-E-A-T signals:
- Produce High-Quality Content: Create well-researched, accurate, and informative content that brings value to your audience. Avoid publishing misleading, sensational, or low-quality content that can harm trust.
- Regularly Update Content: Clearly indicate the publication dates, update outdated articles, and annotate dates of updates when relevant.
- Showcase Expertise: Highlight the credentials, qualifications, and experience of your authors or content creators to demonstrate expertise. Include author bios, professional backgrounds, certifications, or industry recognition.
- Leverage Structured Data: Leverage Article and Author markup to provide clearly annotated information to search engines.
- Cultivate a Reputable Track Record: Consistently publish relevant, high-quality content to establish a track record of consistency and build authority in your niche.
- Ensure Transparency: Clearly attribute sources, cite credible references, and be transparent about editorial policies, fact-checking processes, quality assurance, and any affiliations or sponsorships.
- Improve Website Experience: Create trustworthy, user-friendly experiences by focusing on factors like mobile-friendliness, page load speed, HTTPS, and overall website design.
By following these steps, you can enhance your E-E-A-T factors, provide valuable content, and create a trustworthy and credible presence that improves your chances of being recommended in Google Discover.
Isn’t Google Discover Just News?
Well, kind of.
One of the goals of Google Discover is to serve fresh content – and scrolling through the Discover feed, it is mostly news.
But when clients from other industries started seeing Discover traffic in Google Search Console (GSC), it was time to investigate.
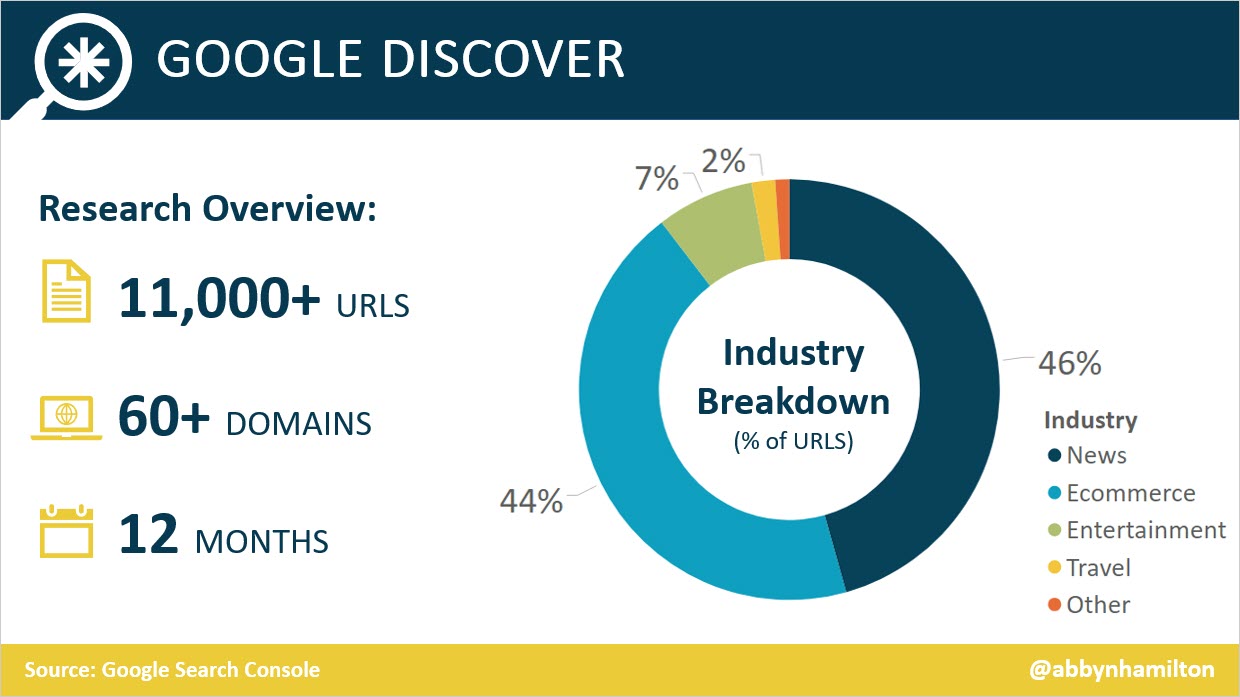
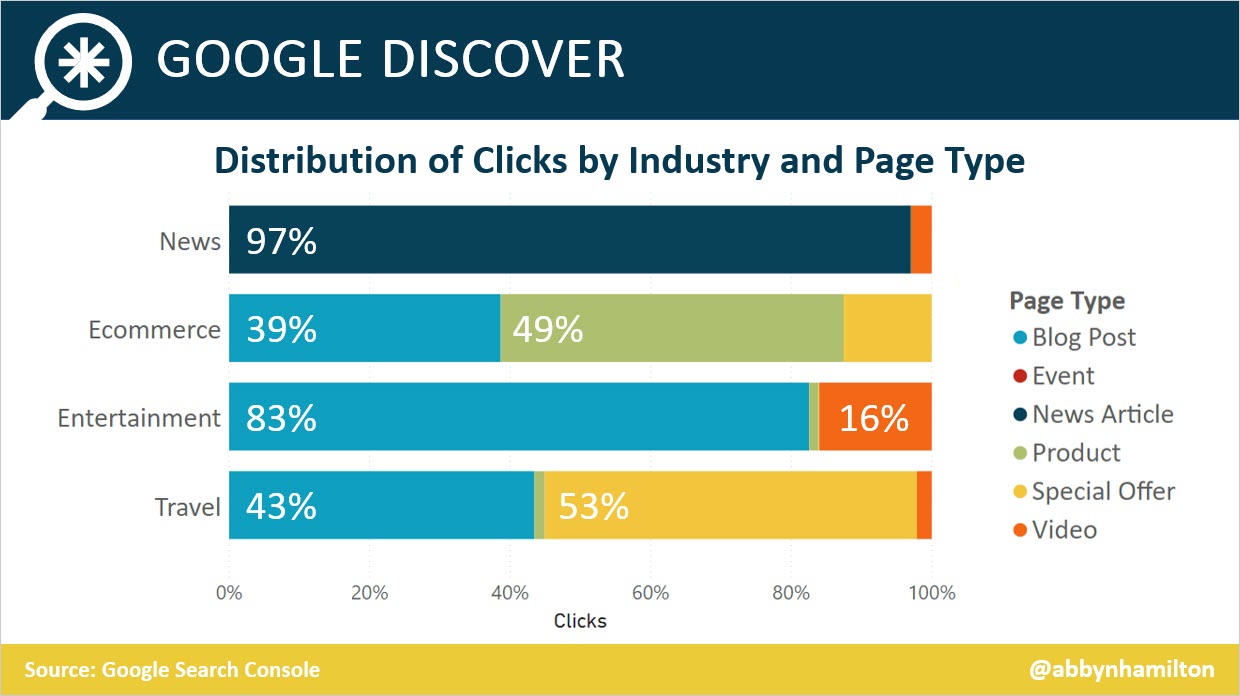
I analyzed 12 months of Google Discover traffic to over 11,000 URLs from 62 domains. Of those 11,000 URLs:
- 46% were from news sites.
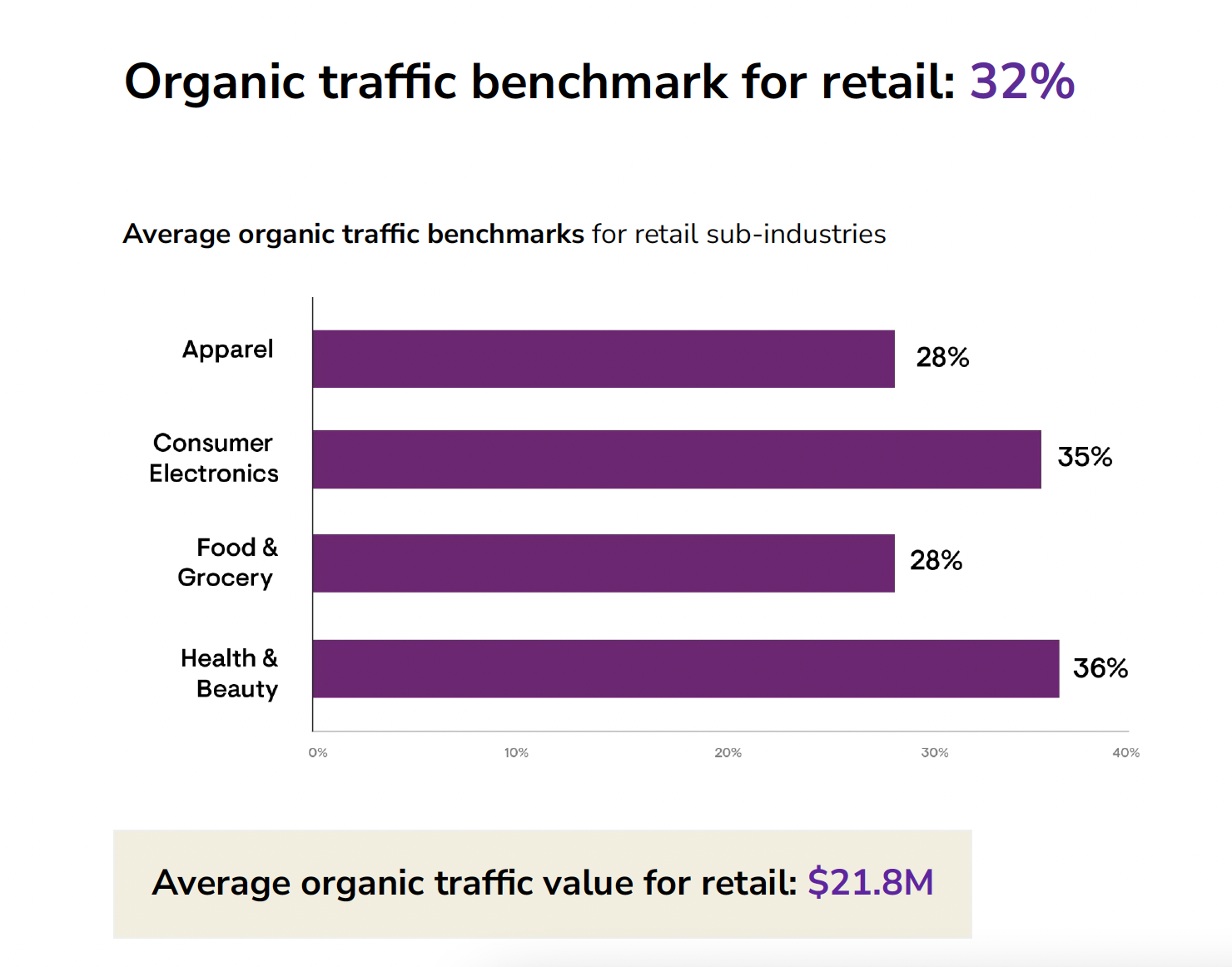
- 44% were from ecommerce sites.
