If your website is struggling to rank in search engine results pages, an enterprise SEO audit can help you identify why.
For any SEO provider or in-house marketer who wants to audit an enterprise website, these 24 items should be on your checklist before moving forward with any SEO campaign.
What Is An Enterprise SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is an evaluation of a website to identify issues preventing it from ranking in search engine results.
Enterprise SEO audits are focused primarily on large, enterprise websites, meaning those with hundreds to thousands of landing pages.
Why Perform An SEO Audit?
Auditing your website is the first step in developing a successful SEO strategy.
Why?
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of a website can help you tailor your SEO campaigns accordingly.
Performing an audit also helps your team direct your time, resources, and budget to the optimizations that will have the greatest impact.
What To Include In Your Enterprise SEO Audit
Auditing a large website can be very demanding, with over 200+ ranking factors in Google’s algorithm.
So to run a more sufficient audit, separate your audit into five parts: content, backlinks, technical SEO, page experience, and industry-specific standards.
You will need to rely on SEO software tools to run your audit successfully.
SEO platforms like SearchAtlas, Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, and others are a must for auditing any large website.
[Technical SEO Audit] The ultimate ebook + workbook bundle
Content
1. Are You Targeting The Right Keywords?
Writing content begins with selecting the topics of interest to your users.
Once the topics are selected you can begin the process of choosing the phrases (keywords) used by potential visitors to search for webpages about those topics.
Not only do your target keywords need to be relevant to your products and services, but they also need to be realistic goals for your website.
So before you analyze whether your enterprise website is properly optimized, make sure your keyword goals are indeed reachable.
It’s possible that your target keywords are too competitive and/or focused on keyword volume.
Choosing keywords is not about selecting the keywords with the most search volume because those tend to be too general and not always perfectly matched to webpages about a more specific topic.
The right keywords are consistently the ones that a site visitor will use to find a webpage that is exactly on the topic of your own webpage. Google aggregates keyword phrases so even if site visitors use variations of your chosen keyword phrase Google will still rank the web page that is about a specific topic.
Google Search Console is the best tool to use for discovering what search terms a website is already ranking for. The keyword ranking data is the most accurate available.
The keyword ranking data from Google search console can then be imported for use with your favorite keyword tracking tool.
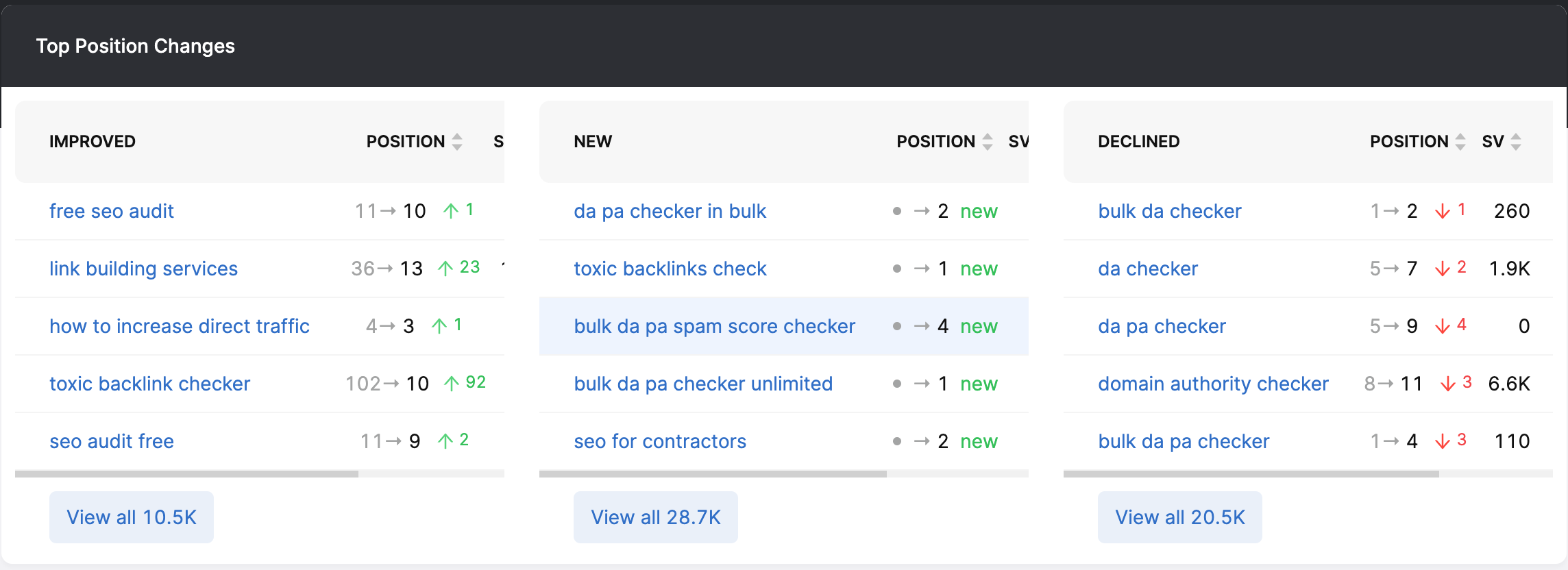 Screenshot from SearchAtlas, May 2022
Screenshot from SearchAtlas, May 2022Then, perform any necessary keyword research to find keywords that may be a better fit for your website.
Once you’ve ensured that improper keyword targeting is not the source of your poor SEO performance, you can move on through the remainder of your audit.
2. Are Your URLs User Friendly?
Google doesn’t use keywords in URLs. However, keywords in URLs help tell users what your page is about and can help increase clicks from search results pages.
URLs should be short and descriptive and use the most important keywords that will signal to your users that this is the page they are looking for.
