It’s an SEO horror story – your rankings have dropped.
Maybe it’s just a few high ranking pages, or maybe it’s a massive plunge across the board.
But either way, your rankings have dropped, and your traffic is down.
What do you do now?
Fluctuations are inevitable (after all, as Google reminds us, they make updates every day), but it’s never good news when your search rankings start trending in the wrong direction.
If you see your rankings take a dive – either when you check the SERPs, or search console, or some other rank monitoring software – don’t panic.
Proactive, attentive troubleshooting can help rescue your rankings and get the needle moving in the right direction.
This 10-step process will help you identify the source of any issues so you can resolve them and get your SEO back on track.
Step 1: Start With the Basics
In deploying and monitoring keyword performance, it can be all too easy to focus on advanced strategies while underestimating the importance of the on-page SEO ABCs.
Why stress about anchor text ratio, link velocity, or citation optimization when the answer to your rankings problem could be an easy fix directly on your site?
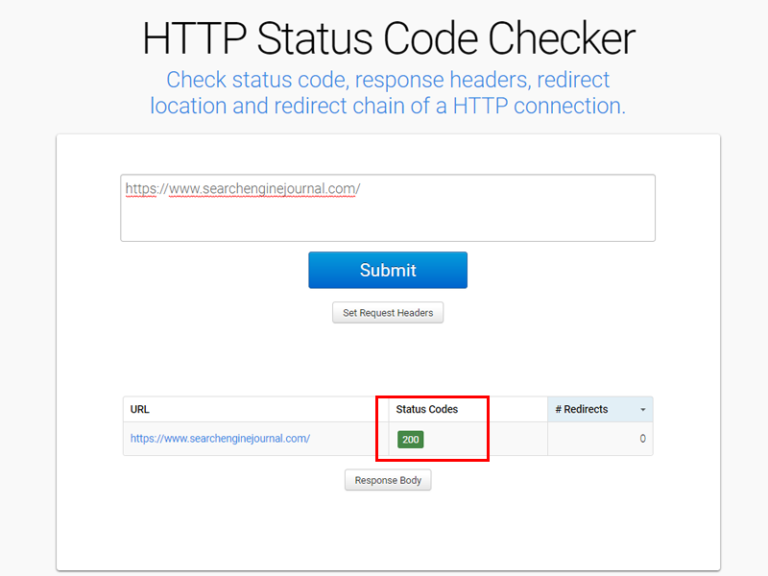
What status code do your pages return? Do they return a 200 status code?
200-series status codes indicate that your site can is communicating successfully.
The standard 200 OK status code indicates a successful HTTP request.
Use a free tool like HTTP Status Code Checker to confirm that your site is returning a successful request.
If not, you can troubleshoot based on the failed status code, like 404 (page not found) or 410 (page permanently removed).
 Can bots crawl your site?
Can bots crawl your site?
Robots.txt is a text file in the top-level directory of your web server that instructs bots on how to interact with your website.
Within the file, you can set inclusions and exclusions to your heart’s content; for instance, disallowing bots from crawling a dev site or indexing duplicate pages.
Have you accidentally set the restrictions too tightly, preventing search bots from crawling any of your main pages?
Double-check the robots.txt file using Google’s free Robots Testing Tool – if you spot anything amiss, upload a more permissive file to the server.
Step 2: Check SEO Basics
The SEO basics don’t guarantee you first place position, but they make sure you can compete in the game.
Title tags might not be a search engine ranking factor but they still have an influence.
Check that the basics like title tags, meta descriptions, and headings aren’t holding back your rankings.
Do you have optimized home page title and meta tags, and do they display correctly in search results?
Your home page’s title tag represents a massive yet simple opportunity to tell search bots what your page is about.
If it’s generic or failing to pull properly, it can affect your rankings.
While its companion meta description doesn’t directly affect SEO, a relevant, persuasive meta can improve click-through rates.
You can customize title and meta tags within the head section of your site’s HTML. If your site runs on WordPress, install a free plugin like Yoast SEO or All in One SEO Pack to easily manage titles and tags across your site.
