Google Research has just published a research paper detailing a new algorithm that proposes a new way to answer queries. If in the future this algorithm is put into place it will further change the influence of traditional ranking factors for determining what gets ranked. In the short term, this research provides an insight into what Google means when they say that an algorithm update was made to improve relevance.
The New Algorithm in Plain English
Google Research published a new paper at the Sixth International Conference on Learning Representations. The publication was announced via Twitter.
The paper is titled, Ask The Right Questions: Active Question Reformulation with Reinforcement Learning (PDF).
The research paper discusses a way of reformulating queries then presenting those queries to a ranking engine. Query reformulation and stemming are already in use at Google. This is a form of that approach.
What is new is that this is a machine learning algorithm that uses Reinforcement Learning approach. Furthermore, the algorithm has no knowledge of how the ranking system works. It is asking questions from what a black box algorithm then learning. This new algorithm uses a learning system that reformulates the user query, asking the ranking engine many questions, then choosing the best answers from the multiple sets of answers.
How this Algorithm Works
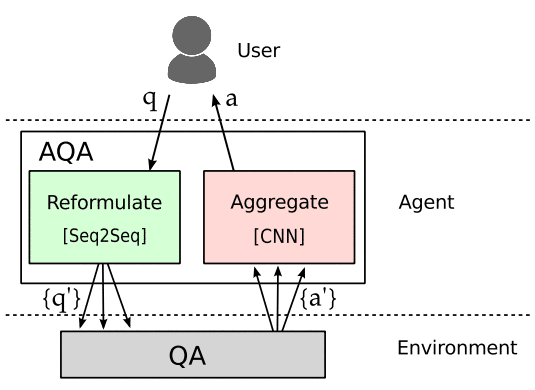
Here is a screenshot of an illustration from the research paper that summarizes how this machine learning algorithm works:
The user asks the question. The machine learning algorithm (labeled as the agent) reformulates that question into multiple questions then submits them to the ranking algorithm. The ranking algorithm returns sets of results and the agent chooses the best answer.
Here is what the research document states:
“In the face of complex information needs, humans overcome uncertainty by reformulating questions, issuing multiple searches, and aggregating responses. Inspired by humans’ ability to ask the right questions, we present an agent that learns to carry out this process for the user. The agent sits between the user and a backend QA system that we refer to as ‘the environment’.
We call the agent AQA, as it implements an active question answering strategy. AQA aims to maximize the chance of getting the correct answer by sending a reformulated question to the environment.
The agent seeks to find the best answer by asking many questions and aggregating the returned evidence. The internals of the environment are not available to the agent, so it must learn to probe a black-box optimally using only question strings.”
Takeaway: Why This Algorithm Matters
This algorithm is a view into a machine learning method called, Reinforcement Learning. Reinforcement learning algorithms have been used to learn how to play Go and can play video games like Doom.
This particular algorithm is interesting to SEO because it shows how an algorithm can sit between a user and the regular ranking algorithm and make the decisions. So instead of the ranking algorithm deciding what to display in search engine results pages (SERPs), this machine learning algorithm is making the decisions.
This kind of ranking is a departure from how the SEO community traditionally believes search engines ranks web pages. The traditional understanding is that ranking factors like links, text in the title tag, anchor text and other ranking factors are the deciding factors for what is ranked one through ten in the search results.
Factors like links are an important ranking factor. But with this kind of algorithm, links contribute to what web pages will be considered for ranking but are not the deciding factor.
It is the job of another algorithm takes those sets of pages and decides what pages answer the question best.
Have you ever seen a web page with less links ranking above other pages with more links? It’s likely that there is an algorithm between the user and the ranking algorithm that is deciding that a certain kind of site is a better answer.
What to Do About Ranking Factors?
The ranking algorithm is no longer the decider of what sites will rank in the top ten. This is why ranking factor studies that aggregate millions of search results may not be accurate. Ranking factor studies presume that ranking factors are responsible for the top ten results.
But ranking factors are not always deciding what ranks in the top ten. That is why ranking factor studies may be unreliable.
While this specific algorithm may not currently be in use, there are other algorithms already in place that perform a similar function by setting aside the ranking algorithm results and re-ranking the SERPs using factors that are not ranking factors.
For example, Google has a patent on a way of re-ranking search results called, Ranking Search Results that mentions the use of a modification engine.
“The search system 114 also includes or can communicate with a score modification engine 140 that generates modification factors that are applied by the search system 114 to initial scores generated by the search engine 130 for resources that match the query 110. The score modification engine 140 can generate the modification factors based at least in part on modification data that associates a respective modification factor with each of a number of multiple groups of resources. The modification data is stored in a repository accessible to the system, e.g., a modification factor database 150.”
Re-ranking search results is not a new idea. Microsoft published a research paper about re-ranking search results as far back as 2005, in a paper titled, Improving Web Search Results Using Affinity Graph. The purpose of that algorithm was to more accurately serve the user intent for vague search queries.
Takeaway #2: How Does this Affect SEO?
This may affect SEO in the future and the result could be a stronger emphasis on satisfying user intent. This is the kind of improvement that is called improving relevance. So when Google announces an update to relevance, the answers for why a site lost rankings is best found by studying the winners. For these kinds of updates, you likely won’t find the reasons for changed rankings by navel-gazing the sites that lost SERP positions.
More resources
Images by Shutterstock, modified by Author
Screenshots by Author






![AI Overviews: We Reverse-Engineered Them So You Don't Have To [+ What You Need To Do Next]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/sidebar1x-455.png)