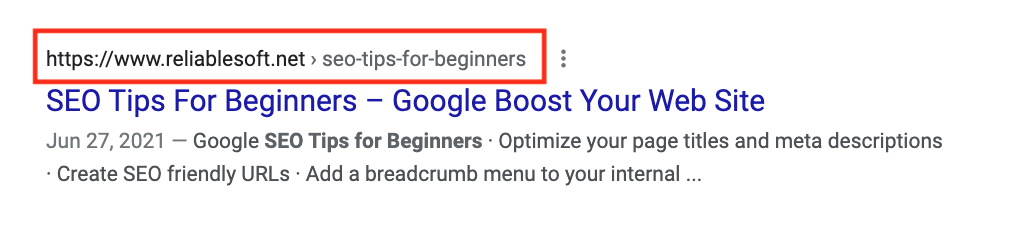 Screenshot from Google, May 2022
Screenshot from Google, May 2022URLs are visible at the top of search results and can influence whether or not a user clicks through to the page.
Use hyphens between words to keep the URL paths readable and omit any unnecessary numbers.
3. Are Your Meta Tags Properly Optimized?
Google uses title tags to understand what your web content is about. Meta descriptions help potential site visitors understand what to expect upon reaching the web page.
Like URLs, these tags are also visible in the SERPs and influence whether or not a searcher clicks.
Your audit should include checking that your web page’s meta tags are unique and following SEO best practices.
Use a site auditor tool to identify the web pages to address to speed up the process.
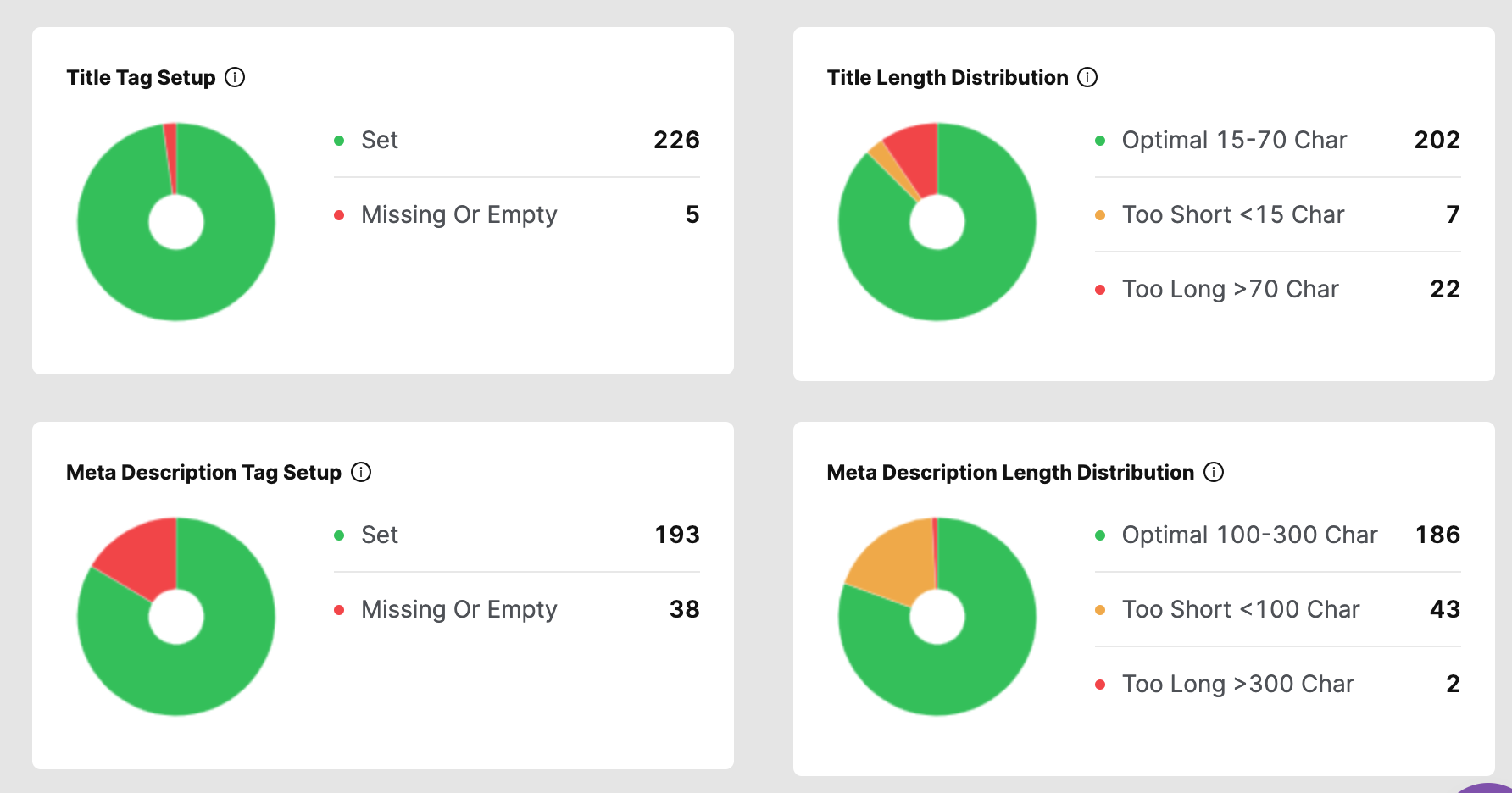 Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022
Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022Make sure to check for:
- Original and unique titles and meta descriptions for each web page.
- Character length: Google search results show 50-60 characters for title tags and 150-160 for meta descriptions. It’s okay to use more words, but be mindful that there are limits to what is shown in the search results.
- While title tags should contain important keywords, the most important function of the title tag is to accurately provide a high-level and short description of what the page is about. So as long as the focus is on properly describing what the page is about then the use of keywords should be appropriate. Google does not use keywords in meta descriptions for ranking purposes.
