Optimizing sites to appear in Google News, Top Stories, and Google Discover is unique in many ways from the process of earning rankings in the 10 blue organic links.
This is because Google uses a variety of different organic SERP features to display recent or newsworthy content, each of which comes with its own set of ranking guidelines and reporting capabilities.
To make this even more complex, Google only provides dedicated reporting on some – but not all – of these News-related features through Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
This leaves some mystery about precisely where in the search results a given article might be driving traffic and impressions.
Google offers guidelines around how to appear in products like Google News and Discover.
However, these documents are often technical in nature (such as this example of Google’s article that explains technical recommendations for preventing content from being indexed on Google News without affecting its performance in regular Search).
While some guidelines exist, it’s hard to find specific advice in Google’s documentation about how best to structure and optimize content for performance in Google News or Discover.
In order to understand how your sites perform in News, Discover, and related features, it is best to analyze the performance of your own content to see what works and what doesn’t.
In this column, you’ll learn about the various Google SERP features that display recent or trending news and find tips on how to optimize and report on them.
I’ll also include some aggregated data and insights related to my own clients’ performance across these features.
Google News
Google News is a news aggregator product available both as a mobile app and by visiting news.google.com in your browser.
Historically, publishers had to manually submit their sites for approval in Google News via the Google Publisher Center, and the approval process was notoriously difficult.
However, Google recently updated its guidelines about which sites are eligible to appear in Google News.
As of December 2019, the documentation quietly changed:
Hidden among this barrage of Publisher Center updates, this is quite a shock:
"Publishers no longer need to submit their site to be eligible for the Google News app and website. Publishers are automatically considered for Top stories or the News tab of Search." pic.twitter.com/yrCZwnly6j
— Barry Adams 📰 (@badams) December 11, 2019
According to Google’s documentation, all publishers need to do to appear in Google News is “produce high-quality content and comply with Google News content policies.”
Complying with Google’s News content policies boils down to not producing content that is violent, hateful, dangerous, or deceptive.
Reading between the lines of these updated guidelines indicates that it is technically possible for content from any site to appear in Google News.
However, that doesn’t happen often for most sites.
Regardless of how frequently a site produces content, Google is strict in its criteria for which publishers to display in Google News.
As stated throughout much of its documentation, News sites must demonstrate good E-A-T: expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
In fact, in Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines, the definition of “YMYL – Your Money, Your Life” content starts with “News and current events” as the first example of the type of site that can affect a person’s future happiness, health, financial stability, or safety.
 Screenshot from Static.googleusercontent.com, March 2021
Screenshot from Static.googleusercontent.com, March 2021This likely indicates that the criteria used to evaluate content and websites for Google News may be subject to greater scrutiny of E-A-T than that of other areas of Google Search.
This would align with other articles and videos Google has published in recent years that confirm that Google increases its focus on the authoritativeness of publishers when it comes to breaking news, misinformation, elections, and times of crisis.
Two other features Google claims to promote in its rankings of News content are “uniqueness” and a “diversity of viewpoints.”
In late 2019, Google published an article emphasizing the importance of original reporting in its ranking of news content, with the goal of providing stronger rankings for “the story that kicked everything off.”
According to Google:
“While we typically show the latest and most comprehensive version of a story in news results, we’ve made changes to our products globally to highlight articles that we identify as significant original reporting.
Such articles may stay in a highly visible position longer. This prominence allows users to view the original reporting while also looking at more recent articles alongside it.”
If your goal is to rank well in Google News, this recommendation can’t be overlooked.
There are numerous aggregator websites and websites that primarily syndicate content from sources like Reuters or the Associated Press, which may be seeing declines in organic visibility in recent years because of this issue.