- 7% were from entertainment sites.
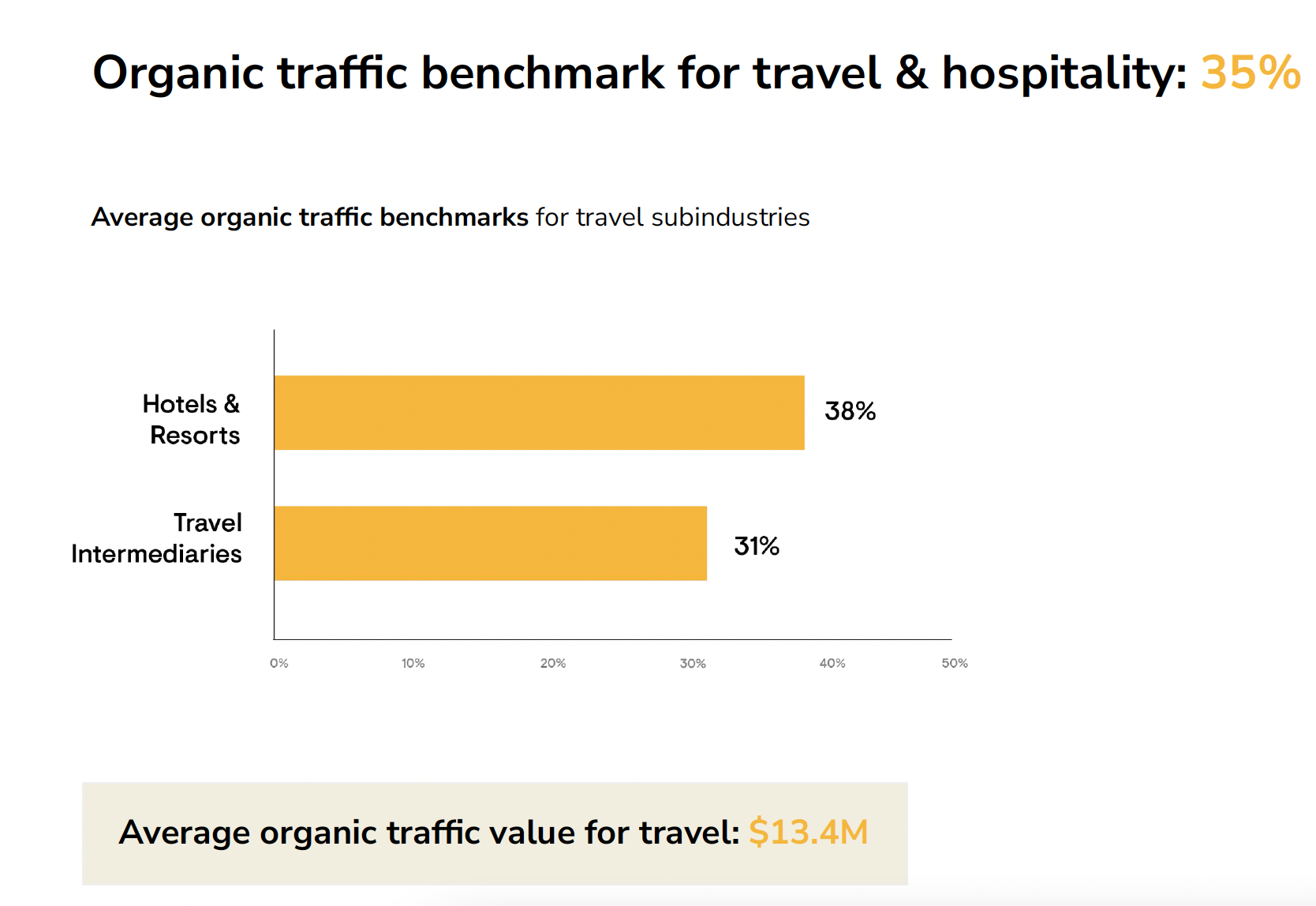
- 2% were from travel sites.
The remaining 1% were from other industries including:
- B2B.
- Automotive.
- Education.
- Finance.