Google sometimes rewrites title tags in the search results. But it only does so when SEOs use the title tag for dumping keywords into them (keyword stuffing) instead of using it to describe what the page is about.
As long as the title tag is concise, descriptive, and unique then everything should be fine. Optimizing these meta tags is still an essential step in on-page SEO.
4. Is Your Content High-Quality And In-Depth?
Although content length is not a ranking factor, in-depth content often displays characteristics that Google likes, such as original insight, reporting, in-depth analysis, and comprehensive exploration of the topic.
Focusing on content depth and expertise isn’t the same as writing long articles. The length of the article is not necessarily correlated with the authoritativeness of the content.
There is no magic number when it comes to content length. Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines state that web pages should have a “satisfying” amount of content.
They also state:
“The amount of content necessary for the page to be satisfying depends on the topic and purpose of the page. A high quality page on a broad topic with a lot of available information will have more content than a high quality page on a narrower topic.”
It may be a mistake to exactly emulate the content of top-ranking competitors because Google doesn’t always rank similar content.
So rather than copy the length and keywords of competitors, use top-ranked content as a starting point to identify what about those pages is lacking and then use those deficiencies to create a better web page.
5. Are Your Landing Pages Internally Linking To Each Other?
Internal links help Google find and index your pages. They also communicate website hierarchy, relevance signals, topical breadth, and spread around your PageRank.
Make sure you evaluate whether or not your pages are leveraging an internal linking strategy. Also, take a close look at the anchor text used to link to other pages of your website.
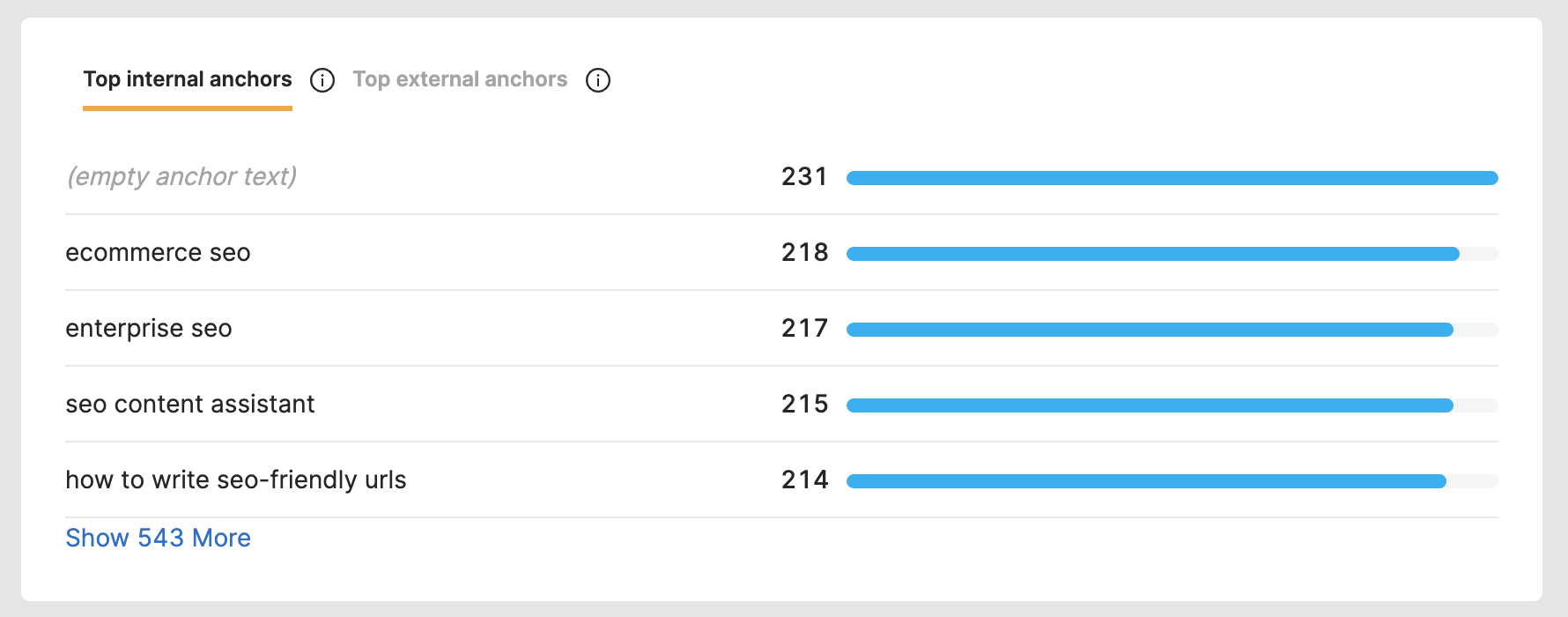 Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022
Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022Your pages need to have internal links pointing to other pages, and be sure internal links are pointing to that page.
Otherwise, you will have orphan pages, meaning pages that Google cannot find and index because there is no linking pathway to them.
6. Does Your Content Show Expert Sourcing With External Links To Relevant Content?
Google may use external links to better understand what a page is about.
So make sure that links to other websites are to useful and high quality web pages that are useful to your reader within the context of the web page.
7. Are You Using Rich Media And Interactive Elements?
Images, videos and interactive elements like jump links can be useful for users and may cause Google to judge the page to be useful.
However, if these elements slow down your page load times, they are counterproductive to your SEO efforts. That will be addressed in a later part of your audit.
8. Do Your Images Include Keyword-rich Alt Text?
Enterprise websites – particularly ecommerce sites – may feature thousands of images.
But because Google cannot see images, they rely on alt text to understand how those images relate to your web page content.
Alt text is used by screen readers by people with vision impairments.
