On January 22, Google announced it was no longer allowing instances of “double-dipping” in the SERPs, which had allowed webpages that appeared in featured snippets to have additional listings on the first page of Google.
To many SEOs, the perceived value of featured snippets had diminished significantly overnight with the reduced amount of real estate available in search.
The questions were loud and clear:
- How much did this update actually impact clicks and click-through rate on SERPs that had previously occupied featured snippets and an organic listing on the first page of Google?
- Is it even possible to measure the impact with any degree of confidence?
Using a statistics package for R, developed by Google, I analyzed the impact of Google’s update across five client websites and arrived at some surprising (and some unsurprising) conclusions.
Before We Get Started
What Is CausalImpact?
CausalImpact is an R package created by Google to estimate the causal effect of a designed intervention (i.e., a campaign) on a time-series.
In short, this package constructs a Bayesian structural time-series model to create a prediction of how a metric would have performed after an intervention (e.g., content updates, optimizations, algorithm updates, SERP changes, etc.), if said intervention had never occurred.
How to Interpret the Output
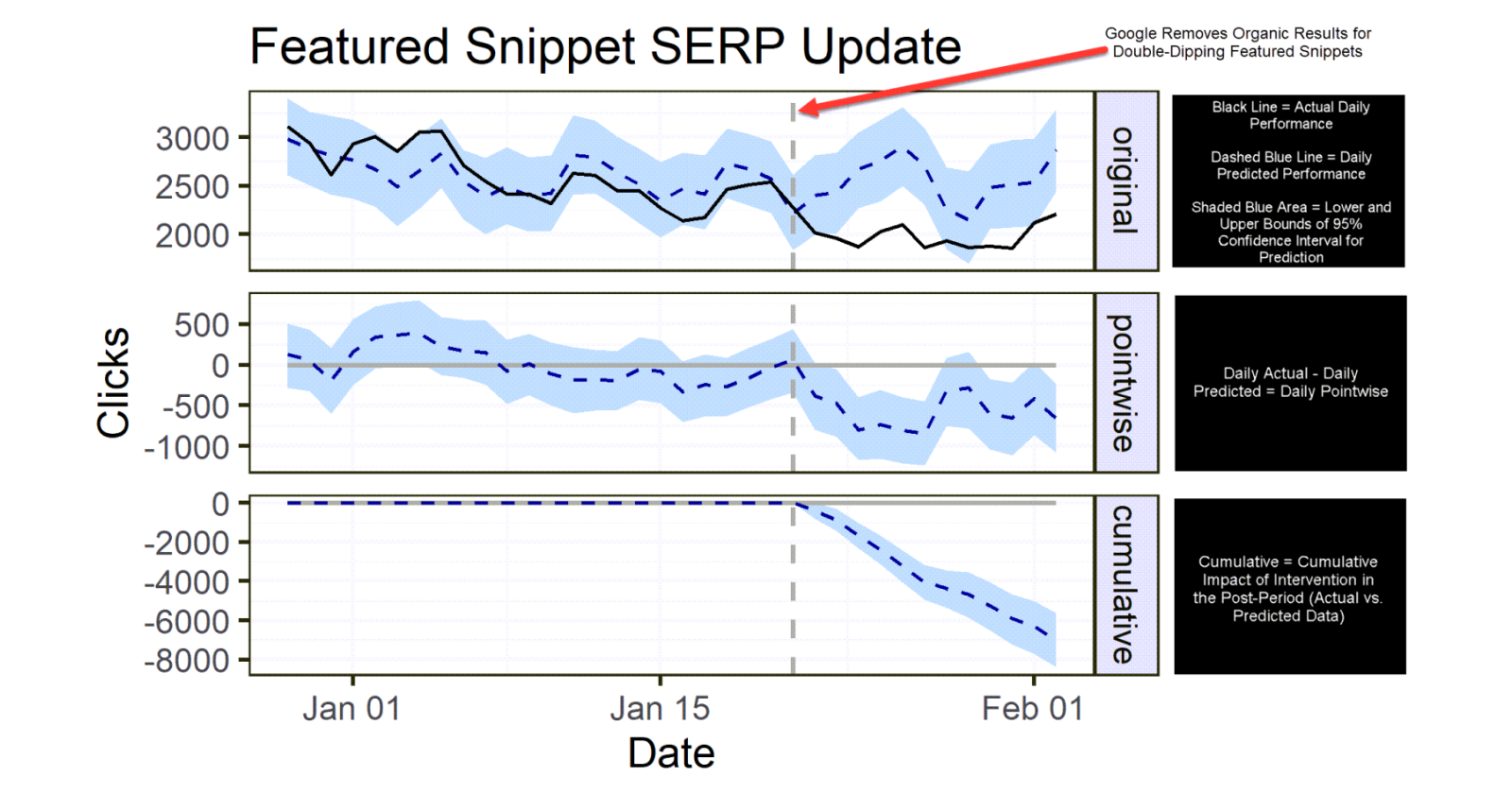
Original Chart
- Black = daily actual clicks
- Dashed blue line = daily predicted clicks
- Shaded blue area = margin of error for predicted daily clicks (95% confidence interval)
- Vertical dashed grey line = date of intervention (January 22, the day Google announced its change to featured snippets)
Pointwise Chart
- Daily variance of actual vs. predicted data.
Cumulative Chart
- Cumulative impact of the intervention in the post-period (actual vs. predicted data).
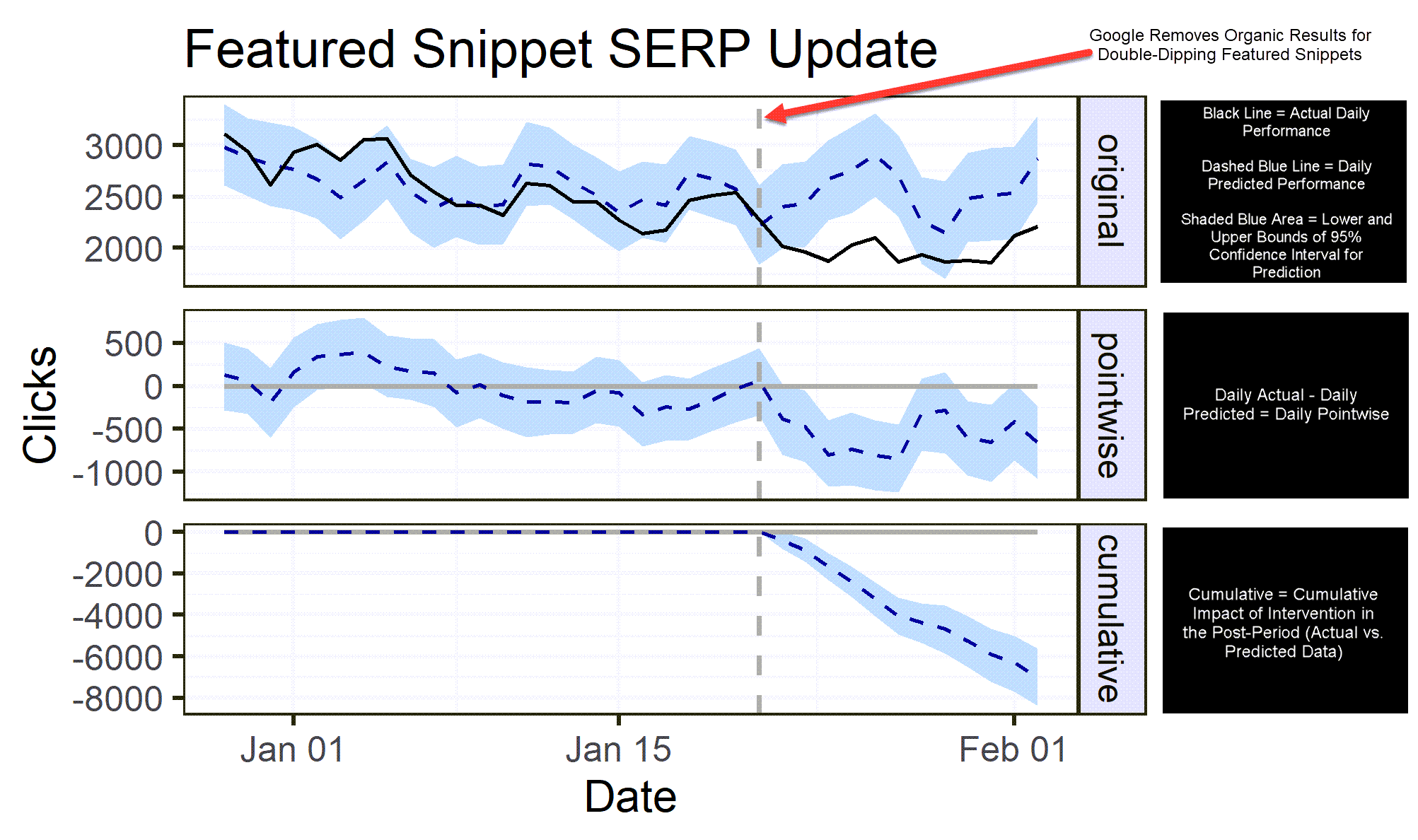
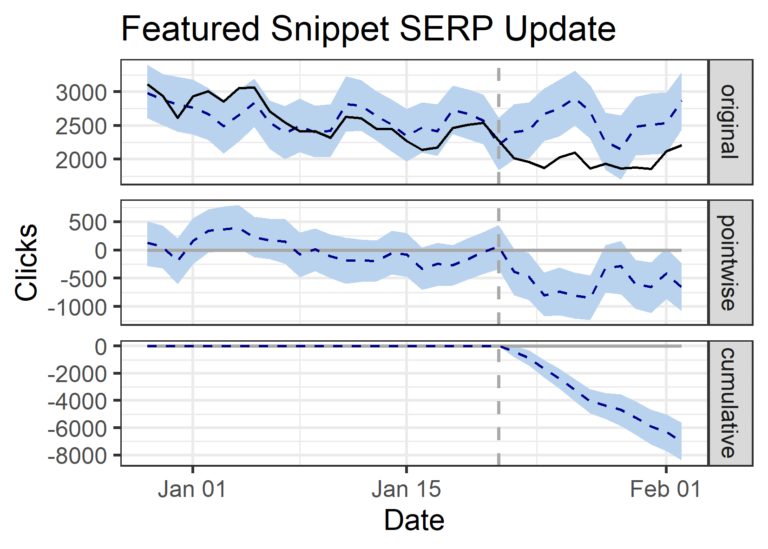
Summary
- The black line above shows actual data clicks for queries that generated featured snippets.
- The dashed grey line shows the intervention on the 22nd (i.e., Google updating the SERP).
- Approximately two days after Google’s featured snippet SERP update, clicks began to diverge away from our predictive model, with a decisive decrease in clicks.
- Had Google never removed “double-dipping” in the SERPs, we see the blue dashed line estimate a lift.
- When we look at the cumulative effect chart, we see a clear negative impact on clicks.
- The cumulative impact of this update was -6,984 clicks compared to our prediction in the post-period (January 23 – February 2).
- Note: example data was pulled from a website in the consumer electronics space.
Methodology
- Because we don’t have a market or set of pages where Google didn’t deploy its featured snippet update that killed off double-dipping, we were forced to fall back on last year’s data to be used as our artificial control group.
- Data was pulled from Google Search Console from December 29, 2019 through February 2, 2020 for our test group and December 30, 2018 through February 3, 2019 for our artificial control group.
- Data was pulled and grouped through Google Search Console’s API by date and query. Only data from queries that generated featured snippets were used.
- Data pulled was overall and not device specific.
- Last year’s data consisted of queries that owned featured snippets in January 2019, per SEMrush.
- 95% confidence intervals were applied to all analyses.