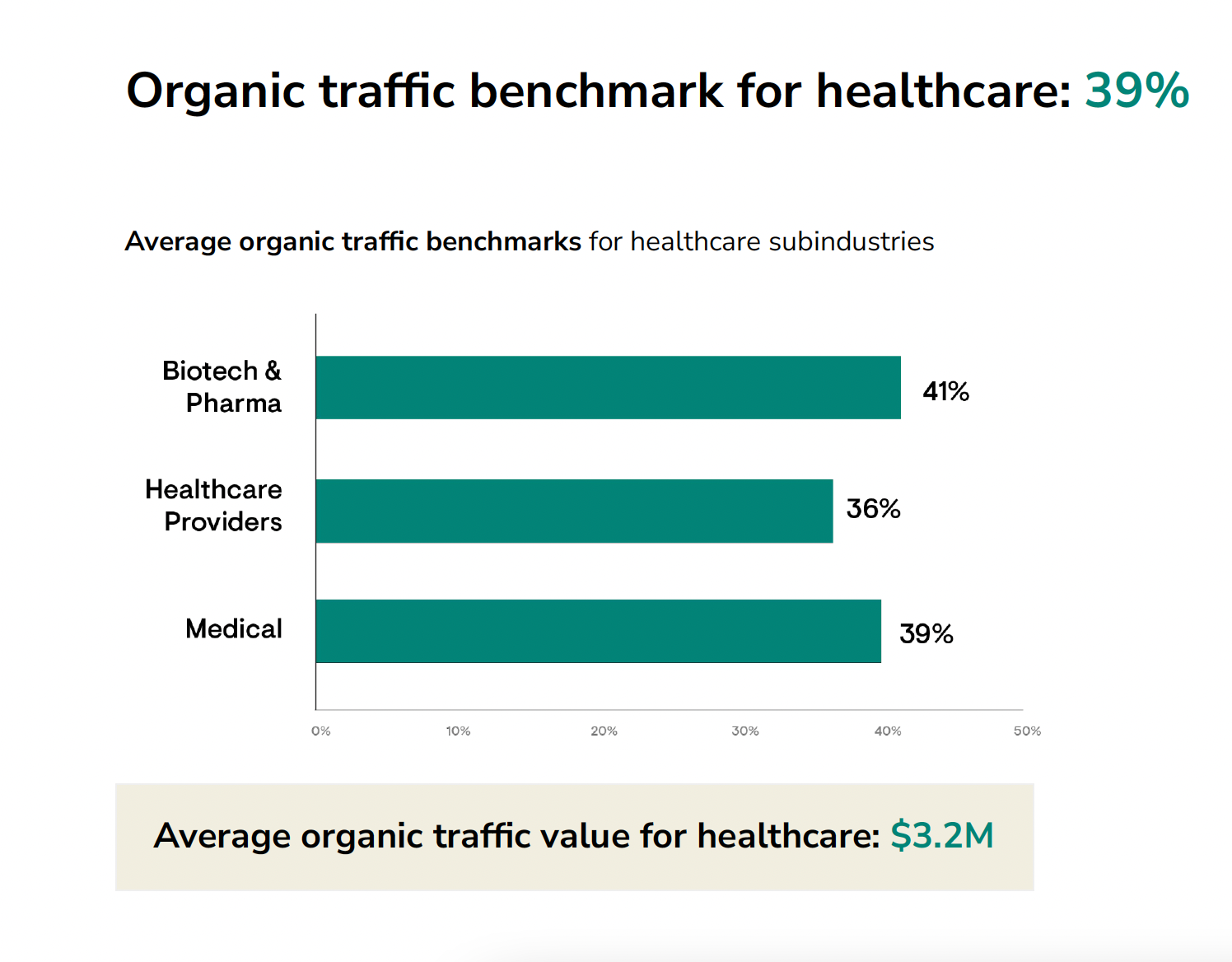
- Health.
 Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020
Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020Research Findings
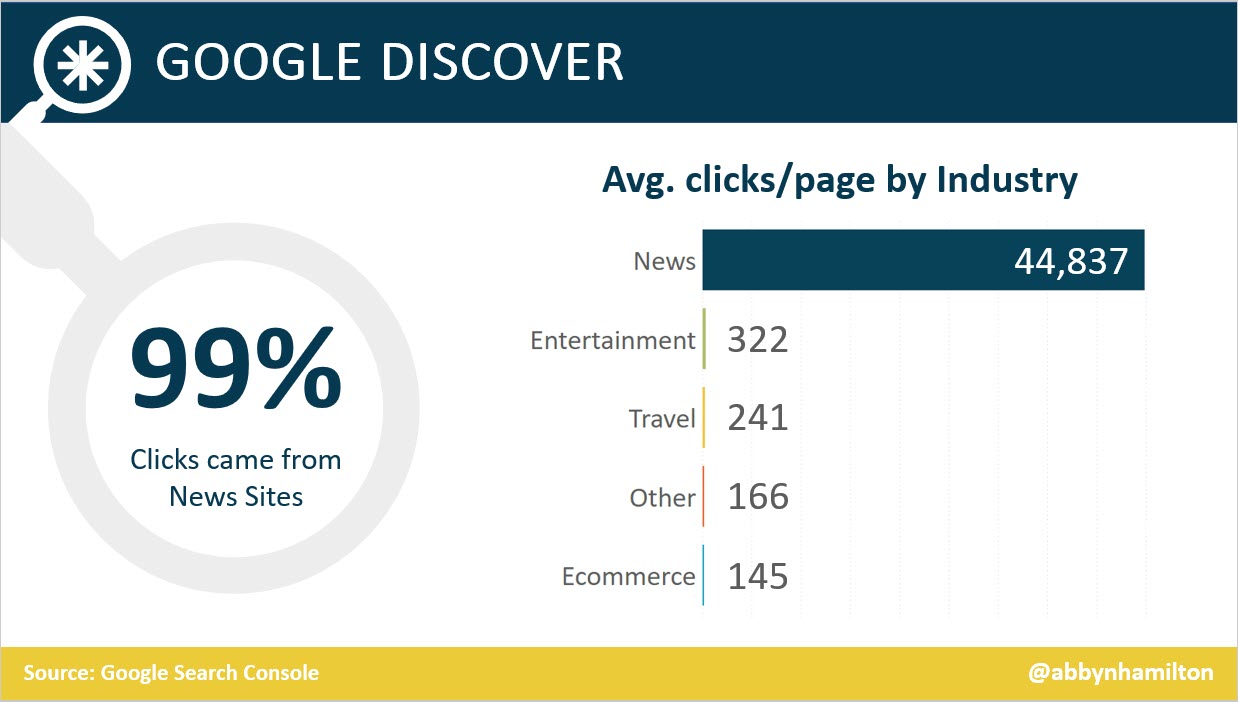
1. News Sites Received 99% Of Clicks
While news accounted for less than half (46%) of URLs analyzed, it received 99% of Discover clicks and got significantly more clicks per page.
 Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020
Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020One news domain in the analysis saw over 30% of its total web traffic coming from Discover, while other publishers have reported that Google Discover drove more traffic than organic search in some months.
It’s likely that news content is shown to a large, broad audience, while content from other industries is targeted to smaller audiences based on specific interests.
Google emphasizes this idea in the announcement of Google Discover, stating:
“When it comes to news, we believe it’s important that everyone has access to the same information.”
Takeaway: Google Discover is a major traffic driver for news publishers and can be used to reach a large, broad audience.
2. Blog Posts Are Prevalent Across All Other Industries
For non-news sites, the remaining 1% of clicks (still totaling over 1 million in the past 12 months) were dispersed across different types of content.
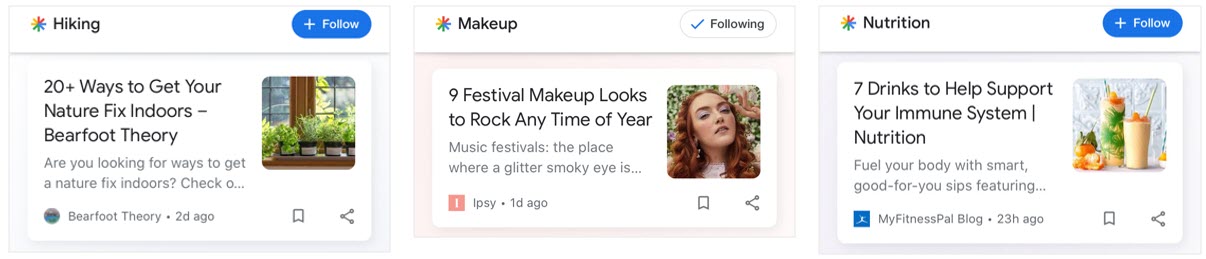
The most prevalent type of content across industries was blog posts.
 Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020
Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020Blog topics that were displayed in Google Discover were highly relevant to specific interests/hobbies, such as hiking, makeup, and nutrition.
 Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020
Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020Additionally:
- 49% of clicks to ecommerce sites went to product pages, which included both product category and product detail pages.
- Entertainment saw the largest percentage of clicks (16%) to pages with a video as the primary content (i.e., cast interviews, and movie trailers).
- Special offers, mostly travel or hotel deals with limited time/availability pricing, accounted for the largest percentage of clicks to travel sites (53%).
Takeaway: Non-news content is heavily interest-focused and will likely be displayed to a smaller, more targeted audience.
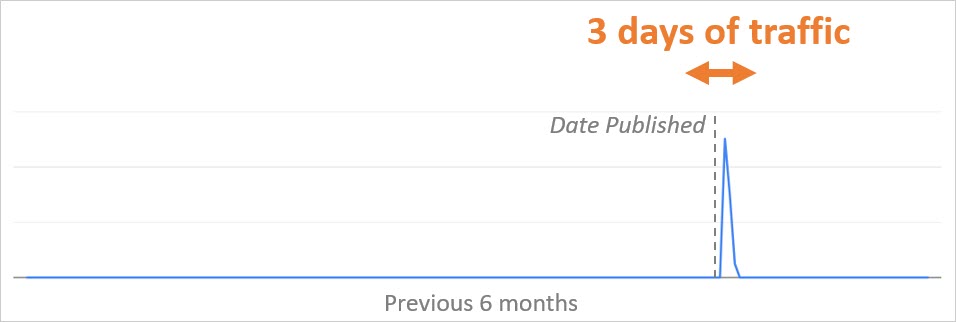
3. Discover Content Typically Has A Short Shelf-life
Aligned with Google Discover’s focus on delivering fresh content, most of the URLs in this study only received traffic for three to four days, with most of that traffic occurring one to two days after publishing.
 Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020
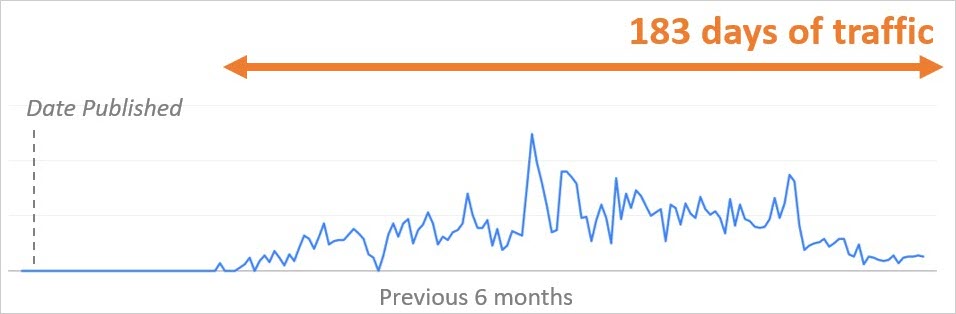
Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020However, some more mature, evergreen content was able to drive longer-term traffic.
 Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020
Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020This is the result of Google Discover serving evergreen content to meet new or evolving user interests.
In the instances where I’ve seen more mature, evergreen content appearing in my personal Discover feed, I was searching for similar topics two to three days prior.
Takeaway: Most pages in Discover have a short shelf-life, around three to four days, but evergreen content can drive longer-term traffic.
4. Users Respond Well To Discover Content
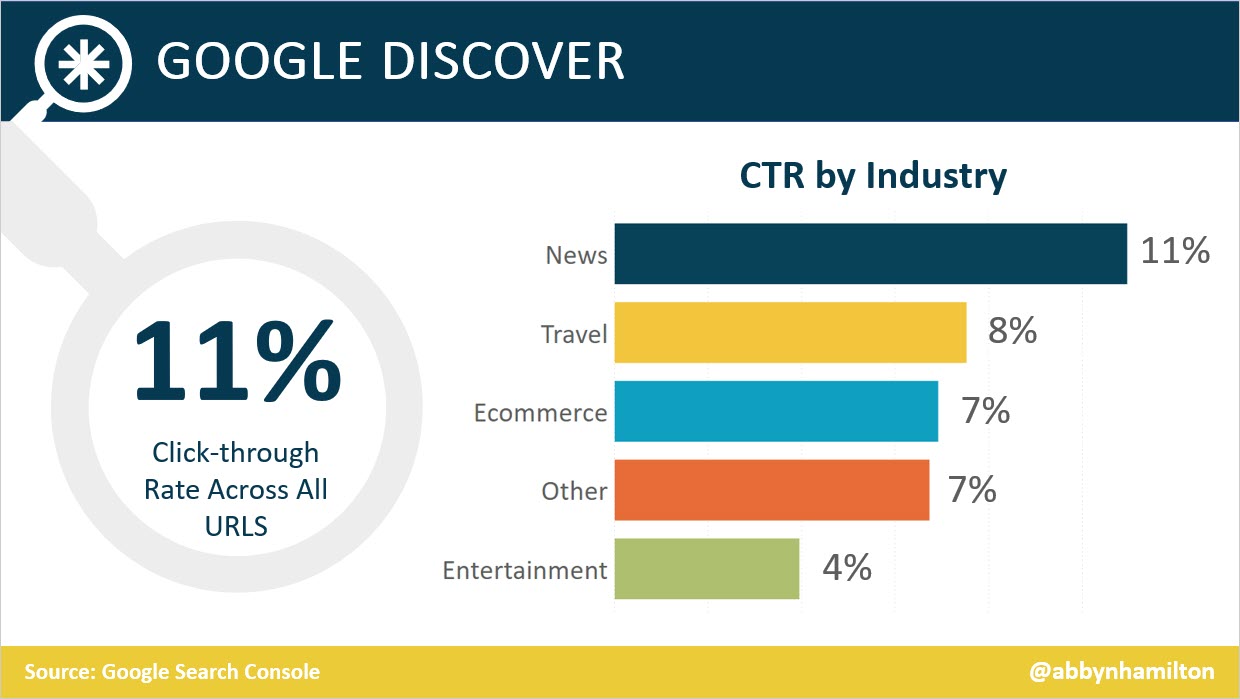
One of the first things that stuck out about Google Discover was a high click-through rate (CTR): 11% across all pages analyzed.
Excluding news sites (which accounted for most of the data), the average CTR was 6%.
 Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020
Screenshot from Google Search Console, April 2020Looking at the same 62 domains, the CTR from traditional search was 4%.
Unfortunately, these numbers can’t be directly compared, as CTR is calculated as clicks ÷ impressions = CTR, and impressions are measured differently in Discover than in traditional search.
Here’s how:
- Search impressions are recorded for a URL when a user opens a search results page containing the URL (even if the result is not scrolled into view).
- Discover impressions are recorded only when a Discover card is scrolled into view.
Takeaway: Pages in Google Discover see higher CTRs than traditional search; however, this may be a result of the difference in how impressions are measured, rather than a difference in user behavior.
