
A month after Penguin 2.0 was released, the dust is settling and most people are eager to know: What exactly is Penguin 2.0 filtering? How does Penguin 2.0 differ from Penguin 1.0? What can I do to recover my site and to protect my site from getting hit in the future? Should I try to recover, or start over with a fresh domain?
First let me give you some context. The first Penguin was a more lethal, shotgun link spam filter. They had to send a message to the SEO community, so they pulled out their shotgun, fired, and took down thousands and thousands of sites. If you got hit by Penguin 1.0, the aftermath was brutal, with rankings completely gone for most head terms, the long tail disappearing, and a loss of between 30% and 80% of organic traffic. What Penguin 1.0 specifically targeted was link networks, paid links, high anchor density, and massive numbers of low quality links. Some sites still have Penguin 1.0 penalites that haven’t been removed.
So what does Penguin 2.0 look for?
After analyzing hundreds of sites, the main commonality I’ve seen with sites affected by Penguin 2.0 is that they have a high volume of Money keywords in Anchor text. Sites that are safe have a high density of Brand anchor terms, and a high number of “Other” or “Noise” terms. One obvious giveaway for most penalized sites is that, if you look at their backlink profile, you see heavy usage of money keywords and the entire profile looks very contrived.
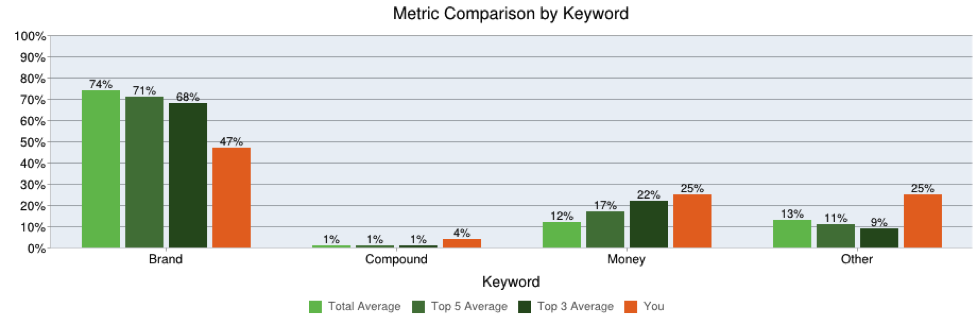
Penguin looks for Ratios and Footprints
What was perplexing about Penguin 2.0 is that you could still find sites that have high Money anchor density, but didn’t get penalized. Why did some sites get hit, while others didn’t? I believe a fundamental aspect of Penguin 2.0’s mechanism is an evaluation of a site’s backlink profile as it COMPARES to competitors.
Each keyword niche should trigger a different type of backlink profile based on the topic and niche. So the backlink ratio has to be comparable to others in the same competitive space.
My hypothesis is that Google uses it’s normal ranking algorithm to come up with a set of sites that should rank for a keyword. Then it runs this set through the Penguin 2.0 filter to determine averages and ratios. Finally, sites with too many red flags, were the ratios are obviously unnatural, get flagged by the algorithm and penalized. Then the positions are adjusted based on the new penalty.
So what ratios does Google look for?
Some of the known ratios that Google looks for are:
- Unique C class links to domain
- Link Velocity Trends
- Number of Keywords Ranking
- Number of Links from N/A or PR0 domains
- .EDU/.Gov links
- SiteWide Link Ratio
- Deep Link Ratio
- Pagerank of Backlinks
- Indexped Pages
- TitleRank
- Traffic to the Domain
- Clickthrough Ratio
- Social Votes
- Percentage of Follow/No Follow Links
- Link Position in the Source Code
- Link Type (text, image, script)
- Anchor density
By comparing a site to the averages of the backlink profile of top competing sites, the algorithmic filter can easily detect unnatural ratios.
