Just recently someone told me they stumbled upon the Google Tag Manager and had no idea how it worked or why it mattered. Believe it or not, this tool has been around since 2005 and it’s free, easy to use, and helps give you a little bit of control over your code snippets and tags (aka no more bothering the dev team). Needless to say it’s an excellent tool that, although it was slow to burn for some, is something just about every small business could use to propel their digital marketing efforts forward. If you need a small tutorial and a way to get familiarized, look no further.
Understanding Tags and Why They’re Needed to Help Your Website
Google Tag Manger is all about the tags and code snippets associated with your website, so it’s important you first understand the purpose of a tag, where you find tags, and how to use tags correctly.
A tag is essentially just a snippet of code that helps you measure traffic, monitor your online campaigns, and learn about user behavior. They essentially help give you all of the information you need to make successful decisions for your digital marketing strategy. A few popular tags include Google Analytics, AdWords, AdRoll, Crazy Egg, Floodlight, and any customized tags you choose to create. Unfortunately, all of these tags and different code snippets that are needed can get confusing, which is where the Google Tag Manager comes into play.
Having your tags and code snippets organized will help improve user experience and help keep your site up and running efficiently. According to Google, it’s easy to have redundant or incorrectly applied tags, which can distort your measurement and result in duplicate costs or missing data. With the Google Tag Manager you can eliminate these problems and run your campaigns when you need them.
A Quick Look at How the Google Tag Manager Works
The Google Tag Manager allows you to update two things:
- Tags on your website. This includes marketing and optimization tags including Google Analytics, AdWords conversion tracking, and Floodlight counter, etc.
- Configuration values. This refers to the mobile apps you’ve created. If you’ve created a mobile app, you can change your configuration values easily. This includes ad position, timeout, game play dynamics, etc.,
The GTM helps save you time and helps you mange your code if you have several different tags associated with your website or if you need to debug your code if something wasn’t working right. It’s also worth mentioning that because placing tags on your webpages helps you have a cleaner code, your site speed could actually improve.
I also highly recommend checking out a video Google created that explains in more detail the Tag Manger and why it matters.
How to Get Started with the Google Tag Manager
If it seems daunting at first, don’t sweat it. Once you get started going through the setup process you’ll start to understand how it all works. Below is s step-by-step guide to getting started with the Google Tag Manager:
Step #1: Create an Account and a Container.
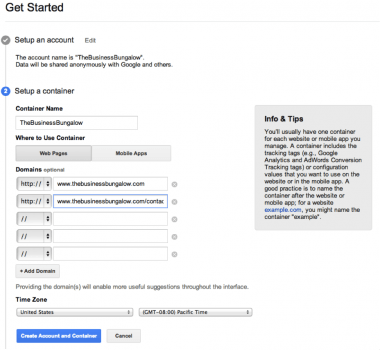
Sign in here. Once you type in the name of your business (or whatever you want to use to indicate your website) you will be asked to set up what is called a container.
As you can see in the little gray box below, most websites have a container for each website or mobile app. Containers include tracking tags like Google Analytics and AdWords. I always recommend including your domain, but if you have a blog or certain landing pages where you want to use the GTM, then you can put those URLs in this same container if they are subdomains of your website.
