Google has been using a technique called neural matching to better understand synonyms, which is said to impact 30% of queries.
According to Google’s Danny Sullivan, the search engine has been using neural matching for the past few months.
“Last few months, Google has been using neural matching, –AI method to better connect words to concepts. Super synonyms, in a way, and impacting 30% of queries. Don’t know what “soap opera effect” is to search for it? We can better figure it out.”
Sullivan is referring to a manifestation of the neural matching technique, which allows Google to return results related to the “soap opera effect” when a user enters a query like “why does my TV look strange?”
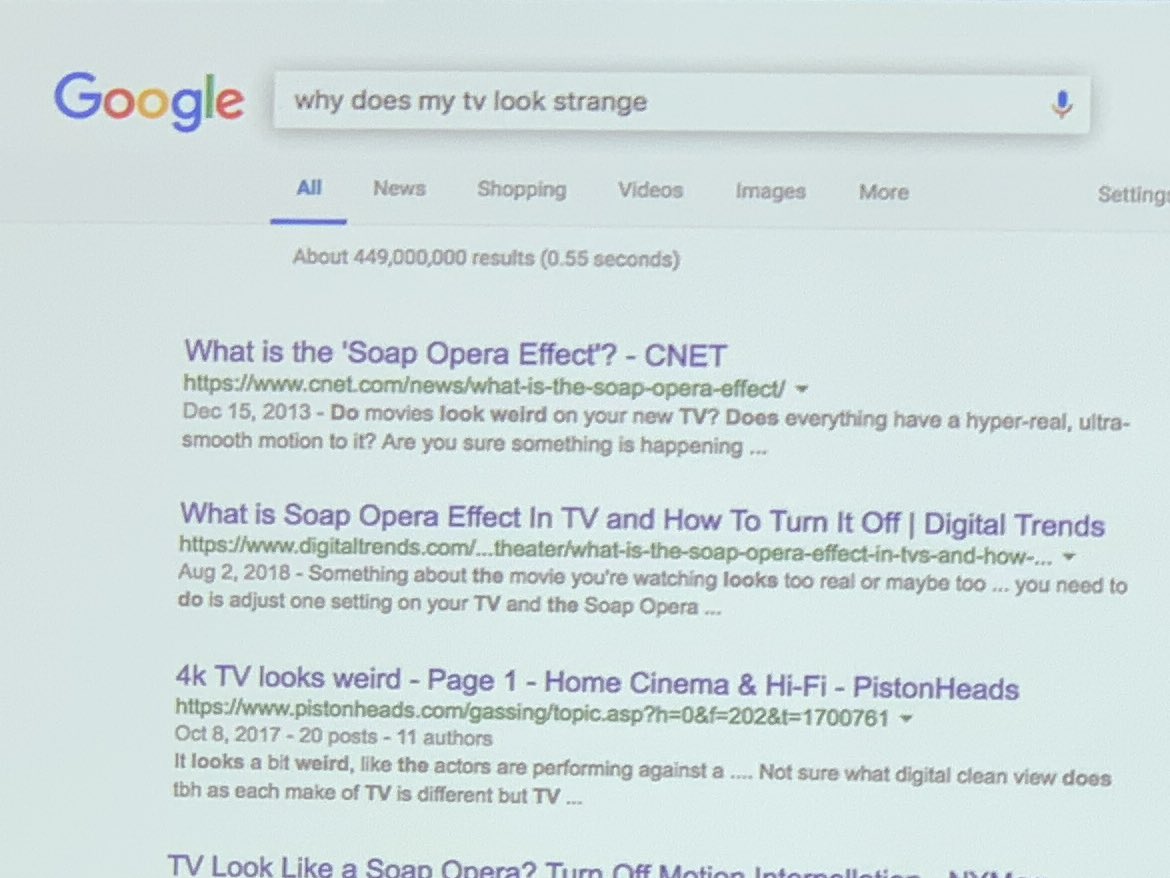
This is significant because “why does my TV look strange?” seemingly has nothing to do with soap operas, but Google is still able to understand what the user may be looking for.
The neural matching technique was discussed today at Google’s 20th anniversary press event, where a number of other search features were announced.
It’s because of Google’s advancements in AI, like neural matching, that these upcoming search features are possible.
Activity Cards
Google’s new activity cards will allow users to pick up where they left off in their search journey.
When a user enters a query related to one they started in the past, Google will display a card with relevant pages they’ve already visited, along with queries that returned those pages.