Does your homepage have an optimized H1 tag?
In addition to the info you provide in the title tag, the main heading lets users know the primary purpose of the page. However, unless it’s contained in an H1 tag, search bots won’t be able to differentiate it from the rest of the content on the page.
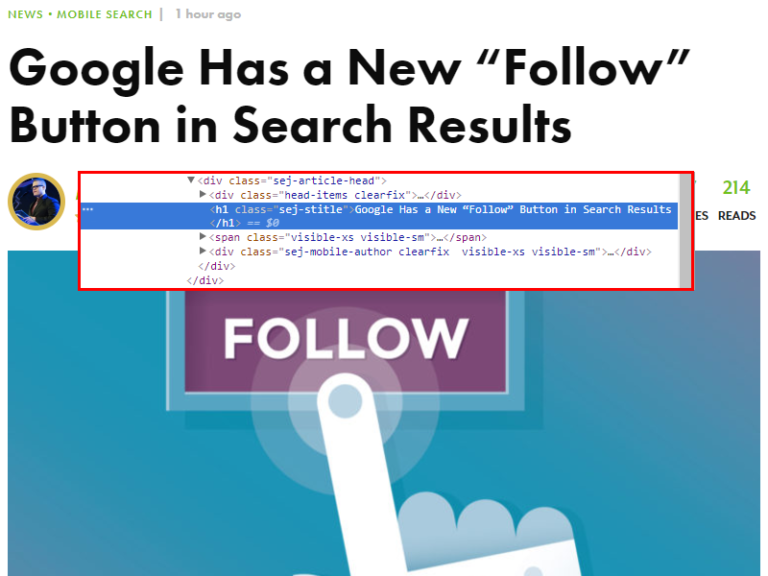
Check your site’s code to ensure a single, relevant H1 is being used on each page.
You would be surprised how often ranking drops are caused by one (or more) of these essential elements.
Fix the problem, and search performance will improve in kind.
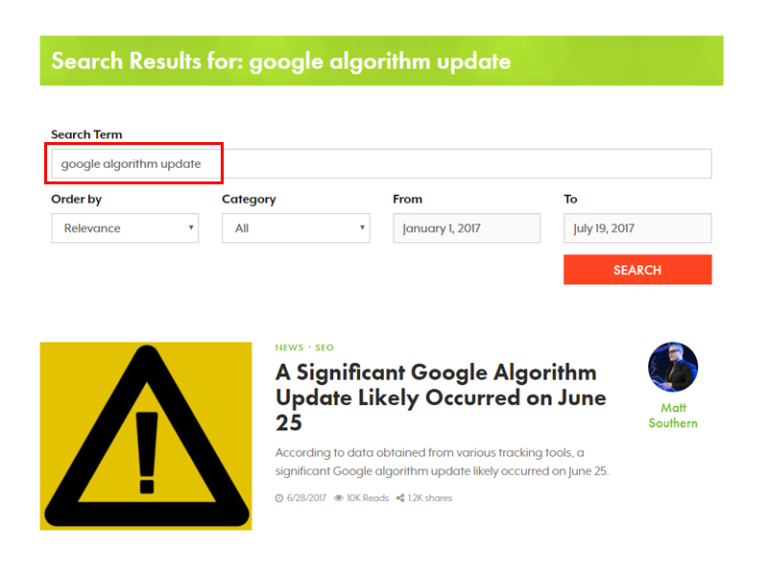
Step 3: Check for Google Algorithm Updates
Now that link algorithm Penguin and quality algorithm Panda are part of Google’s core algorithm and updated in real-time, you always have to be on your toes about how small tweaks can affect your rankings.
There are dozens of algorithm updates every day!
