One of the most popular questions which our potential customers usually ask is the following question: which domain name to choose for work with western search engines?
However, it`s good when this question is asked at once, but not at the stage when it is necessary to promote a site for the residents of Lincolnshire with the domain “ru” in Google.co.uk.
I want to clarify one important point: there are two levels of geo targeting:
- A country level
- A level of a city or region (state, province, etc.)
In terms of promotion these levels are two separate planets with almost different methods of promotion. We`ll consider only geo targeting at a country level and main questions related to this theme in this article. We will speak about choosing a domain name, using “correct” language, hosting and other small but important tricks:
- Correct geo targeting: general provisions
- Choosing a domain name for sites promotion in the U.S. and Europe
- Countries localization within the same domain
- Other factors related to geo targeting
Correct geo targeting: general provisions
For the beginning, let’s consider such private and “pure” cases, as a promotion of a French site in Canada or an English site in the UK. Most of the examples given below are based on these cases.
I would like to list some features of western sites promotion:
1. The first thing which is important to consider is that most of countries in the world (except Russia, China, Japan, South Korea, and Czech Republic) are countries which use Google, so this article will be all about geo targeting in this search engine.
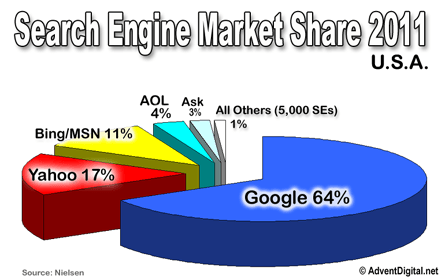
Fig. 1. Search engine market in the USA
Google has about 65% of search market in the USA now (the USA are the most popular object of interest from the side of sites owners), so you need to be guided by Google while promoting sites in the United States. Although, it is worth mentioning that other reputable search engines (Yandex in Russia, a bunch of Yahoo / Bing in the U.S. and others) do not differ from the “champion” a lot.
2. The second point is that Google has its own local versions of the basic search engine for each country. I.e. French users search not in Google.com, but in Google.fr, German users search in Google.de etc.
3. The third moment which needs to be remembered – if target audience speaks, for example, Spanish or English, selecting countries and search engines for their promotion needs to be specified exactly.
Speaking with a client about promotion for Spanish-speaking audience, we always try to concretize whether he wants promotion in Google.es (Spain), Google.com.ar (Argentina) or for Spanish-speaking audience “in general”. By the way, as a reader will be convinced, promotion “in general” doesn’t exist at all, and while promoting by language (not country) SEOs face a range of obstacles.
4. The fourth (and main) moment which needs to be strongly remembered by any SEO specialist who works with western sites:
The main factor for good positions in SERP of any country is usage of domain of this country.
That is, if you want to promote site in any languagein the Google.co.uk search engine, you need to use the domain site.co.uk. You need a domain site.ca for promoting a site in Google.ca both for English and French-speaking audience (one-fifth of Canada’s population speaks French language). For a successful promotion in the Swiss Google use site.ch etc.
There is nothing more important than this rule for geo targeting. All other details, tips, tricks, and so on (we will touch them further) will be useless if you don`t follow this rule. Conditionally, we can say that site presence in a corresponding domain zone is 90% of success in terms of localization.
I want to give a particular example. Owners of inetgiant.com (one of the leading sites of classified ads sites marketing the U.S.) decided to enter the UK search market, i.e., as we have already understood from the information given above, to get customers from google.co.uk.
The main site (. com) was ranked in google.co.uk well, it brought some traffic, but couldn`t raise higher then 10-15th place in SERP. Much weaker resources (in terms of trust, a domain age, abacklinks number etc.) usually were ahead of it, because they had co.uk domains.
A solution suggested itself: they needed to create a new site with original English-language content based on domain co.uk. Just in 2-3 months this new site had bypassed inetgiant.com for the majority of queries in Google.co.uk, and then it overtook many competitors’ sites, beginning to bring a large and stable traffic to their owners.