Your audit should highlight opportunities to use descriptive image alt text that will help Google and vision-impaired site visitors understand what the images are about.
Don’t use the image alt text for keyword stuffing.
[Recommended Read] → The Ultimate Technical SEO Audit Workbook
9. Are Web Pages Thin Or Obsolete?
A common pitfall for content is when webpages are repetitive or so short they are not useful.
For example, pages that are designed for every state or province in a country, with very little to differentiate one page from another can be seen as a low quality webpage (doorway pages).
Your audit should highlight pages that are too short to be useful or repetitive and make suggestions for consolidating them with better pages, rewriting them, or removing them entirely (if the information is obsolete).
Backlinks
10. Do You Have Fewer Backlinks Than Your Competitors?
An important ranking factor is backlinks, links from other websites that link to your webpages.
If your enterprise website is competing against well-known incumbents in your industry, it’s likely they have a robust backlink profile, making it difficult for your website to compete in the SERPs.
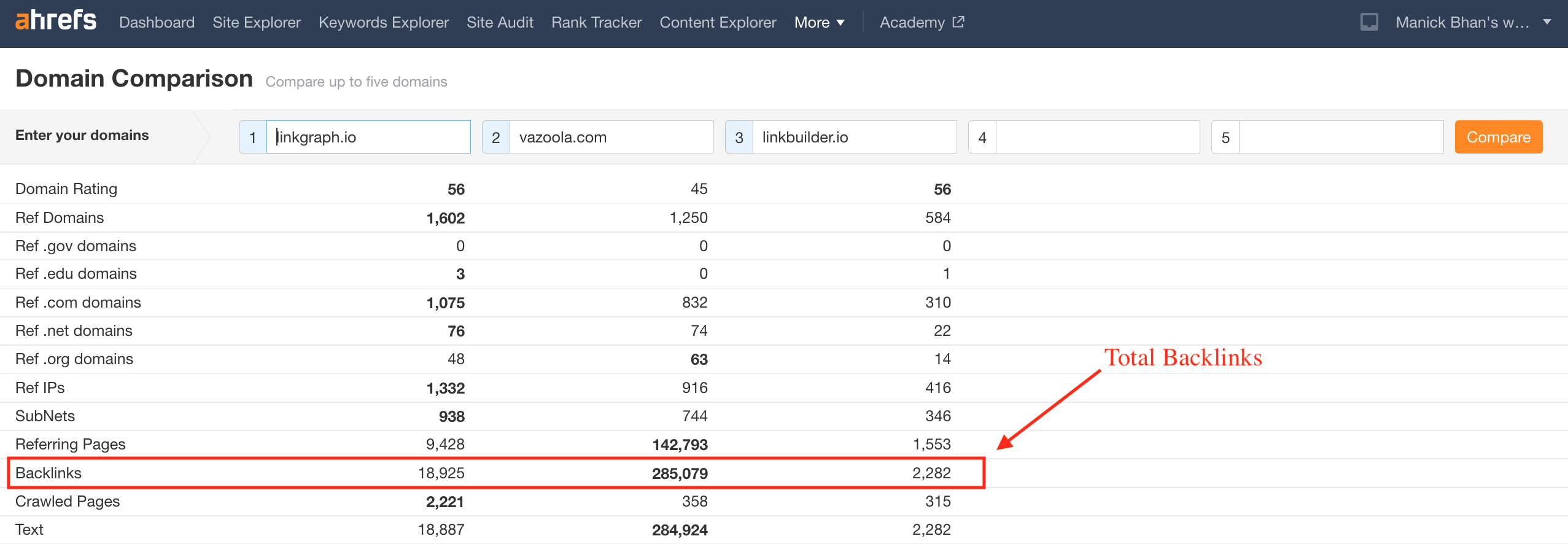 Screenshot from Ahrefs, May 2022
Screenshot from Ahrefs, May 2022You can use a backlink tool like Ahrefs to identify your competitor’s total backlinks and unique referring domains.
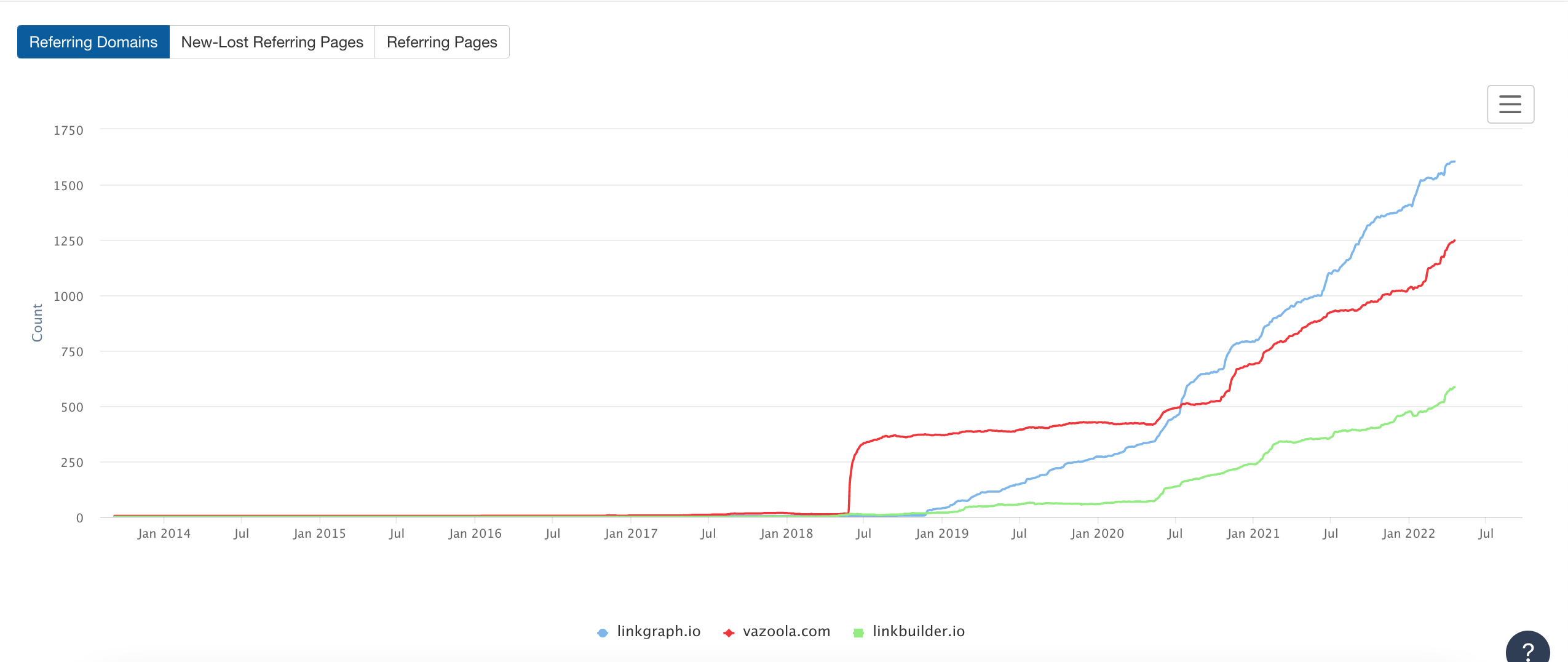 Screenshot from Ahrefs, May 2022
Screenshot from Ahrefs, May 2022If there is a significant gap in backlinks or referring domains, this is likely a source for fewer keyword rankings or lower-ranking positions.