The SEO visibility of one such aggregator website is shown below, with blue letters indicating Google Core Updates:
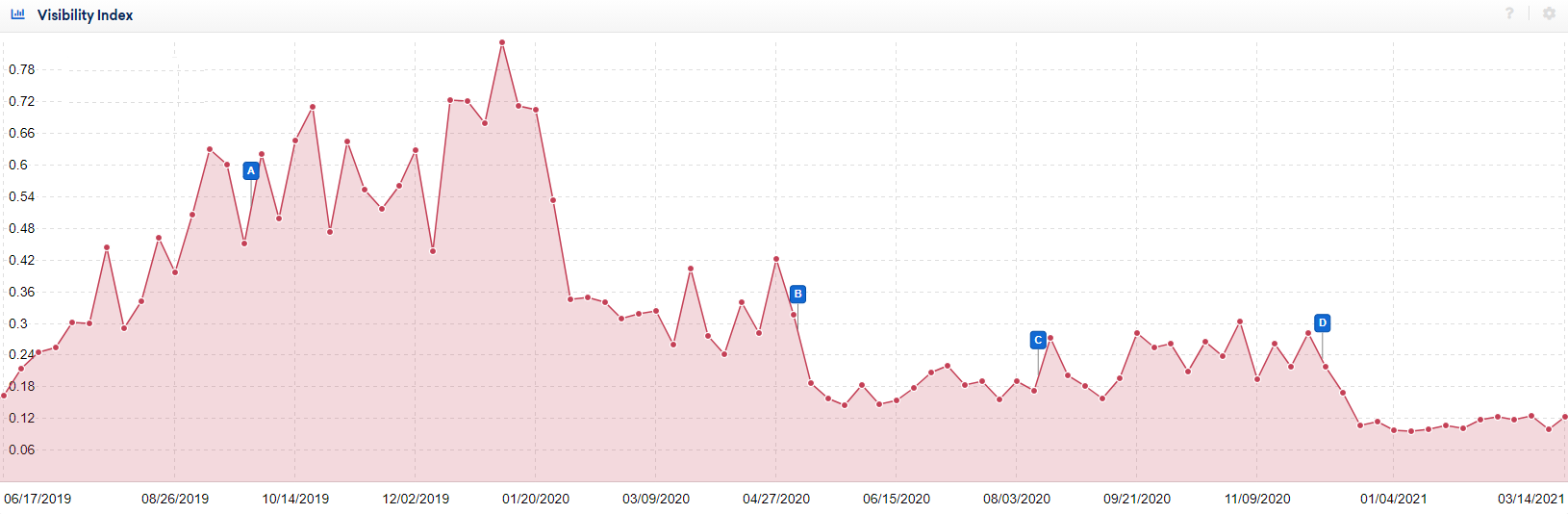
While it’s not uncommon for syndicated content to drive traffic, achieving long-term, sustainable performance in Google News requires differentiating your content by providing original reporting or offering a unique angle not found on other sites.
In fact, Google recommends that syndicated content not be indexed, although, in reality, this type of content often drives significant organic traffic for many publishers who choose to index it.
When it comes to optimizing content for Google News, Google offers some advice about its criteria for ranking content in Google News, including:
- Relevance.
- Prominence.
- Authoritativeness.
- Freshness.
- Location.
- Language.
Publishing quickly is key.
Unlike traditional search, where timeliness may be more of a muted factor (depending on the query), in Google News, timeliness is everything.
This is especially true if a breaking news event takes place.
The sites that publish quickly will be the first to start accruing links and social shares, which will only amplify their performance on Google News.
Using NewsArticle structured data and News XML Sitemaps are also technical requirements for inclusion in Google News.
Google’s Publisher Center
Google offers news publishers a Publisher Center they can use to manage their Organization’s information. This includes general information about the organization, which categories are included on the site, official brand logos, feeds, and more.
If ranking in Google News is your goal, you should absolutely make use of the Publisher Center to control important information about your brand.
Visibility In Google News
While Google News aims to show a variety of viewpoints and not skew towards any end of the political spectrum, highly authoritative publications have been dominating in recent years.
Meanwhile, many fringe publications appear to have lost visibility.
Looking at the news publishers with the strongest visibility on Google over the last 12 months can shed some light on what it takes to be considered a news authority in various categories.
I pulled a list of the 100 highest traffic websites in “News and Media” from Similarweb’s list of highest traffic domains in that category.
I then cross-referenced this list with the Sistrix Visibility Index (VI) scores for these domains, which measures the overall visibility of a domain over time and assigns it a Visibility Index (VI) score based on how it ranks on Google across Sistrix’s set of 1 million tracked keywords.
These are the news domains that capture the most organic visibility on Google.com as of March 1, 2021, using the U.S. index:
| Domain | 3/1/21 VI |
| nytimes.com | 243.4 |
| usnews.com | 212.1 |
| theguardian.com | 123.2 |
| cnn.com | 102.9 |
| yahoo.com | 100.7 |
| forbes.com | 97.4 |
| bbc.com | 77.8 |
| finance.yahoo.com | 70.0 |
| usatoday.com | 59.0 |
| businessinsider.com | 57.1 |
| washingtonpost.com | 55.7 |
| chron.com | 50.7 |
| nbcnews.com | 46.4 |
| bloomberg.com | 46.0 |
| cnbc.com | 45.3 |
| theverge.com | 44.8 |
| bbc.co.uk | 32.3 |
| theatlantic.com | 29.7 |
| time.com | 29.0 |
| cosmopolitan.com | 27.5 |
| latimes.com | 26.4 |
| people.com | 26.4 |
| reuters.com | 26.3 |
| wsj.com | 26.3 |
The sites listed above are good sources of inspiration when determining how to structure your headlines, subheadlines, URLs, taxonomy, internal linking, and other considerations that are important for ranking in Google News.
