Last year brought us a meteoric rise in the importance of SEO with a redoubled focus on creating the best user experience possible.
From the roll-out of mobile-first indexing through to the impending introduction of Google’s page experience update and Core Web Vitals, staying on top of core SEO concepts is critical.
Through the remainder of 2021, it is essential to understand these five critical SEO concepts as we gear up for success.
1. Core Web Vitals
Set to roll out in June this year, Google’s Page Experience and Core Web Vitals is something that both technical and non-technical SEO professionals need to be on top of now.
Core Web Vitals are a new set of standards that Google will use to evaluate if a page provides a good user experience.
These metrics are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the speed at which a page’s main content is loaded. This should occur within 5 seconds of landing on a page.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures the speed at which users are able to interact with a page after landing on it. This should occur within 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures how often users experience unexpected layout shifts. Pages should maintain a CLS of less than 0.1.
Google has stated the minimum threshold for all Core Web Vitals must be met in order to benefit from the associated ranking signal.
Some of the key things to focus on include:
- The mobile experience.
- Image compression.
- Informational page content.
- Site speed and technical structure.
Read more on Core Web Vitals below:
- Google: Core Web Vitals Becoming Ranking Signals in May 2021
- Research: Core Web Vitals Ranking Boost by Industry
- Google On Expected Impact of Core Web Vitals Update
2. Mobile-First Indexing
Google announced late last year that mobile-first indexing is going to be the new norm.
Mobile First has arrived. This means that your ranking signals are now going to come from the mobile version of your site, not the desktop version.
Around 55% of all web traffic comes from mobile devices, which is only expected to increase. What you may not be aware of is that having a mobile-friendly site isn’t enough anymore – now you need to be “mobile-first.”
In other words, it’s time to stop thinking of mobile as an adjunct to your desktop site and start prioritizing your mobile SEO first.
Here are a few practical ways to improve your mobile SEO:
- Take the Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Fix broken links and incorrect redirects.
- Compress any uncompressed images.
- Remove unplayable content and blocked resources (e.g., JavaScript, CSS, specific images).
- Eliminate intrusive pop-ups and interstitials.
- Improve mobile usability (e.g., text size, viewport configuration, tap target size).
- Run an audit of your mobile site to find any additional site elements (e.g., structured data, title tags) you can optimize for mobile.
Read more on Mobile-First below:
- Google Shares How to Succeed in Mobile-First Index
- Google SEO 101: Mobile-First Indexing Problems
- Google Redesigns Mobile Search Results
3. Machine Learning and Automation
Machine learning is now an integral part of search engine ranking algorithms – Google announced in March 2016 that RankBrain is their third most important ranking signal.
Machine learning is closely related to the topic of semantic search. It’s a way for search engines to make educated guesses about what ambiguous queries mean and to deliver better search results as a whole.
RankBrain and other machine learning systems examine user behavior to deliver the best search results possible. Unfortunately, what’s deemed best for one query might not be the best for another, making machine learning very difficult to optimize.
The best practice is to keep creating robust resources optimized for search and the user experience.
Beyond Google and its algorithms, machine learning and automation are becoming a powerful combination to SEOs, feeding real-time insights and automating repetitive tasks.
This can range from:
- SEO insights and audits.
- Content activation and syndication.
- Internal linking.
- Reporting.
- Automated website error detection and quick fixes.
Read more on Machine Learning and Automation below:
- A Complete Guide to the Google RankBrain Algorithm
- Why SEO & Machine Learning Are Joining Forces
- Real-Time Insight & Real-Time Action in SEO: How Automation Bridges the Gap
4. E-A-T
Some may be surprised that the E-A-T concept is not actually new. It first appeared in Google Quality Guidelines in May 2014.

This concept focuses on Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
While E-A-T is not an algorithm, it will have an indirect effect on rankings when not following best practices that focus on ensuring your site has expert and authoritative content that users trust.
For example:
- Subject matter content indicating expertise and knowledge.
- Credibility and authority of your website.
- Structure, security, and quality of your website.
- Off-page content by experts.