Dedicate a significant portion of your SEO campaign to link building and digital PR if you want to outrank your competition.
11. Does Your Website Have Toxic Backlinks?
Although backlinks are important for improving site authority, the wrong type of backlinks can also harm a website.
If your website has toxic backlinks from spammy, low-quality websites, Google may suspect your enterprise website to be guilty of backlink manipulation.
Google has gotten better at recognizing low-quality links, and after their 2021 Link Spam Update, Google also claims to nullify spammy links and not count them against websites.
The only spammy backlinks you should be concerned about are links that the Enterprise site itself is responsible for or had a hand in obtaining.
For example, paid links should be disavowed if it’s not possible to have them removed.
Multiple guest posts with highly optimized anchor text that the enterprise site is responsible for should also be considered potentially troublesome and cause of a manual action penalty and therefore should also be disavowed.
Some SEO software tools can identify toxic links and create disavow text for you.
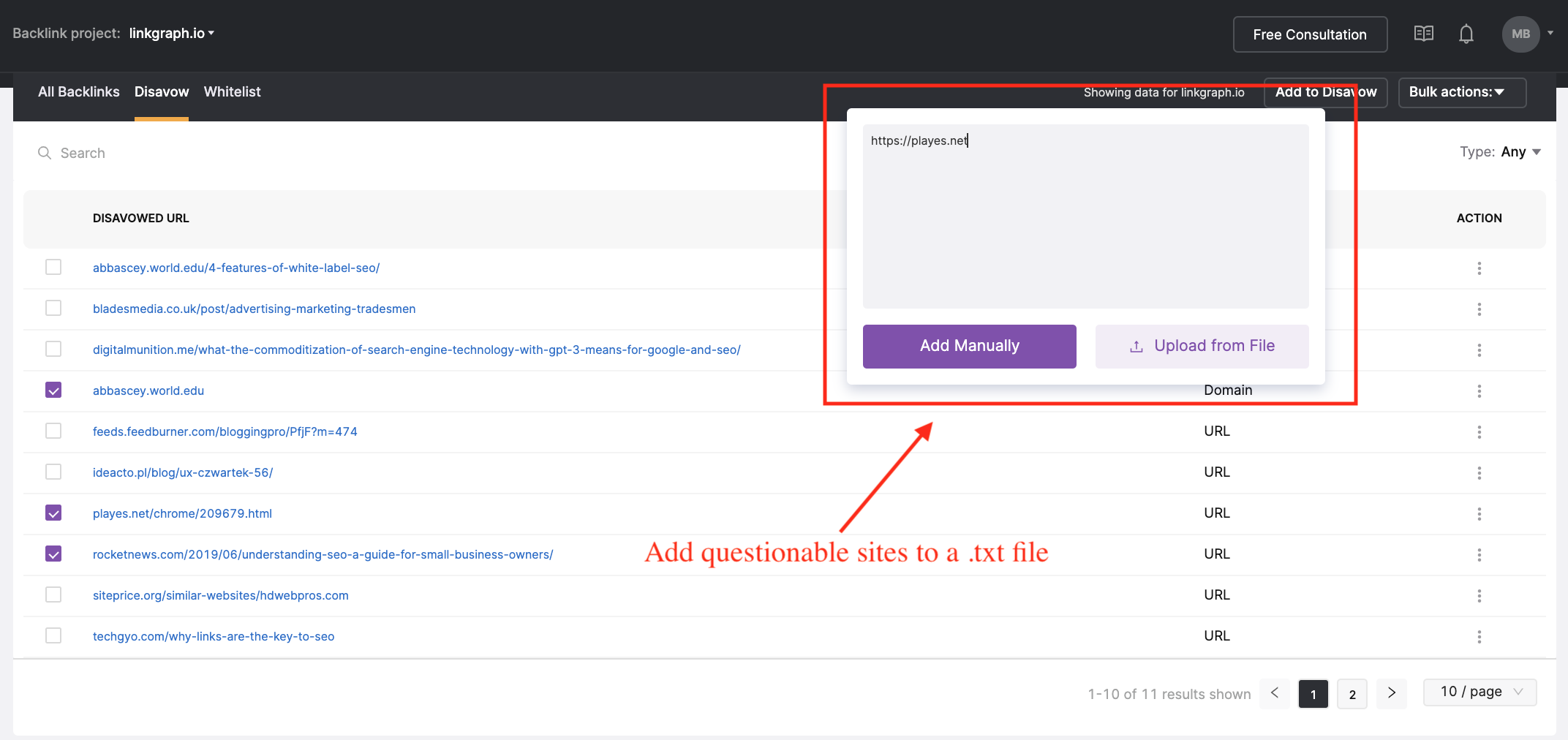 Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022
Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022Disavowing the wrong way can actually harm your SEO performance, so if you are unfamiliar with this Google tool, make sure you seek the assistance of an SEO provider.