Step #2: Add Snippet of Code to Your Website
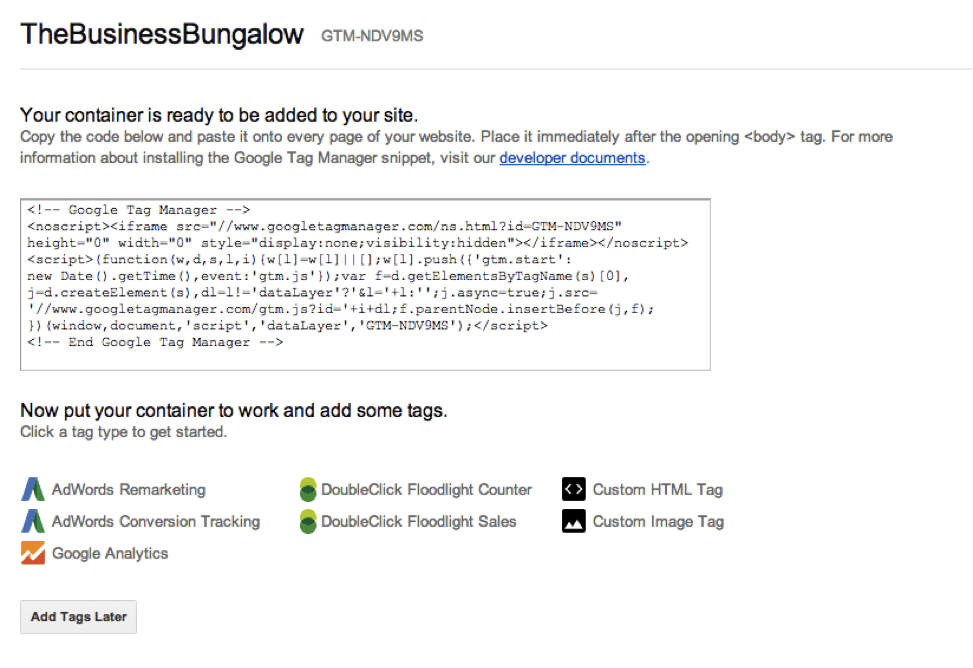
Once your account and container is created and you click the blue button, you’ll be shown a new page with a snippet of code. You use this code on your site just after the opening tag and it should be pasted onto every page of your website where you want to use the GTM. You will also notice that at the bottom of the page you have quite a few options to add tags. You can add them later, but I recommend at least adding Google Analytics right away, which brings us to our next point.
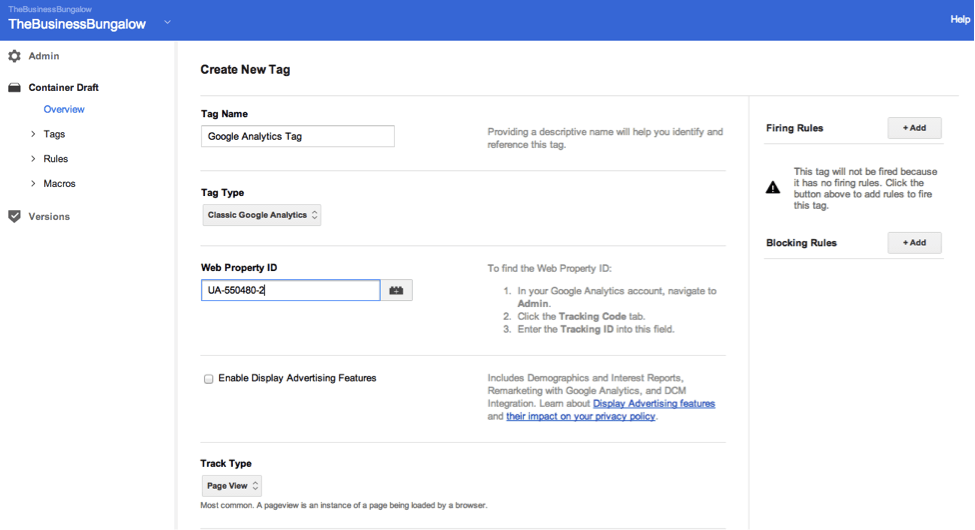
Step #3: Add Tags Including Google Analytics.
If you click on, for example, the Google Analytics button as shown above in the screenshot, you’ll be taken to a new page that asks you to fill in information about your Google Analytics account. This includes letting the tool know whether you have a Classic or Universal account as well as your Google Analytics ID (if you don’t know how to find your ID, it tells you how right on this page, which you can see below in the screenshot).
Remember: You will not need your Google Analytics code once you have the Google Tag Manager.