Read more on E-A-T on SEJ below:
- Google’s E-A-T: Busting 10 of the Biggest Misconceptions
- Google’s Mueller Asked About Increasing E-A-T with Structured Data
- How to Improve Your Website’s E-A-T
5. Knowledge Gap, Semantics, and Entities
The goal of Google’s Hummingbird update in 2013 was to improve search accuracy by better understanding searcher intent.
Today, semantic search has evolved even more, and search engines are better than ever at understanding query context and the relationships between words.
The goal of semantic search is for search engines to understand natural language queries better.
So if a user asks Google “what’s it rated?” and they’re standing in front of a French restaurant, ideally Google would be able to know that in this context, “it” refers to the restaurant and the searcher wants to know a star rating.
Structured data and schema.org can also play a role in E-A-T.
With E-A-T, for example, you have to pay close attention to the knowledge graph.
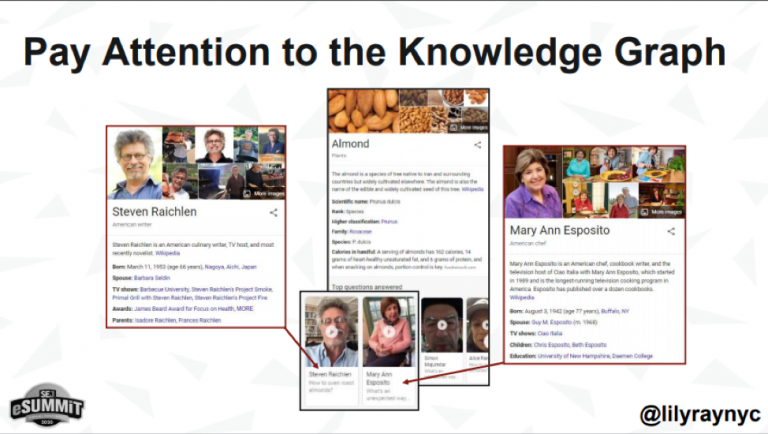
There are many subtle nuances to the mechanics of semantic search. Ultimately, what it means for you is that an authoritative page that dives into one specific topic in-depth will usually rank better than dozens of pages built around different keywords.
That’s because one comprehensive resource is better at giving Google (and, by proxy, its users) all the context it needs to satisfy searcher intent.
Knowledge Graphs help Google leverage structured data about topics and, using semantic data, populate its knowledge graph.
This creates opportunities for SEO professionals to create content on topics that could influence the graph and Google’s understanding of their content.
Here’s how to build content that better embraces semantic SEO:
- Choose a broad topic that’s relevant to your audience. For example, a pet adoption center might create a page about different dog breeds.
- Ask questions that will help you discern searcher intent. For example, the page on dog breeds might aim to answer “temperaments of different dog breeds” or “easiest dog breeds to train.”
- Once you understand searcher intent, create content that matches. Make your resource as rich and in-depth as possible.
- Create additional landing pages to satisfy other searches that match user intent.
- Focus on creating “complete guides” and other comprehensive pieces of evergreen content. Include relevant short- and long-tail keywords wherever appropriate.
- Check Google’s Knowledge Graph for an entity on your business and products.
- Try to feed Google as much info as you can.
Read more on Semantics and the Knowledge Graph below:
- What Is Latent Semantic Indexing and Why It Doesn’t Matter for SEO
- Google Image Search Labels Becoming More Semantic?
- Tracking Google Knowledge Graph Algorithm Updates & Volatility
- Get to Know the Google Knowledge Graph & How it Works
Conclusion
As Google continues its push and focuses on the user experience understanding how key SEO concepts help the end-user is vital to success.
Optimizing content for the consumer experience and adopting technology and technical traits to help scale your SEO efforts is becoming the new normal.
SEO has now moved wholly away from stuffing the right keyword into a page description and toward providing more significant and better experiences for our users through our content and our website structures and performance.
More Resources:
- 3 Strategic SEO Insights & Tactical Advice for 2021
- How to Future-Proof Your Brand with the Help of SEO
- A Complete Guide to SEO: What You Need to Know
Image Credits:
All screenshots taken by author, April 2021





![AI Overviews: We Reverse-Engineered Them So You Don't Have To [+ What You Need To Do Next]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/sidebar1x-455.png)