12. Is Your Anchor Text Distribution Diverse?
Highly optimized anchor text could be a sign that the enterprise site engaged in link buying or guest posting for links.
Normal sites that don’t engage in sketchy link building tactics should not have to worry about their anchor texts.
Technical SEO
13. Have You Submitted An XML Sitemap And Did it Include The Right Pages?
Because enterprise websites have thousands of landing pages, one of the most common issues uncovered in enterprise SEO audits is related to search engine indexing.
That’s why generating and submitting an XML sitemap is important. It communicates your website hierarchy to search engine crawlers.
It also tells them which pages of your website are the most important to crawl regularly and index.
If your enterprise website adds new product pages or content to your website, you can also use your sitemap to show Google the new pages rather than wait for crawlers to discover them through internal links.
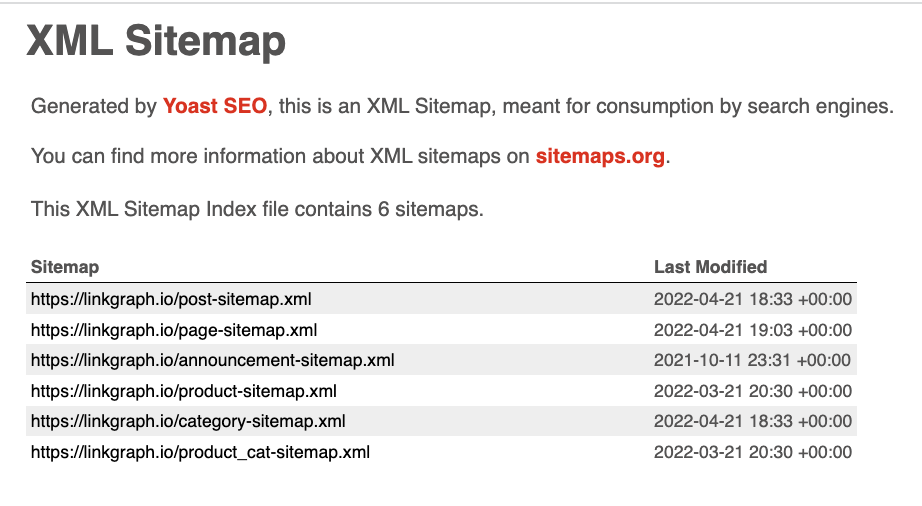 Screenshot of Yoast SEO, May 2022
Screenshot of Yoast SEO, May 202214. Have You Maxed Out Your Crawl Budget?
Google’s web crawlers will only spend so much time crawling your web pages, meaning your enterprise website may have pages that don’t end up in Google’s index.
Although improving your page speed and your site authority can lead to Google increasing your crawl budget, that takes time. So in the meantime, focus on making sure you’re using your crawl budget wisely.
If your audit uncovers essential pages that are not being indexed, your enterprise website may benefit from crawl budget optimization. You want your highest value, highest converting pages to end up in Google’s index.
15. Is Your Schema Markup Properly Setup?
A very powerful optimization that your enterprise website can utilize is schema markup.
If your enterprise website already includes schema on some of your pages, you will want to confirm that your schema is validated and eligible for rich results.
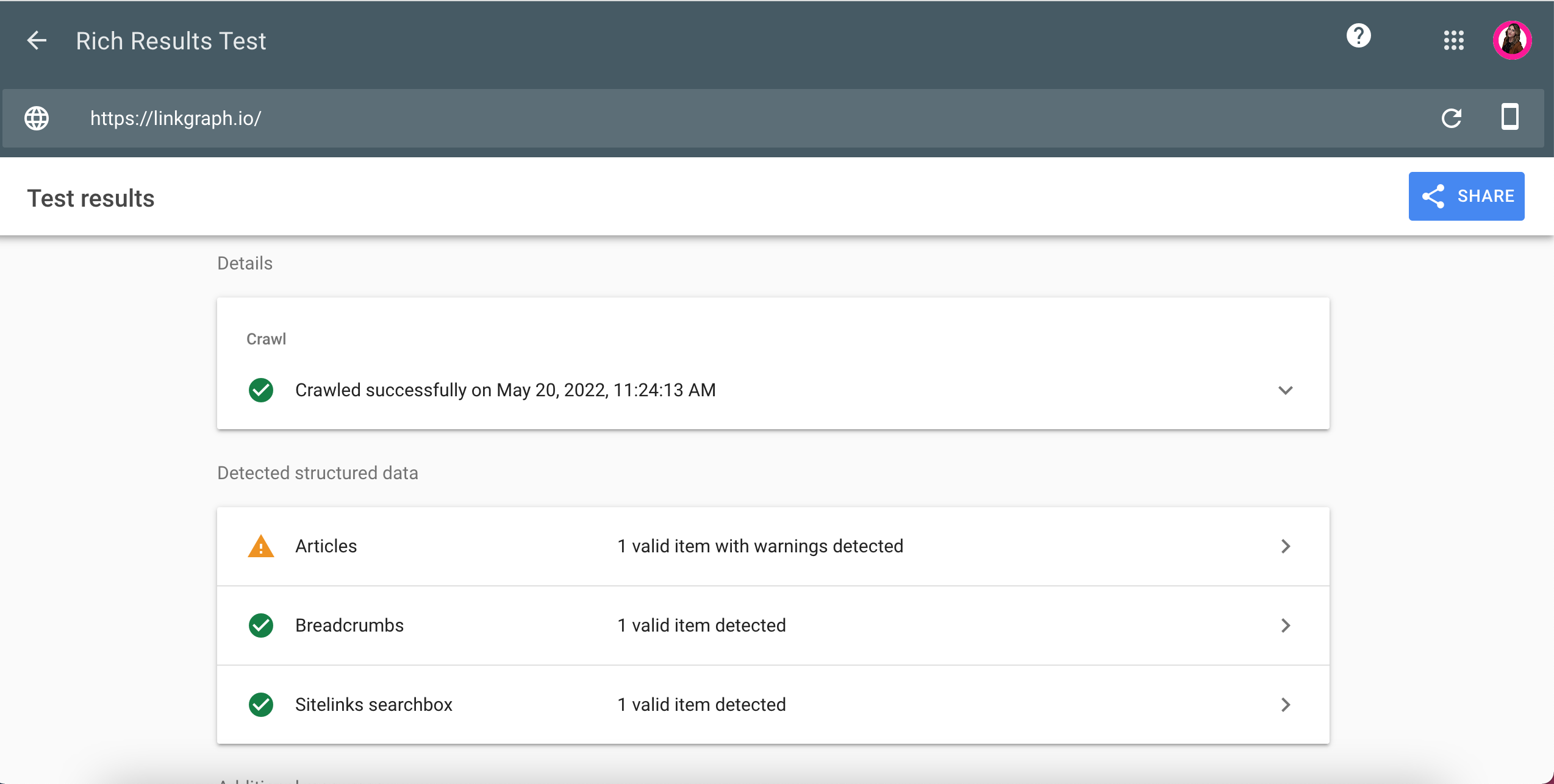 Screenshot of Google, May 2022