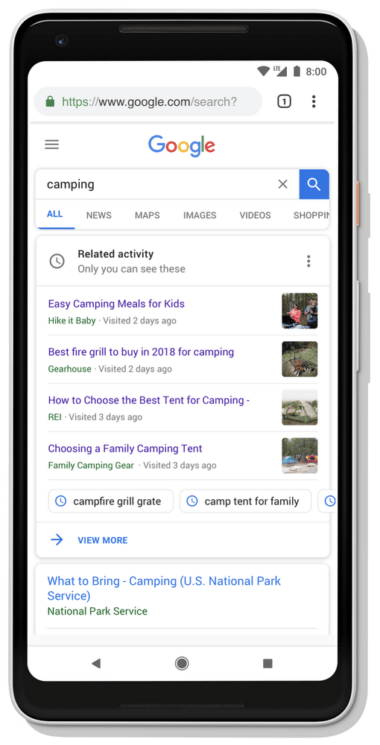
Activity cards will be available in search later this year, and shown only when they’re determined to be useful.
Search Collections
Collections in Google search will allow users to manually keep track of content they’ve visited, such as websites, articles, or images.
Content surfaced in Activity Cards can also be added to collections.
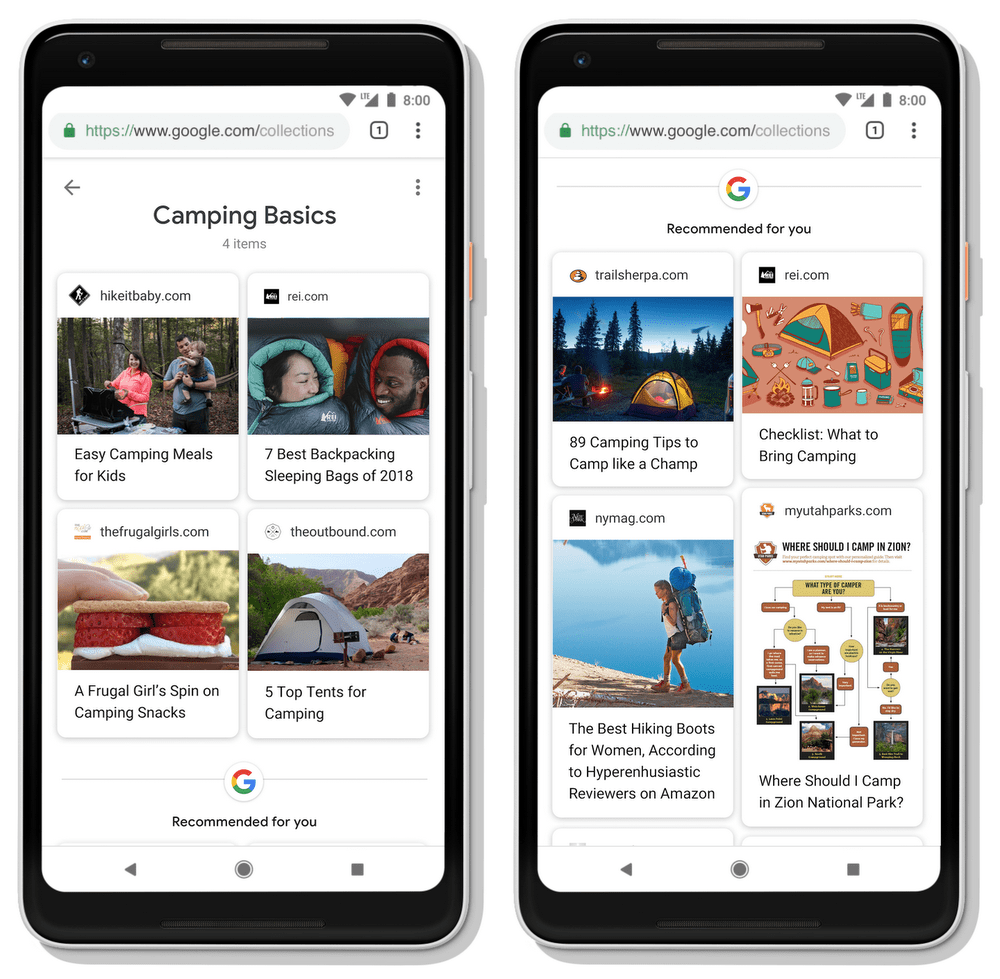
To help users discover new content, Google will offer suggestions based on what people have saved in their collections.