For a comprehensive rundown of how best to optimize content for Google News, I recommend John Shehata’s article on Google News optimization.
Reporting On Google News Traffic
Google News traffic can be reported on through Google Analytics as well as Search Console.
In Google Analytics, Google News traffic will show up under the referral source news.google.com.
Google Search Console also recently introduced a dedicated Performance report for Google News traffic in the Google News tab of the left sidebar. By combining Google Analytics and Search Console, you can get a deeper view of the data, such as seeing click-through-rates for your article headlines in Google News (by adding Page Title as a secondary dimension in Google Analytics).
Hiding most of this for client confidentiality purposes, but being able to easily join GA & GSC data from Google News makes it much easier to analyze which headlines generate the strongest CTRs in Google News, which is a gamechanger for many clients.
Thank you @googlesearchc pic.twitter.com/5iAzkZwpVC
— Lily Ray 😏 (@lilyraynyc) January 13, 2021
Google Top Stories
For news publishers, Google’s Top Stories carousel is a goldmine of organic traffic. According to Richard Nazarewicz, the Technical SEO Manager of the Wall Street Journal:
“The Top Stories carousel for Mobile and Desktop SERPS is the most coveted spot for fresh or breaking news to surface within the Google Search ecosystem. Every newsroom is working hard with their SEO Editors or SEO desk, if they have one, to optimize using Google Trends, competitor analysis, and A/B testing SEO title tags (headlines) to ensure their article is surfacing in the top 3 Top Stories results.
Just like any regular article they need to be linked to from a prominent position like the Homepage and included in a dedicated sitemap for fresh or breaking news from 48 >= 72 hours before being moved into a regular article archive sitemap depending on your setup.”
It is important to note that currently, only AMP articles are eligible for the Top Stories carousel on mobile devices.
However, Google stated that this requirement will be dropped in conjunction with the Core Web Vitals update set to roll out in May 2021.
After that date, any article can potentially appear in the Top Stories carousel.
However, if the major publishers continue using AMP, this will make it hard for non-AMP publishers to compete with the lightning-fast load times of AMP articles.
The Top Stories carousel currently does not have a dedicated reporting section in Google Search Console or Analytics.
One way to approximate performance data from Top Stories is to navigate to the Search Appearance tab in Search Console, filter by a mobile device, and select AMP article.
This is by no means perfect, as it’s still possible for AMP articles to be surfaced in other areas of Google. But it can serve as a representative set of clicks and impressions from Top Stories (and other places).
It can be helpful to navigate to this view after launching AMP to see if the articles are gaining traction in Top Stories.