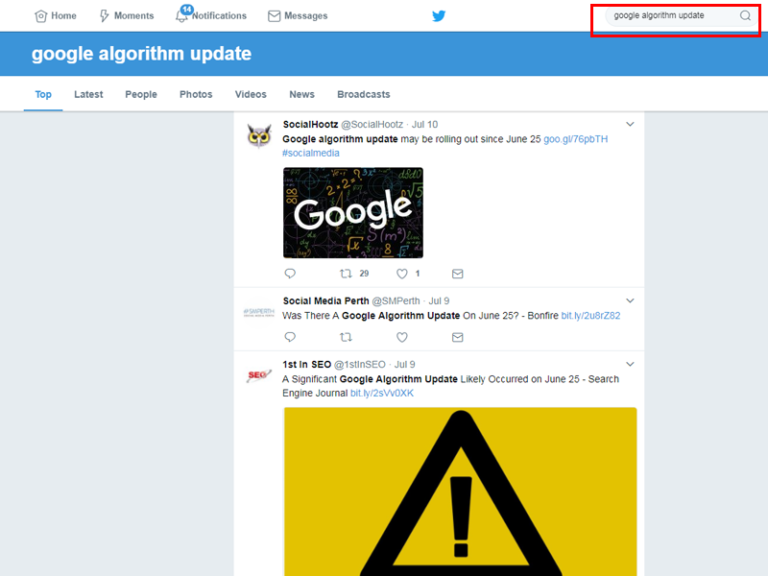
Take a look at SEO news sites and follow influencers like Danny Goodwin, Barry Schwartz, and Google’s Gary Illyes to stay on top of breaking developments.
Another great place to get information is to search on Twitter.
If you see other webmasters panicking, it’s a sure sign something has been adjusted.
If you’re doing things the right way – think in-depth content, clean and intuitive site layout, fast load times – don’t stress about rankings fluctuations due to algorithm updates.
You’re doing it right and will be rewarded in the long run.
Step 4: Check Google Search Console
As opaque as algorithms can be, Google is clear about what they expect from a website.
Follow its guidelines and act on its feedback for improved search performance.
Google Search Console is a free service provided by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and optimize your site’s visibility in search results.
Check GSC to see if there are any crawl errors interfering with the indexing or visibility of your site.
Do you see DNS errors, server errors, or URL errors?
Navigate to the Index Coverage report to see if there are any issues.
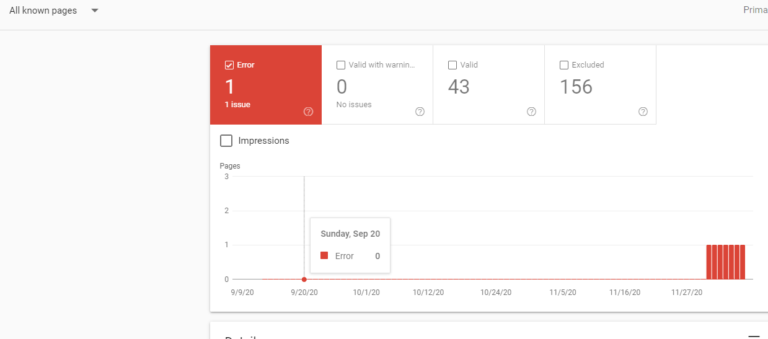
Through Google Search Console, you can submit an XML sitemap that charts the structure of your site.
Once loaded, check to see if there is a discrepancy between the number of URLs submitted and the number of URLs indexed by Google.
If the numbers don’t add up, it’s possible important pages are being blocked from search bots.
Crawl your site with a scanning software such as Screaming Frog, which will zero in on the issue.