Screenshot of Google, May 2022You can use Google’s rich result to test your pages that include schema markup to confirm they are properly validated but to be even more efficient, use your favorite site crawler to test all of your pages at once.
16. Do You Have Excessive Broken Links Or Redirects?
Over time, links naturally break as websites update their content or delete old pages.
It’s important to check your enterprise website to confirm your external and internal links are pointing to live pages.
Otherwise, it will appear to Google that your website is not well-maintained, and Google will be less likely to promote your web pages in the SERPs.
[Technical SEO Audit] Download the free workbook →
17. Do Similar Pages Include Canonical Tags?
Enterprise websites (particularly ecommerce sites) may have duplicate content that targets different regions or is programmatically built out.
If those pages don’t have canonical tags, they will look to Google as duplicate content.
It’s important to confirm that the best, most in-depth version of the page has a self-referential canonical tag. All of the similar pages include canonical tags that identify the master version of the page.
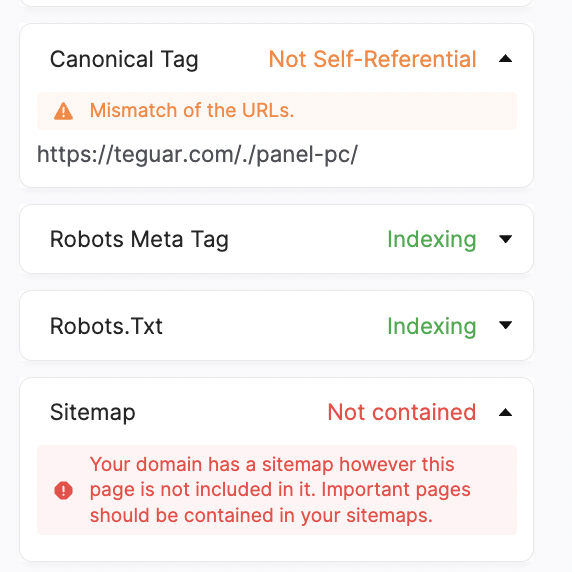 Screenshot from SearchAtlas, May 2022
Screenshot from SearchAtlas, May 2022A site auditor tool like SearchAtlas can confirm whether your canonical URLs are properly implemented and if Google crawlers understand which page to promote in the SERPs.
18. Does Your Multilingual Content Leverage Hreflang Tags?
For multilingual enterprise websites, hreflang tags can help you show the right language content to the right searchers.
This improves your relevance signals and can have a huge impact on your conversion rates.
However, it’s easy to make mistakes when implementing hreflang and canonical tags.
As a general rule, only add hreflang tags to your web pages with self-referencing canonicals – not duplicate copies of the page.
Page Experience
19. Do Your Pages Meet Google’s Core Web Vitals Standards?
If your pages do not meet Google’s Core Web Vitals standards, they are unlikely to rank.
CWV (Core Web Vitals) are important for helping enterprise sites achieve their goals. They are also a known Google ranking factor (although a small one).