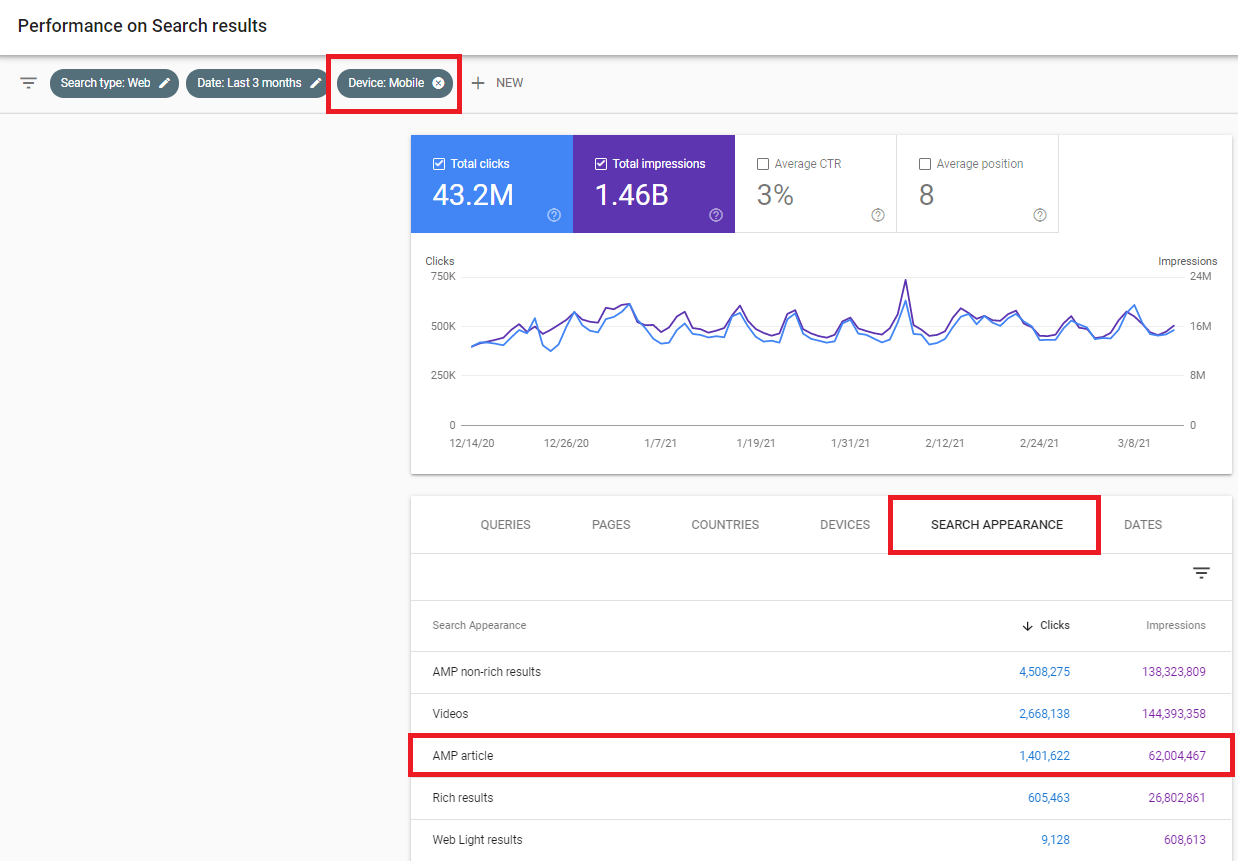 Screenshot from Google Search Console, March 2021
Screenshot from Google Search Console, March 2021For ranking in Top Stories, one of the most important ranking factors is the use of keywords in headlines. Unlike Google’s standard organic blue links, which display the <title> element as the title of the ranking page, Top Stories show the <h1> headline as the primary title of the page.
 Screenshot from Google SERPS, March 2021
Screenshot from Google SERPS, March 2021It’s therefore important to focus on optimizing the article headline, such as by ensuring the name of the targeted entity (person, place, or thing being written about) is stated clearly and early in the headline.
Article headlines should generally stay under 22 words for optimal performance.
It is also important to avoid profanity, clickbait, or anything inappropriate or unclear in article headlines.
Google Discover
Google Discover is a personalized feed of articles that is available to mobile users via Android devices or the Google App on iOS.
Google Discover can also be accessed by visiting the Google.com homepage while logged into a Google Account on a mobile device using Google Chrome.
What makes Google Discover unique from other areas of search is that the list of articles is curated before the user types anything, using other user behaviors across Google to determine what the user might find interesting.
Therefore, a user who frequents publications about dogs, or perhaps shares dog articles on social media, or uses dog-related apps on their phone, may be more likely to see dog content appearing in their Discover feeds.
Content is eligible to appear automatically in Google Discover without using any specific structured data or sitemaps.
Google does require a “compelling, high-quality image,” that is at least 1,200px wide and enabled by the following meta tag:
<meta name="robots" content="max-image-preview:large">
or by using AMP.
Google’s Discover guidelines recommend focusing on content that’s “timely for current interests, tells a story well, or provides unique insights,” while “avoiding clickbait headlines” and providing “clear dates, bylines, information about authors, the publication, the publisher, company or network behind it, and contact information.”
According to Richard Nazarewicz,
“Discover Traffic tends to average around 20-40% of all Google traffic (GSC), whereas in Europe, it is more like 40-60%. The reason it is higher in Europe as well as the Middle East is that Android has a much higher percentage of the mobile market, as opposed to the U.S., where we are predominantly using the Apple iPhone, myself included!
Google continues to say that Discover traffic should be reported as search traffic and is only split out in Google Search Console which can be exported to sheets. But it is currently not available in the API, along with the recently added Google News Tab traffic.”