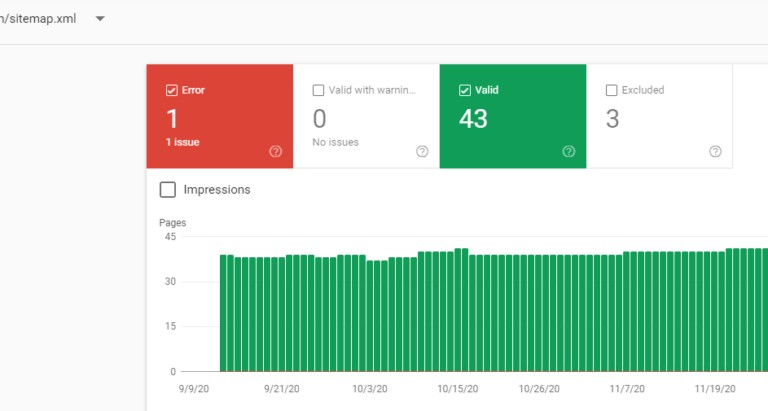
You can also inspect individual URLs in the Search Console, which will allow you to see if individual pages have errors or issues that need to be fixed.
In your Search Console Preferences, be sure to check Enable email notifications so you’re quickly alerted to any big issues, but make it a habit to check in with Google Search Console on a regular basis.
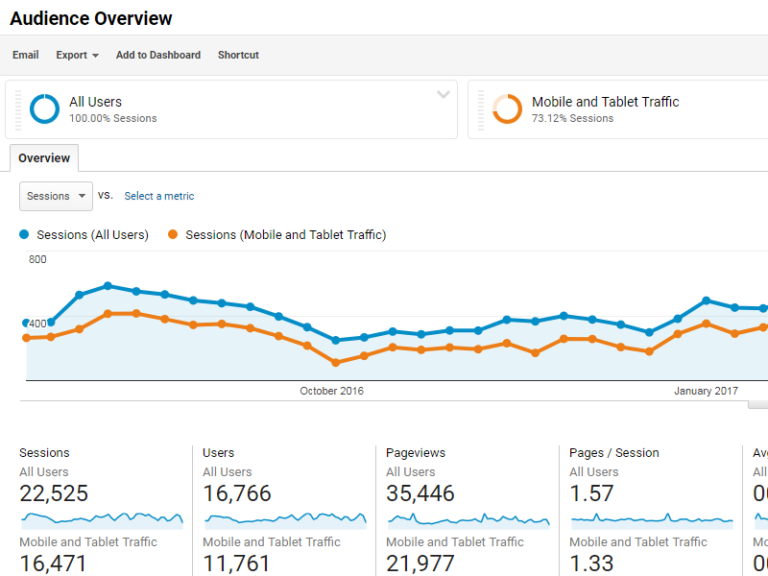
Step 5: Check Google Analytics
Google Analytics shows if there is a drop in traffic or user metrics like time on page, pages per session, or bounce rate.
Did you make any changes to the site content, design, or functionality that coincide?
If so, reverting the changes or going in a different direction can help traffic bounce back.
Google Analytics is a treasure trove of information about how people find your site, how they behave while on your site, and what pain points cause them to leave before completing an action.
For even more insight, segment your audience by mobile and desktop browsers, because they have different intentions and interactions with your site.
For more, check out 6 Ways to Use Google Analytics You Haven’t Thought Of.
Step 6: Check Content
Quality content has never been more important.
Is your content unique, rich, and interesting? Or is it duplicate, thin, and low value?
This can have a major effect on rankings.
Are your competitors answering more questions, or answering them better?
It can be useful to look at what competitors might be doing better than you – and avoid tactics worse competitors are using.
Users don’t connect with bad content.
While the value of content is mostly subjective, there are a few metrics you can reference.
For instance, if users aren’t staying on a page for long or if they are exiting the site without clicking deeper, it indicates that the content isn’t connecting.
In addition to manual analysis of your site’s content, Copyscape and Siteliner are helpful tools to check that your site is original.
If any issues with internal or external duplicate content are flagged, you can correct them by rewriting or expanding the content.
Ready to take your content to the next level? Check out 17 Tips & Tricks to Improve Your Content.
Step 7: Check Site Speed
Does your site take more than three seconds to load? If yes, you’re behind the curve already.
Speed is essential – and a ranking factor on mobile.
Free tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights tell you how fast your page is, and give actionable recommendations to improve load times.
There’s also the Core Web Vitals report in the Search Console, where you can see metrics like Largest Contentful Paint and First Input Delay.