This feature will be rolled out in the fall.
Dynamic Organization of Search Results
Google is introducing a new way of dynamically organizing search results to help users determine what to explore next.
“Rather than presenting information within a set of predetermined categories, we can intelligently show the subtopics that are most relevant to what you’re searching for and make it easy to explore information from the web, all with a single search.”
You can see this change demonstrated in the example below. If a user is searching for Pugs, they’ll see dynamically generated subtopics such as breed characteristics and names.
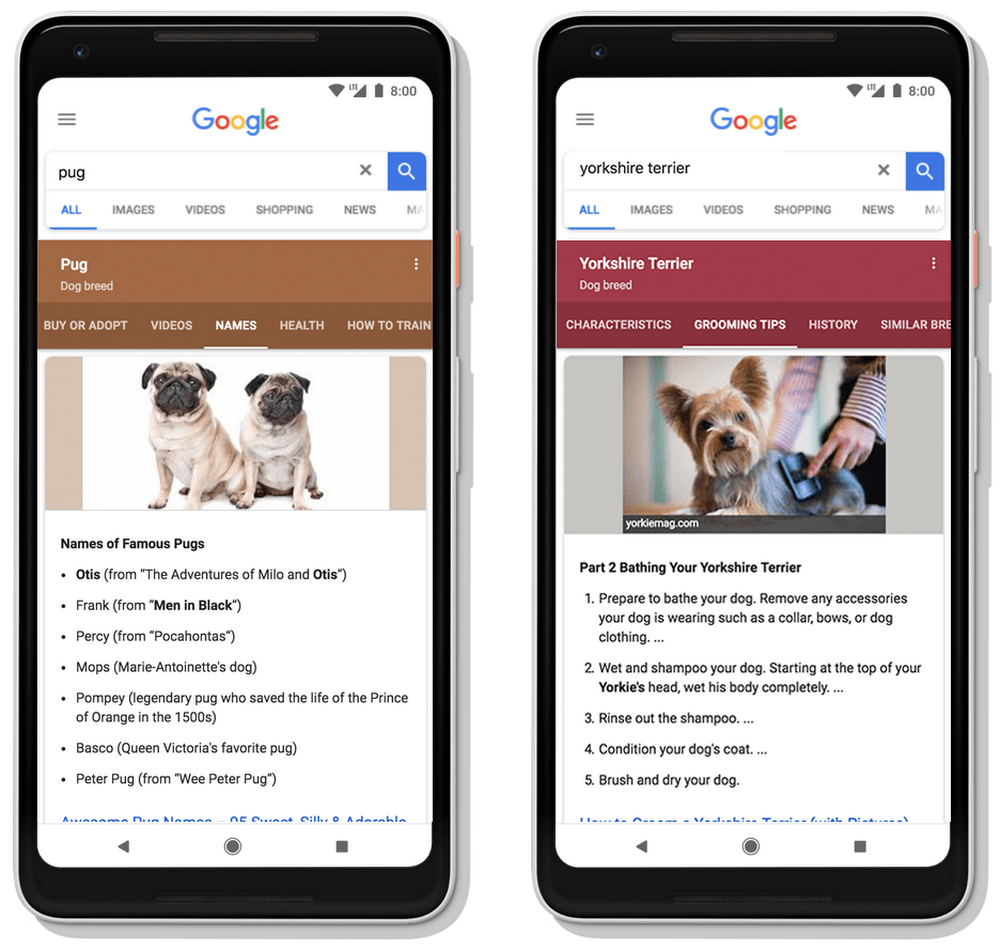
These tabs will continue to stay updated, reflecting what’s most relevant to the topic at that time.
New Topic Layer in the Knowledge Graph
Bringing all of this together is a new layer to Google’s Knowledge Graph, called the Topic Layer.
The Topic Layer is engineered to deeply understand a topic space and how interests can develop over time.
“The Topic Layer is built by analyzing all the content that exists on the web for a given topic and develops hundreds and thousands of subtopics. For these subtopics, we can identify the most relevant articles and videos… We then look at patterns to understand how these subtopics relate to each other, so we can more intelligently surface the type of content you might want to explore next.”
With this technology in place, Google aims to serve users’ ongoing information needs for years to come.






![[SEO, PPC & Attribution] Unlocking The Power Of Offline Marketing In A Digital World](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/sidebar1x-534.png)