Last year, Abby Hamilton published this extensive resource on what Google Discover is and how to optimize for it, including original research about which articles tend to appear there.
I conducted a similar analysis, in which I analyzed over 5,000 URLs ranking in Google Discover across a variety of Path Interactive clients over the past year.
General Observations About Google Discover:
- Articles with strong performance in Google Discover tend to be highly entertaining and evoke strong emotion, without being too clickbaity or “catering to morbid curiosity, titillation, or outrage” (which is Google’s own language in its Discover Guidelines, and failure to comply can now result in a manual action)
- Not every page ranking in Google Discover is a news or blog article. Our clients have seen examples of local service pages or other local resources receiving significant traffic from Google Discover.
- Articles that are several years old can be resurfaced in Google Discover, even without making any changes to those articles
- It appears to be the case that websites that are flagged as “adult” content may not be eligible for Google Discover, and this is not just limited to extremely adult content. Google’s Discover documentation states that content containing “nudity, sex acts, sexually suggestive activities, or sexually explicit material” violates their content guidelines, and may cause publishers not to appear in Discover.
Below are some correlations we observed related to our clients’ performance in Discover.
As always, it’s important to note that correlation is not causation, but the trends can illuminate some insights about what content tends to perform well in Discover.
In Google Discover, the article’s <H1> is often (but not always) displayed as the article headline. Therefore, the length of the headline could potentially impact CTRs.
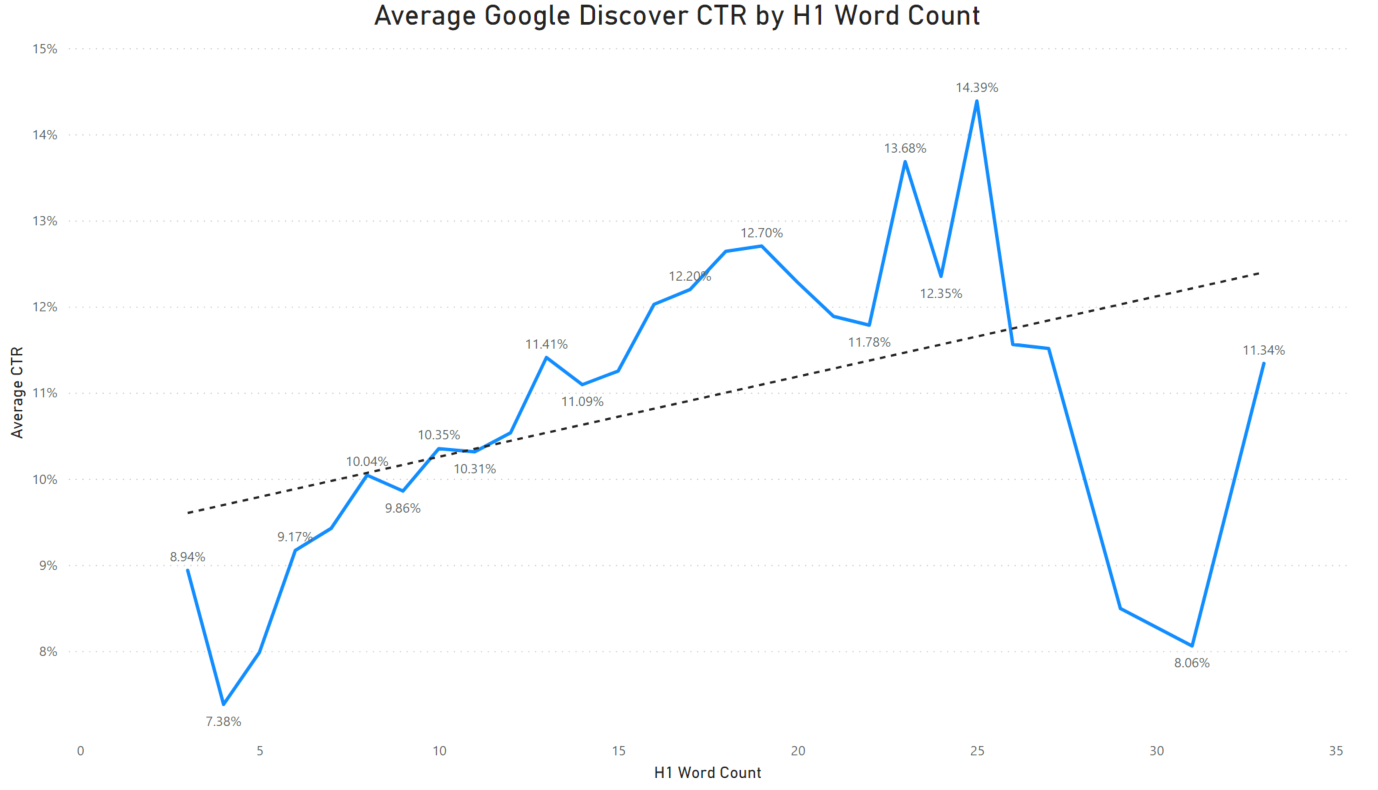
Our analysis showed that there is a positive correlation between H1 word count and increased CTR, up until about 27 words, where the CTR drops dramatically.