Even blazing fast sites can take it to the next level with optimizations like leveraging browser caching, minifying code, optimizing images, and enabling resource compression:
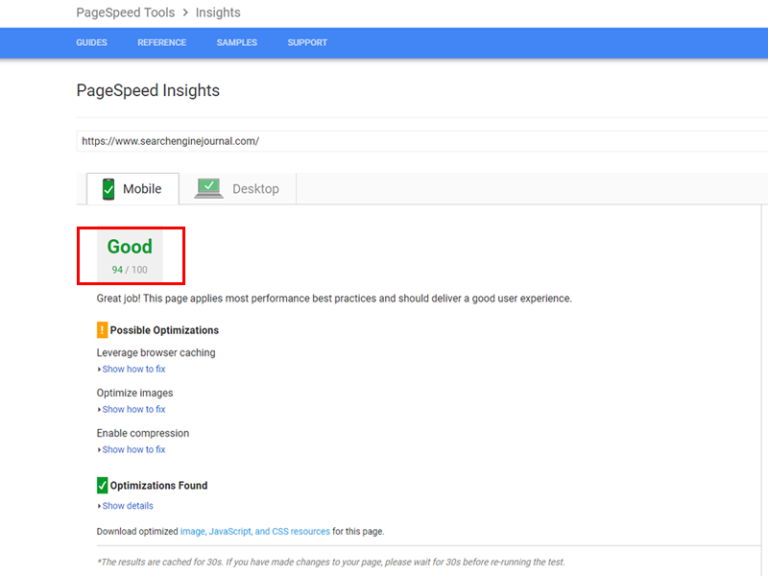
Find even more info on How to Improve Page Speed for More Traffic & Conversions.
Step 8: Check Mobile
Google is now almost entirely a mobile-first, mobile-only venture.
Not having a good mobile experience is inexcusable.
Not every element or function that works on desktop makes sense for mobile, and you don’t want to turn away searchers with a clunky, slow, or complicated site.
To see if mobile compatibility could be affecting your rankings, run your site through Google’s free Mobile-Friendly Test.
If your site is not considered mobile-friendly, this tool will provide recommendations, such as removing intrusive pop-ups or fixing or removing unplayable content, among others.
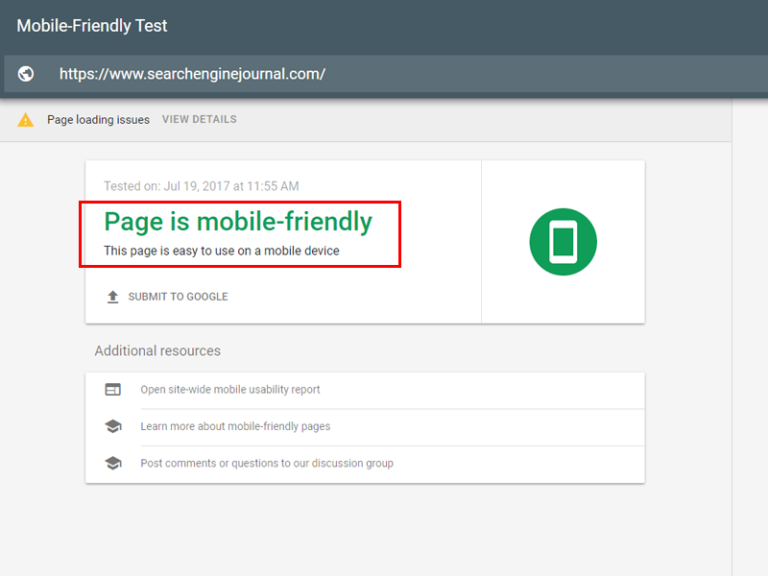
You can also check the Mobile Usability Report in Search Console.
Here’s How to Achieve Mobile-First Success.
Step 9: Check Backlink Profile
Backlinks are instances of another site linking to a page on your site.
Backlinks matter because they prove to search engines that your site matters; that it says something of value, and is trusted by others.