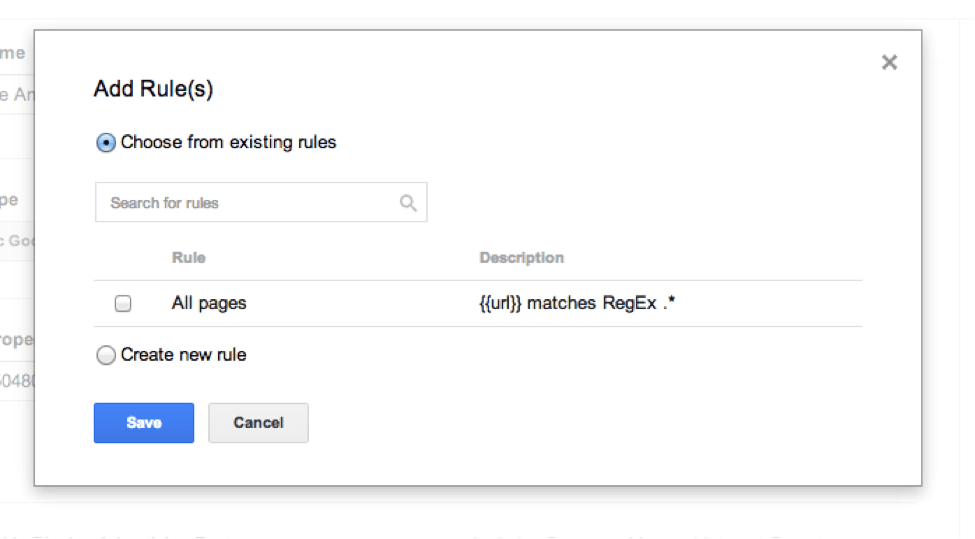
Step #4: Add a Firing Rule.
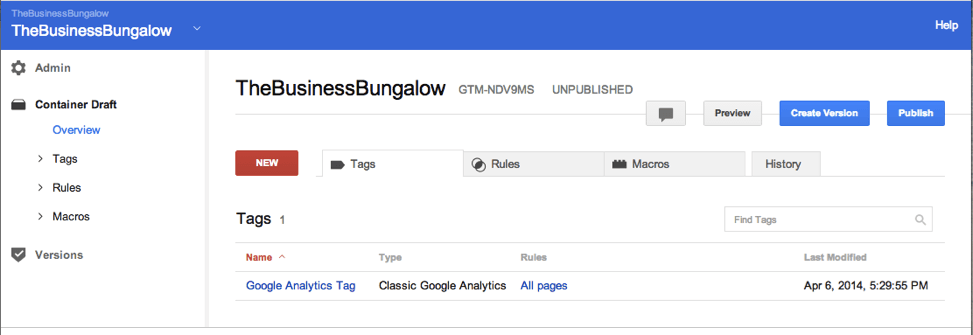
As you can see in the screenshot above, you can add what is called a Firing feature. This means that if you have certain rules you want your Tag Manager to know about certain pages, you can add them here. You can choose from existing rules, select All pages (usually a good option for beginners), or create a new rule.
Extra Suggestions: On this same page you can add what is called a Blocking Rule as well as go into Advanced Settings, which allows you to enable a custom tag firing schedule or add different versions to each container. The options you have go pretty deep, so I recommend checking out this link once you have a feel for how the tool works and are ready to move on to more custom and advanced features.
Step #5: Click Publish.
Lastly, the tool will show you a preview of what you have just setup and you can click Publish.
Then what? You can constantly go back to your GTM dashboard and add new tags or make changes to your containers at any time by simply signing in to your Google Tag Manager dashboard. In the above example we went through the Google Analytics tag, so that means that the code for Google Analytics will be working and information will be logged to your account.
The Takeaway
It might seem like a lot of busy work when you could just use Google Analytics (like you probably already had set up in the first place), but remember that you have options for all of your other tags. They’re all in one place, so the more you use the tool the more beneficial it will be.
Have you used the Google Tag Manager in the past? Is there anything you’ve found particularly helpful? Let us know your story and your thoughts in the comments below.
All screenshots taken April 6, 2014. Featured image via Shutterstock