The strongest CTR (14.39%) was found on articles using 25 words in their headlines.
According to this data, writing a headline of about 15-25 words could be a good target for Google Discover.
The same general pattern is true for overall clicks to Discover content, although the highest-traffic articles had even shorter headlines, ranging from about 10-20 words.
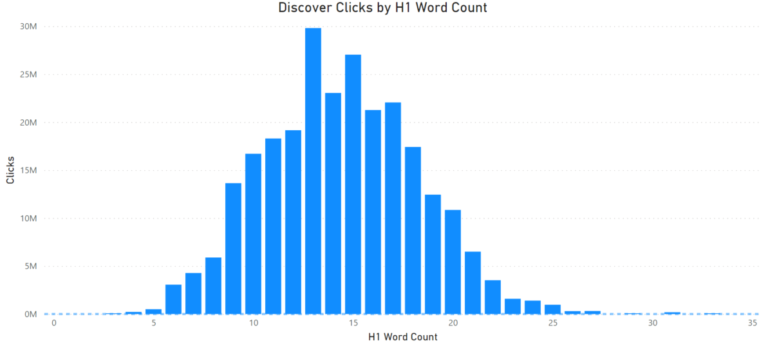
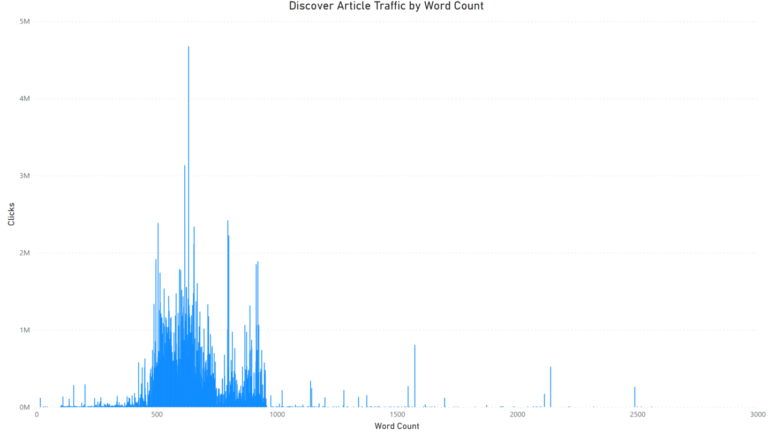
Looking at overall article length, the articles that received the most traffic in Google Discover ranged from about 500-1,000 words in length, with the strongest performance in the 600-700 word count range.
It’s important to remember that word count is not a ranking factor across any Google Search feature, but we thought the trend was nonetheless interesting to observe for Discover specifically:
These correlations certainly should not dictate how to write your content – focusing on the quality of the content and engaging your users is the optimal approach for appearing in Discover.
Keep an eye on how your articles perform in Discover by navigating to the Discover Performance report on the left sidebar of Google Search Console.
Your own performance data is the best source of truth to see which articles and topics your site tends to rank well for.
Google’s relatively new visual news feature, Web Stories, is also used in Google Discover, making them a great source of traffic and a good way to stay ahead of the competition.
2021 SEJ Christmas Countdown:
- #12 – The New Google Business Profile: A Complete Guide For Local SEO
- #11 – How To Automate SEO Keyword Clustering By Search Intent With Python
- #10 – Get to Know Google Analytics 4: A Complete Guide
- #9 – 7 Things I Wish I’d Known Earlier In My SEO Career
- #8 – A Guide to Optimizing for Google News, Top Stories, And Discover
Image Credits
Featured image: Sammby/Shutterstock
All screenshots taken by author, March 2021





![AI Overviews: We Reverse-Engineered Them So You Don't Have To [+ What You Need To Do Next]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/sidebar1x-455.png)