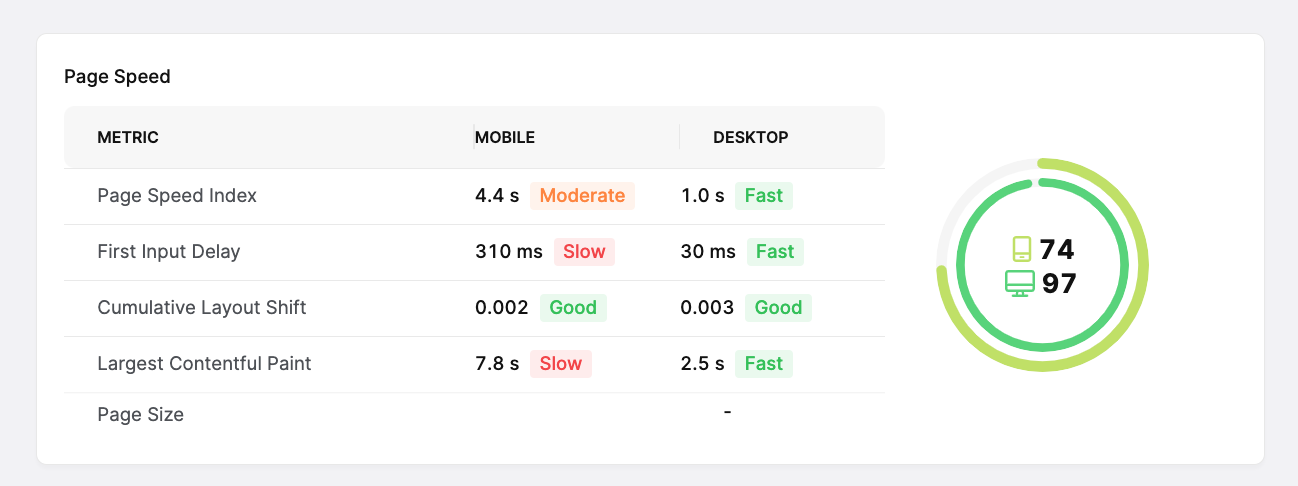 Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022
Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022You can see your Core Web Vitals metrics in your Google Search Console account.
You can also use the free platform to validate any fixes and see whether or not they improve your CWV metrics.
 Screenshot of Google Search Console, May 2022
Screenshot of Google Search Console, May 202220. Do Your Web Pages Include HTTP Or HTTPS Protocols?
A secure website is also essential to the quality of the user’s experience.
If your web pages are not utilizing HTTPS protocols, you are not providing users with a secure browsing experience.
Insecure HTTP pages are blocked by Google Chrome and require an extra step for a site visitor to reach a web page, defeating any SEO that was done to help the page.
While HTTPS is a minor ranking factor, the more important consideration is that failure to provide a secure web page will result in less site visitors.
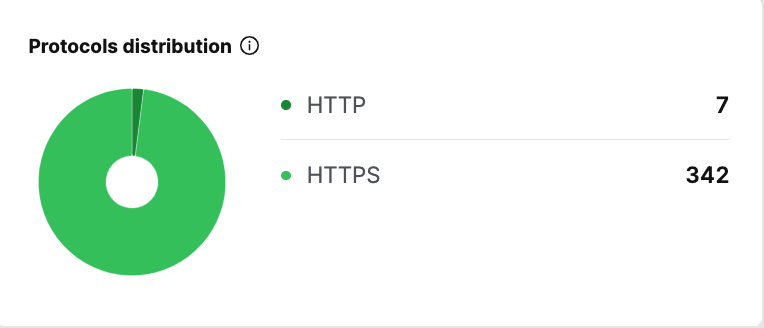 Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 2022
Screenshot of SearchAtlas, May 202221. Are Your Mobile Pages Responsive And High-Performing?
The majority of searches now happen on mobile devices.
Also, with mobile-first indexing, Google predominantly uses mobile pages in its index.
It is also more likely to use your mobile pages when determining where to rank your pages compared to your competitors.
Some common mobile mistakes that occur include:
- Unresponsive design.
- Intrusive pop-ups.
- Bad UI/UX elements like button size.
- Unplayable or missing content.
Industry
22. Are You Considered A Your-Money-Your-Life (YMYL) Website?
If your enterprise website is considered a health, financial, legal, or other YMYL website, Google has extremely high standards for the content that it will promote to searchers.
Although this does not impact all enterprise websites, it’s important to know whether your website falls under this banner to make sure you meet Google’s specific standards for your YMYL industry.
23. Does Your Website Show High Levels of E-A-T?
Google wants to see that your content is relevant to users’ keywords.
It also wants to see that your website, as a whole, displays industry expertise.
E-A-T stands for expertise, authority, and trust. It’s hard to quantify, but some more tangible factors include:
- In-depth, well-researched content (e.g. blogs, ebooks, long-form articles).
- Expert authorship and sourcing (e.g. an author byline that shows industry-specific expertise and credentials).
- A clear purpose and focus for each page.
- Off-site reputation signals (e.g. an article in a reputable online publication that mentions or links to your website).
If you’re still not sure what E-A-T looks like in your industry, look to the top-ranking content of your competitors to see the topical depth, expertise, and sourcing, and model your content accordingly.
24. Does Your Website Have Strong Reputation Signals?
If your goal is to rank for branded searches, other authoritative websites may feature content about your brand competing with yours in the SERPs.
If your enterprise has a Wikipedia page or press in online publications with high Domain Authority, those digital locations may rank higher than your domain.
If this is the case, you may need to take a more unique approach to link building to improve the branded signals of your content.
Optimizations like schema can also help ensure that information about your brand is featured at the top of the SERP, particularly if those websites that mention your enterprise brand do so negatively.
[Free Download] Your complete guide to the ultimate technical SEO audit
Final Thoughts On Conducting Your Enterprise Audit
Sitewide audits can be daunting, but they are worth the time and effort to craft a tailored, custom SEO campaign strategy.
Make sure to leverage the best SEO software tools throughout your audit to speed up the process and ensure the most accurate evaluation of your website.
Once your audit is complete, you can easily prioritize those optimizations that will be the most impactful.
More resources:
- How to Perform an In-Depth Technical SEO Audit
- Evolution Of The Web: 4 Future Enterprise SEO Considerations
- Enterprise SEO Guide: Strategies, Tools, & More
Featured Image: Yuriy K/Shutterstock