The same thing was repeated while running other versions of the site in English – in Canada, Australia, etc. Having an appropriate domain name (“.ca”,“.com.au”, etc.) a site with a competent internal optimization received a significant “bonus” in eyes of local search engines (google.ca, google.com.au, etc.)from the start.
By the way, you may ask me how did we choose a domain for “inetgiant.com” website promotion in the USA? Why have we chosen “.com” but not “.us”? To answer these particular questions we must ask the following general question – how to promote a site in the U.S. or in several European countries at once?
Choosing of a domain name for sites promotion in the U.S. and Europe
We`ve considered a “clean” situation, I mean a case when an audience of a site is limited by a single country. But what to do if a site represents interests of American or European audience in general, without specifying the country?
A separate domain “.us” was created for the USA not so long time ago, but it hasn`t caught on as a typical ccTLD for the U.S. for some reasons. (ccTLD country code top level domain – a top level domain bound to a specific country).
The most of American or American-oriented sites have the domain “.com”, which formally is considered as a non-national domain, concerning simply to commercial sites. The domain “.com” is recommended for promotion in the search engine Google.com in most cases.
As to a site promotion in Europe, a universal solution (as in the case with the U.S.) doesn`t exist. A domain google.eu belongs to Google Inc. (or if to be more exact to Irish affiliated company), but it`s not in use currently for search purposes. So it doesn`t make sense to purchase a European domain «.eu».
So, what to do?
- In this difficult case it is better to get relevant domains of those countries where the greatest demand of production is expected or in largest countries of region (Great Britain, Germany, France, Spain, Italy etc.), and to make sites on corresponding national languages. Such sites mustbe promoted separately.
- The second option is less expensive but not better at the same time. You may buy a site in the domain zone “.com” (or, perhaps, “.net”, “.org” – if a site is non-profit) and create several language versions within it. For example, a local version for a “site.com” will look as “en.site.com”, “fr.site.com”, “de.site.com etc.”
And we’ve gradually moved to the third part of the article – countries localization within the same domain
So it is necessary to answer a question: how to make site local versions within one domain? The Google search engine recommends using one of following three variantsin this case:
- The first variant (and we think the best from all points of view) was noted above. Itoffered to use sub-domains:“en.site.com”, “fr.site.com”, “de.site.com etc”.
- Another quite good variant is to use subdirectories (“site.com/en/page1”, “site.com/fr/page1”, “site.com/de/page1” etc.) with content on corresponding languages (English, German, French).
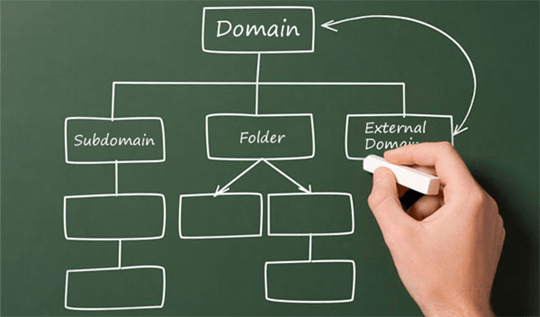
- If the difference between the first two variants isn’t considerable (Google representatives think so), then the worst variant is to use addresses structures such as “site.com? loc=de” or, for instance, “site.com? country=france”.
 But why are the 1st and the 2nd variants good and why is the variant 3 bad?
But why are the 1st and the 2nd variants good and why is the variant 3 bad?
- The 1st and the 2nd variants allow setting of geographical targeting with the help of Google Webmaster Tools (i.e. to specify preferred region).
- The 1st variant is better than 2nd also because you can use several servers for different subdomains placed in different countries and division of one site for language versions is maximum (subdomains are actually separate sites in terms of Google ranking algorithm).
- The 3rd variant is bad because it is hard for Google to identify language versions, and geo targeting through Google Webmaster Tools is impossible.
The last thing required to be mentioned is usage of the same content in different regional versions (for example, the same French text on pages “site.fr/page” and “site.ca/page”). A unique content should be written at each language version in such case because it is the most preferable option in terms of search engines.
However, we all live in the real world where writing of a unique content, especially for the whole site, can be quite expensive. So usage of a non-unique content for different site versions can be acceptable, but in special order.
- The first variant recommended by Google for this case is the 301st redirect from a page “site.ca/page” to a “site.fr/page”. But we don`t advise to do in such way, because a user located, for example, on a Canadian site will not always be happy to move to a French site, which can contain some unique services and offers for France(but not for Canada)on other pages.
- Therefore it is more preferable from our point of view to use the meta-tag canonical for such pages. An original page is indicated at the meta-tag canonical (for example, “site.fr/page”in our case).
Nothing happens from the point of a userview when you use the meta-tag canonical (he still stays on “site.ca/page”), but everything is according to rules in terms of a search engine, because a source page is specified.

A page “site.ca/page” is a kind of defective in terms of a site promotion (this concerns subtleties of pages ranking which mention an original text at the meta-tag canonical). Therefore, if you have serious ambitions (you expect a really high traffic), we recommend you to go back to the first option – to write a unique content for this page.
As a reader can fairly notice, everything looks a little unreliable. How to raise chances of a successful geo localization when you use several language versions within one site? I would like to give some pieces of advice related to this question.
Other factors related to geo targeting
Thus, let’s consider all factors of geo targeting, sorting them by significance:
- The 1st factor is a presence of a top-level domain which corresponds to a country of promotion (ccTLD – country code top level domain, such as“co.uk”,”ca”, “fr”, etc.). It is the decisive factor for high ranking in most cases.
- Manual geo targeting in Google Webmaster Tools (section “Settings”, ”Geographic Targeting”) is the decisive factor which determines a geographic locationfor gTLD (generic top level domain – the top level domain without regional binding, e.g. “.com”, “.net”, “. Org”, etc.). By the way, it is impossible to change targeting for ccTLD. For example, it is impossible to establish the USA targeting for a “site.ru”, because it invariably concerns to Russia by default from the point of Googleview).
- If targeting for gTLD isn’t established in Google Webmaster Tools, then the search engine determines it by IP-address (that is actually a server location). However, this factor is rarely evaluated on its own (search engines usually take an amount of factors into account, including language, phone numbers, etc.).
- Finally, the last “level of influence” is all other signals which help search engines to determine the geo targeting correctly. Google accounts such facts:
- Language of site pages
- Local telephone numbers and addresses
- Links from other sites (if their accessory to a certain region is known).
- Targeting by Google Places.
Thus, knowing about these factors and correctly applying the received knowledge, it is possible to predetermine the outcome of promotion almost for 90-95 % at a stage of selecting a domain for a site.




![AI Overviews: We Reverse-Engineered Them So You Don't Have To [+ What You Need To Do Next]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/sidebar1x-455.png)