How To Connect With Users On Google Discover
In traditional search, queries serve as a connection point between a user’s need and relevant content (i.e., the user is hungry, searches [food near me], Google displays local restaurants).
Google Discover shows content before a user’s need is realized, “powered by the strength of the match between an article’s content and a user’s interests.”
Without keyword research and query reports, the traditional content creation process is limited – but there are still ways to increase the chances of appearing in Discover.
Be Mobile-Friendly
Google Discover is only accessible on mobile devices, so this one is obvious.
But it’s always good to cover your bases by checking Google Search Console’s Mobile Usability Report and making sure there are no errors. If you discover any, remedy them right away.
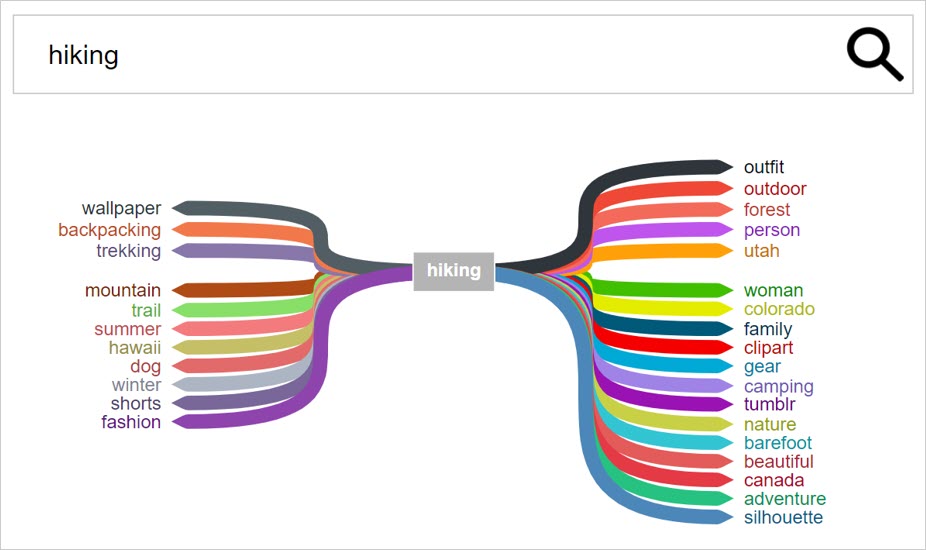
Focus Content Around Entities
Interests are entities, objects, or concepts that can be uniquely identified.
They can be anything from general hobbies, to niche interests, to specific brands and businesses.
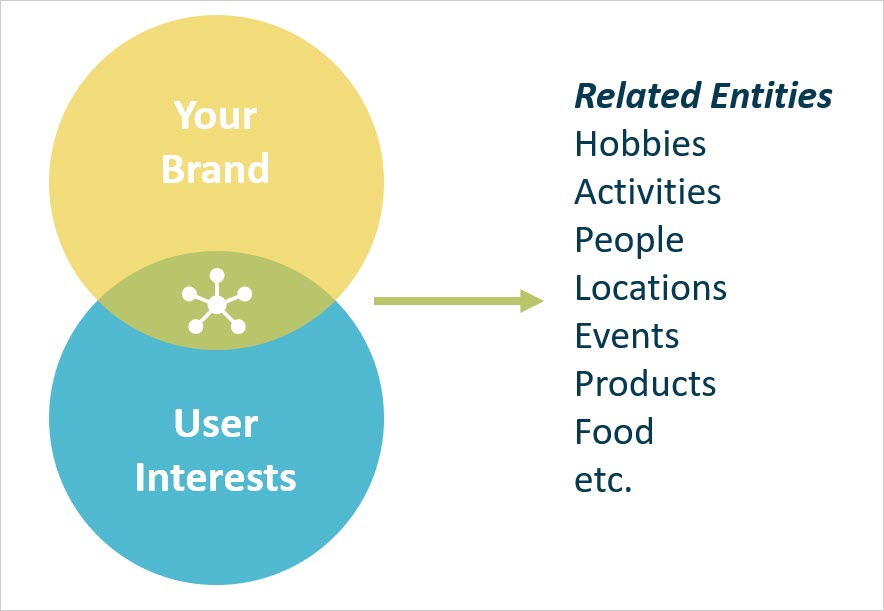
Using the Entity Explorer by Marketer’s Center, you can view the relationships between entities and see what entities are associated with your brand, your industry, products, etc.
 Screenshot from Entity Explorer, April 2020
Screenshot from Entity Explorer, April 2020Identify what entities serve as a connection point between your brand and your users.
 Screenshot from Entity Explorer, April 2020
Screenshot from Entity Explorer, April 2020Hop On What’s Trending
Google Discover works in much the same way as a feed on a social networking platform.
To increase your chances of being featured, keep an eye on what’s happening on social media. Focus on trending events and topics.
Make sure you have optimized your social sharing buttons on your website.
Create Content That Is Relevant, Useful & Interesting To Your Audience
You are no longer bound by search volume.
Embrace this newfound freedom.
Once you’ve identified connection points – get specific and go in-depth.
Interest-based content is personalized, so write content that will resonate with your most passionate users.
One way to do this is to identify intersections and relationships between topics (i.e., “best ski resorts near Pennsylvania”, “running tips for winter”).