If you have a small backlink profile, Google might see you as less reliable than other, better-linked sites.
On the other hand, if you have a lot of links, just a few links from authority sites, or tons of links from spammy sites, it can hurt your ability to rank.
When your rankings drop, it’s always wise to audit your backlink profile to make sure nothing is wrong.
Tools such as Ahrefs, Majestic, Moz, and SEMrush can show you what sites are linking to you, which pages they’ve linked, and what anchor text is used.
They also try to give a sense of how authoritative a linking domain is, based on its own link metrics.
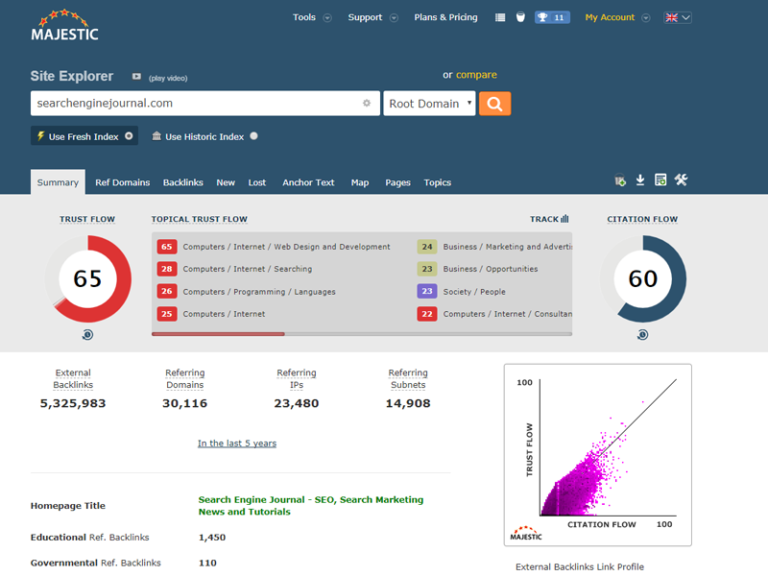
If you see a thin backlink profile, work to build it with proven link building strategies – check out Link Building Strategy, Tips & Techniques That Work for best practices.
Spammy backlink profile? Read How to Find Unnatural Links to Your Site & What to Do About Them.
Step 10: Check Keyword List
If you’re tracking the wrong keywords, does it matter if your rankings fall?
For instance, say you run a digital marketing agency but stopped providing graphic design services and removed that service page from your site.
You’re naturally going to fall for that keyword, and that’s OK.
However, if you start to trend downward for primary keywords that drive traffic and leads, an intervention is needed.
The right keywords should check all of the following boxes:
- Most highly searched by your target audience.
- Most realistic to rank on page one.
- Most likely to result in a conversion.
The targeted keywords that make sense today may not be the ones that made the most sense when you started the campaign, so make sure to re-evaluate periodically.
If you aren’t proactive with adding or removing the keywords you are tracking, it can become an echo chamber that distracts you from true ranking success.
If you have a high-value keyword that has you on page one but it’s not in your reporting software, you’re missing an opportunity to optimize and hit top position for that term.
Ditch the keywords that are unrealistic or won’t result in conversions.
They aren’t doing you any favors and can cloud the true picture of your search performance.
Instead, strategically monitor high-value keywords that you can dominate with small on-page optimizations like writing new targeted content or tweaking titles, meta tags, and H1s.
Conclusion
If your site experiences a drop in rankings, you can reverse the trend with small and simple optimizations.
Sometimes a simple optimization can be the difference between a good page and a great one.
Follow these 10 steps and you’ll likely be alerted to issues you can correct on the spot.
Keep your eye on the rankings and watch them rebound over time.
More Resources:
- 5 Proven Ways to Increase Your Google Rankings
- 11 SEO Tips & Tricks to Improve Indexation
- 10 Important 2021 SEO Trends You Need to Know
Image Credits
All screenshots taken by author, December 2020