Breakdown of Causal Impact Across 5 Different Websites
Enterprise Consumer Electronics Website
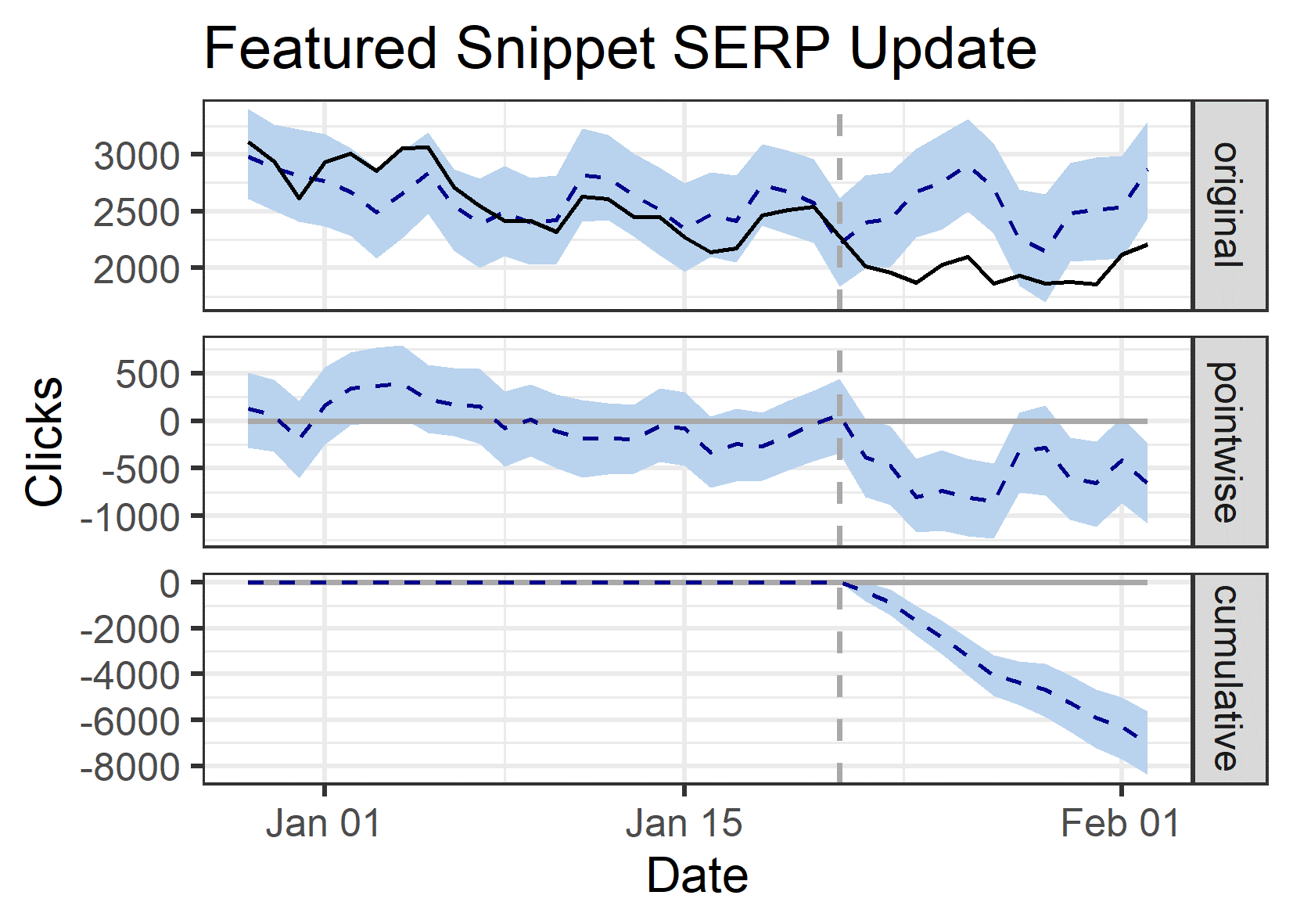
- 4,726 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2020 (test)
- 5% brand keywords
- 5% non-brand keywords
- 1,437 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2019 (control)
- 8% brand keywords
- 2% non-brand keywords
- -23% decrease in clicks (-6,984 clicks)
- -16% decrease in impressions (-22,008 impressions)
- -9% decrease in CTR (20.42% actual daily CTR vs. 22.37% predicted daily CTR)
Enterprise Travel Website
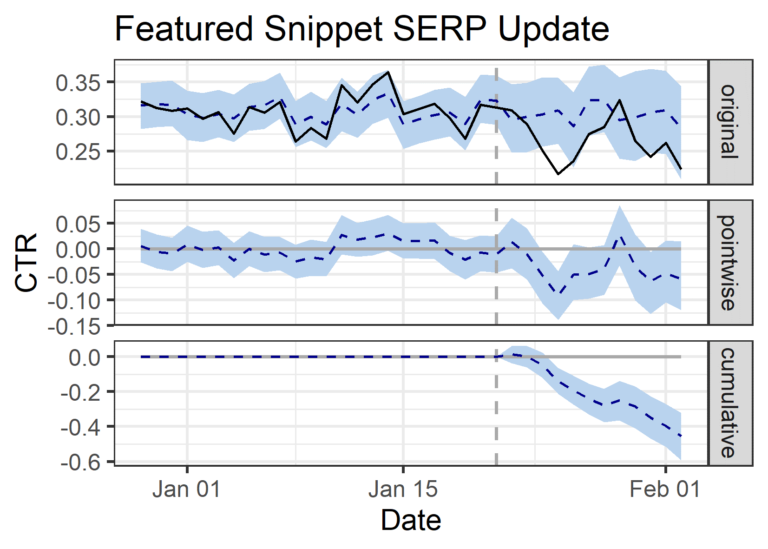
- 468 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2020 (test).
- 4% brand keywords
- 6% non-brand keywords
- 324 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2019 (control).