Bonus points if you can tie content into current events.
As mentioned above, make sure your topics also align with your expertise and your content and site demonstrate strong E-E-A-T.
Write Good Page Titles
To increase your chances of showing up in Discover, you should ensure all your page titles capture the essence of the content on that page – without being clickbaity.
This helps the algorithm quickly determine what your content is about and whether it is relevant to a particular user.
Include High-Quality Images
Aside from creating content your users will find interesting, the best way to boost content on Discover is to use large, high-quality images that are at least 1,200 pixels wide and enabled by the max-image-preview:large setting or by using AMP.
Avoid using your site logo as your image.
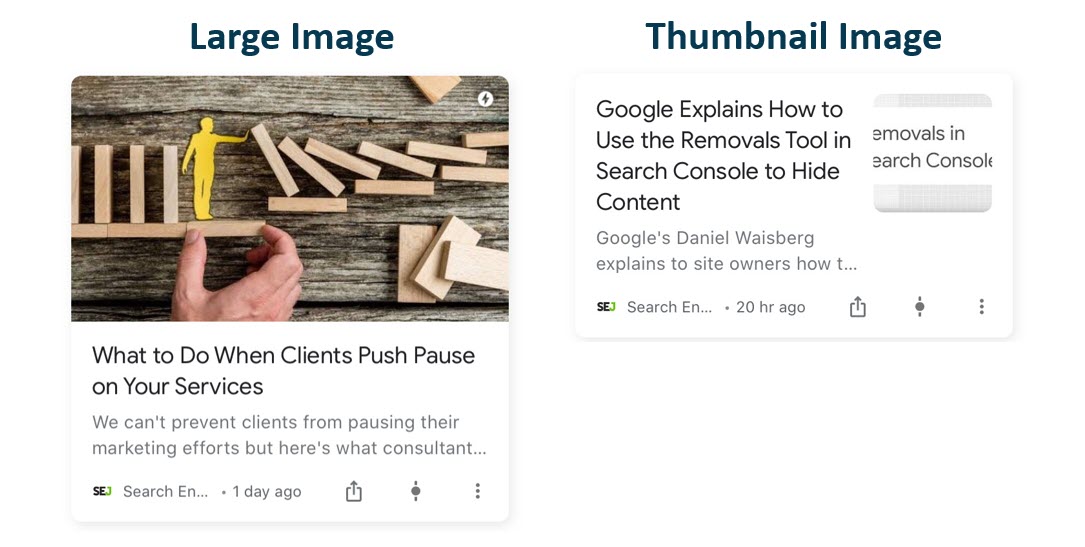 Screenshot from author, February 2023
Screenshot from author, February 2023For more ways to optimize images in Discover, check out Brodie Clark’s case study, Google Discover: An Image Could Be Worth 1,000 Clicks.
Revisit Your Video Strategy
Videos have a huge presence in Google Discover, which aligns with Google’s shift in focus from text to more visual ways of finding information.
While videos made up only 17% of the content in this analysis, this doesn’t include data for YouTube, which hosts a majority of videos appearing in Google Discover.
It may be hard to measure, but creating engaging videos and optimizing your YouTube channel could help increase your brand’s presence in Google Discover – and in traditional search too, as 19% of desktop search results include video carousels and 92% of those videos come from YouTube.
Avoid Exaggeration And Shock Tactics
Google Discover seeks to provide relevant and trustworthy information to mobile users. One way it does this is by penalizing sites that use misleading information or exaggerated details in preview content.
Similarly, any tactics designed for “cheap clicks” like content intended to outrage, titillate, or offend should be avoided.
Take Advantage Of The Follow Feature
One of the great parts of Discover is the Follow feature, which allows users to get the latest update from websites they’re following. Did you know that over 600 million people now explore content daily through their Google Discover Feed?
Available in English to people using Chrome Android, this feature uses RSS or Atom feeds by default.
If you have more than one feed on your site, you can optimize your Follow feature by telling Google which feed to follow in the <head> section.
To ensure Google can find your feed, make sure it’s not blocked with your robots.txt file, that your feed is up-to-date, and that you’ve included title and link elements.
Track Your Performance
Once you have content on Google Discover, you can monitor how it’s working via the Performance Report for Discover.
Here you’ll provide information on impressions, clicks, and click-through rates for any of your content that has appeared on Discover in the last 16 months. Note that you need a minimum number of impressions for this data to show.
For more tips on optimizing your content for Discover, Lily Ray has provided a list of 10 effective strategies.
Key Takeaways
Google Discover provides incredible opportunities for forward-thinking webmasters and search engine optimizers – and it’s definitely one you should take advantage of.
The best part is it should fit neatly in with your existing strategies. You still want to create high-quality content aimed at your target audience.
You’ll want to ensure your content is indexed and your site is mobile-responsive. But these are all things you should have been doing anyway.
Just remember that, like all things SEO, optimizing for Google Discover is an ongoing process.
But if your content is good and you follow the best practices discussed here, Google’s bots will begin picking your content more often as an automatic suggestion to users.
And that means more visibility, more traffic, and hopefully more conversions.
More resources:
Featured Image: Krakenimages.com/Shutterstock