You’ve had your domain for a long time and it has served you well. Today, though, you’re looking to expand your online business and the old domain just won’t do the trick. You need something new, fresh and exciting and perhaps you’ve already registered the ideal name.
There’s just one problem.
Your old site has earned a good search engine ranking for your best keywords. You’ve got tons of “link juice” to both give and receive – and you don’t want to lose that.
Keep in mind, we’re not just moving files or folders here – but moving an entire site to a new domain name without it affecting your ranking. To do this, you’ll need two tools – .htaccess and mod_rewrite.
The following tips will work on a Linux/Unix server running Apache – which most web hosting companies use. Before you start, check with your respective web host to ensure they support the mod_rewrite module and .htaccess.
What are .htaccess and mod_rewrite?
.htaccess is a file that tells the server how to handle certain things like security, error messages and, most importantly for us, redirection. The mod_rewrite module lets you “rewrite” URLs. It’s hosted on your web server so you won’t need to download or install anything. This is the preferred way to redirect your site or pages to your new domain name without losing valuable ranking or back links.
To start, make sure your new domain is properly directed to your hosting account. Upload your files from your old domain to the new one exactly as they appeared on the old domain. Now it’s time to make your .htaccess file. If you already have one on your new server, name it .htaccessBACKUP. Don’t delete it in case you need to restore the old settings for any reason.
Open Notepad by going to Start > Accessories > Notepad or use another simple text editor of your choice. Don’t use Microsoft Word or another word processing program though – they will automatically add an extension to the filename like .doc – which is what we don’t want.
In this new file, copy and paste the following:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.yournewdomain.com/$1 [R=301,L]
Replace “yournewdomain.com” with your actual new domain name. Then save the file as:
.htaccess
Ensure it doesn’t have an extension (like .txt) – you can do this by choosing “All Files” in the dropdown menu – like so:
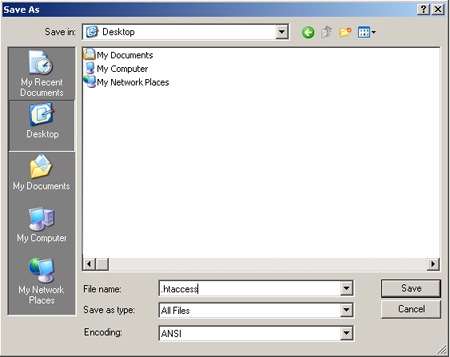
Once you save the file, upload it to your root directory for your old domain name. Try it out by typing in your old domain in your browser. You should immediately be directed to the new site. The old domain name will still show in the address bar. To make sure you’re browsing the new site and not the old one, just right-click on an image and choose Properties. The full image URL should be displayed with the new site URL.
It Worked! – Now What?
Now every time a person visits your old domain, they’ll instantly go to your new site. Keep in mind that when search engines visit your page, they’ll see that it has been redirected and will follow the new one just as they always did for your previous domain name. Within a few weeks to a few months, the old domain name will gradually be replaced by the new ones as the search engines update their databases.
If you see some initial rankings drop or a drop in traffic, it should all return to normal within a few weeks as your new redirection makes its way through the web. Make sure any sites linking back to you know your new URL if you’re going to delete your old domain since those links will no longer work if your old domain doesn’t point to the new one.
Try using .htaccess and mod_rewrite the next time you want to change your domain without losing your search engine ranking. It’s a simple, search engine friendly way to keep all the popularity and reputation you’ve built up!
Sherice Jacob is a web designer, copywriter and author of “Get Niche Quick!” – The Definitive Guide to Marketing Your Business on the Internet. You can also follow @sherice on Twitter





![[SEO, PPC & Attribution] Unlocking The Power Of Offline Marketing In A Digital World](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/sidebar1x-534.png)