- 7% brand keywords
- 3% non-brand keywords
- 3% decrease in clicks (didn’t reach statistical significance with 10.1% probability of occurring by chance).
- +10% increase in impressions (+782 impressions).
- -13% decrease in CTR (26.48% actual daily CTR vs. 30.27% predicted daily CTR).
Enterprise Ecommerce Website
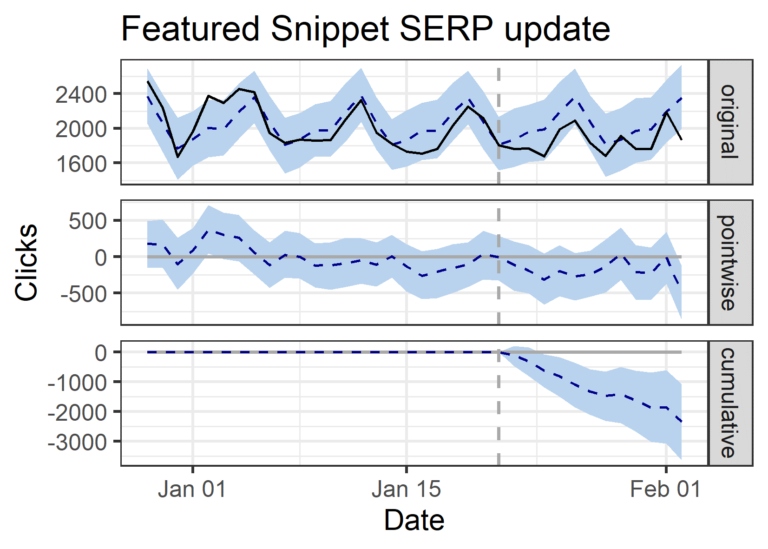
- 599 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2020 (test).
- 3% brand keywords
- 7% non-brand keywords
- 510 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2019 (control).
- 8% brand keywords
- 2% non-brand keywords
- -10% decrease in clicks (-2,342 clicks).
- -6% decrease in impressions (-3,511 impressions).
- -8% decrease in CTR (41.03% actual daily CTR vs. 44.37% predicted daily CTR).
Enterprise Ecommerce Marketplace Website
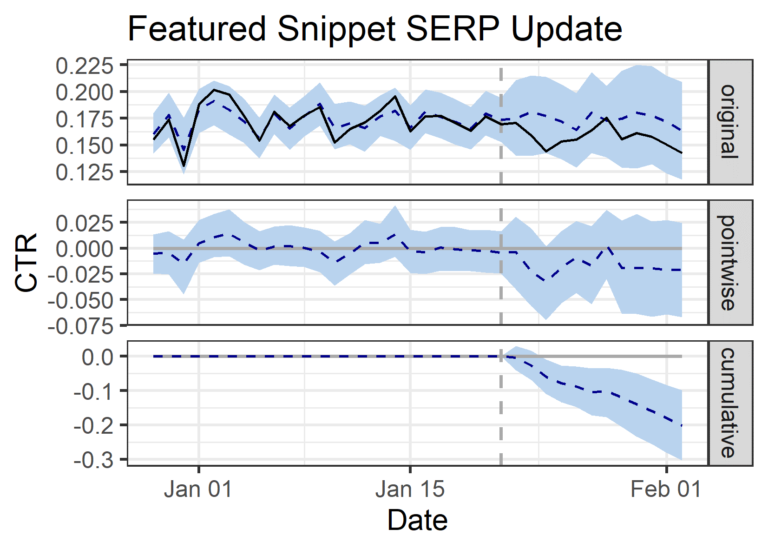
- 1,417 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2020 (test).
- 5% brand keywords
- 5% non-brand keywords
- 1,733 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2019 (control).
- 13% brand keywords
- 87% non-brand keywords
- -4% decrease in clicks (didn’t reach statistical significance with 10.3% probability of occurring by chance).
- +3% increase in impressions (didn’t reach statistical significance with 25.3% probability of occurring by chance).
- -10% decrease in CTR (15.73% daily actual CTR vs. 17.41% predicted daily CTR).
Enterprise Software Website
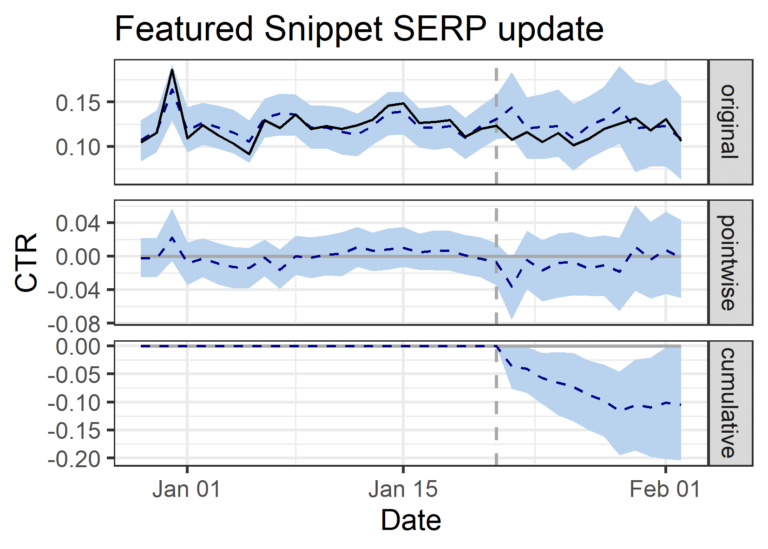
- 330 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2020 (test).
- 5% brand keywords
- 5% non-brand keywords
- 191 keywords analyzed that generated featured snippets in January 2019 (control).
- 2% brand keywords
- 8% non-brand keywords
- -3% decrease in clicks (didn’t reach statistical significance with 32% probability of occurring by chance).
- +6% increase in impressions (didn’t reach statistical significance with 7.2% probability of occurring by chance).
- -7% decrease in CTR (11.54% daily actual CTR vs. 12.41% predicted daily CTR).
Conclusion
Although five websites and thousands of featured snippet-generating queries are a relatively small sample size, we saw consistent statistically significant declines in CTR across all of the websites analyzed.
While not all sites saw statistically significant declines in clicks, all saw declines in clicks with varying probabilities of the results having occurred by chance.
In my opinion, the value proposition of featured snippets has declined somewhat; however, I had anticipated more drastic declines in CTR and clicks as a result of this update on featured snippet queries.
Depending on the query, I do think that featured snippets can still represent strong business opportunities for brands over traditional organic listings.
However, it’s more important than ever to make sure you target the right featured snippets and capture clicks without fully answering a query.
It’s possible that some branded queries may have been better shielded from the impact of this update, due to keyword cannibalization across multiple pages or subdomains.
You might observe in the SERPs multiple listings from the same brand from different pages, subdomains, and domains for branded queries (see “youtube com activate” as an example with a featured snippet result from a support Google subdomain, www Google subdomain, and an organic listing from YouTube):
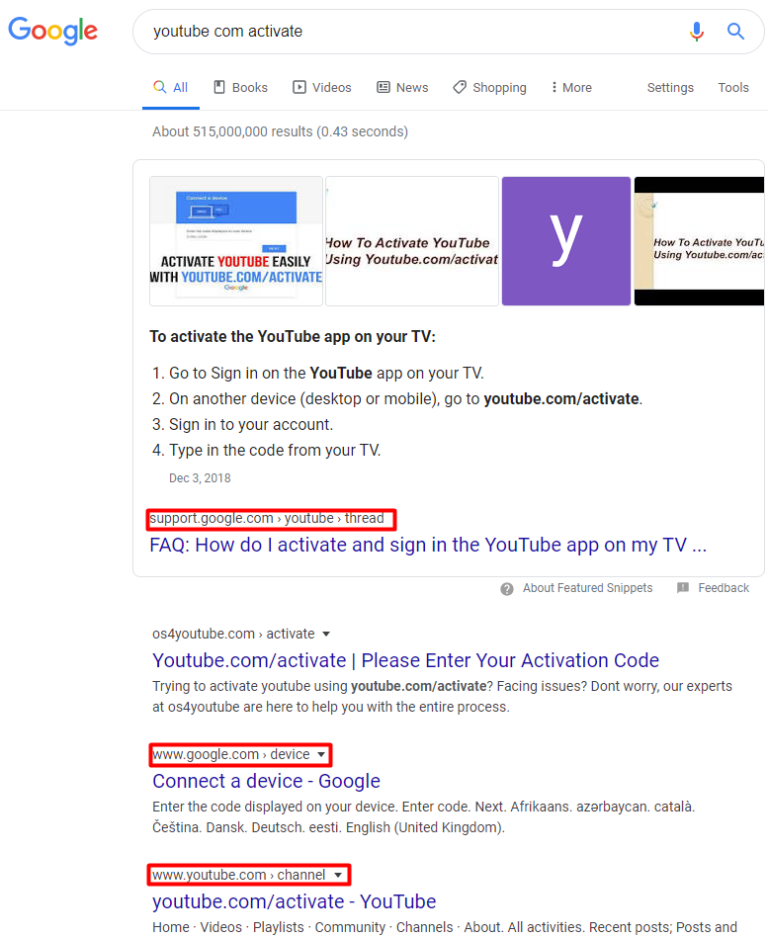
The impact of this update on featured snippet query performance varied significantly by site, industry, queries, and the proportion of branded keywords generating featured snippets.
So we recommend running your own investigations to evaluate the impact of Google’s update relative to your site’s performance.
Takeaways
Across the five sites analyzed, we saw:
- Consistent statistically significant declines in CTR for 5/5 sites ranging from -7% to -13%.
- Statistically significant declines in clicks for 2/5 sites ranging from -10% to -23%.
- Statistically significant declines in impressions for 2/5 sites between -6% and -17%.
- Statistically significant improvement in impressions for our travel website at +10%.
- Note: this may have been influenced by general growth in impressions for the branded keywords included in this analysis.
More Resources:
- Google: Webpages with Featured Snippets Won’t Appear Twice on Page 1
- Google Offers Guidance on Featured Snippets Update
- Google’s Featured Snippet Changes & Impact on Organic Traffic [STUDY]
Image Credits
Featured & In-Post Images: Provided by author, February 2020
Screenshot taken by author, February 2020