It is my belief that having a couple of unnatural ratios doesn’t lead to negative consequences. Having TOO MANY red flags, or ratios that fall too far outside of the averages of competing sites, will trigger the Penguin Penalty.
Even if your site has significantly better ratios than your competitors, this can be seen as a sign of manipulation of the search results, which is what Google is openly declaring war against.
What Google wants is for people to focus on producing great sites, with amazing, shareable content, instead of link building and SEO tactics. By penalizing harshly for footprints and unnatural ratios, they are pushing people to be cautious of their backlink profiles and avoid spammy backlink building tactics.
So what can you do to protect your site from Future Penguin Penalties?
Your SEO processes have to change. Just as we do keyword research, on-page seo, and link building as part of a cohesive online marketing strategy, link audits now also have to be a part of the process.
LinkDetox is a fantastic tool to expedite and facilitate the process. I use LinkResearchTools to help me with all link analysis and backlink profile audits. With LRT I can look at all of the ratios of sites, and determine where there are danger zones.
Link audits should include an evaluation of all of your current backlinks and an analysis of all of those backlinks. Look for the following elements:
- Is the page indexed in Google
- Does the page have any external links
- Does the page have more than 10 backlinks from 1 C class
- Does the page rank in Google for it’s exact match title
- Does the page have any rankings in SEMrush
- Is the theme listed as suspicious
- Do other domains share the same registration information
- Is the link velocity trend above 150%
- Does the page have sitewide footer links
- Does the page have PageRank
- Does it have link directory links
- Does it have article directory links
- does it have massive number of outgoing links
- What is the Page Authority of the page, and the Domain authority of the root domain
By checking your backlinks against these metrics, you can then determine what links are toxic and which ones are healthy.
You also want to take a look at the site and make an assessment based on value. Is it obvious that the site is an expired domain that was purchased for the sole purpose of linking? Is there any social engagement? Does the site have a free, basic template, or is it obvious that the site is owned by someone how is devoted to producing content and maintaining it? These elements can help you make a decision. If the site is low quality and looks like it might have potential to suffer from a future penalty, mark it as suspicious or toxic.
Request the Toxic links to be removed
Create an outreach campaign to attempt to have some of the links removed. Document your efforts, including when you sent out emails, to what email address, and what, if any, response you received.
I recommend sending out at least 3 emails over the course of a month to give yourself plenty of time and documentation.
Upload a Link Disavow File
Disavow the toxic links in your Google Webmaster Tools account, and wait 2-4 weeks to see how your site reacts.
Submit a reconsideration request
Although penguin penalties are algorithmic, not manual, I suggest submitting a reconsideration request documenting your efforts to clean up your backlink profile.
Google is publicly stating they are trying to be more transparent and communicative to webmasters, so it’s possible that you will hear back with further news about this site from the reconsideration request.
Build Positive Signals to Balance your Backlink Profile
As you clean up your backlinks, it’s possible that you have eliminated many of the signals that were helping you rank in the first place.
To have hopes of seeing your site rank again in the serps, you have to build positive, high quality signals.
Social Media Signals
As we all know, Google is pushing their Google Plus platform, as it gives them a massive social analytics platform. Building a strong, viable social media marketing campaign, particularly focused on Google Plus, will help create positive social and engagement signals.
High Quality Links
Links continue to be a fundamental aspect of the ranking algorithm, so you have to continue to build high quality links.
So what kind of links are still safe?
- Guest Blog links
- Infographic Links
- Links from Competitors
- Giveaway Links
- Broken Links
Be mindful of your ratios!
I believe that the key to link building, at this point, is balance and moderation. Too much of a good thing can become a very bad thing. If you go out and focus only on guest blog links you might end up in the penalty box just as much as the guy who went out and bought 2000 links from a network.
Focus on VARIETY and MODERATION! Create a 6 month link building plan, where every month you focus on building different kinds of links. This variation has protected our client’s sites from Penguin penalties.
Most importantly, we are very cautious of our money vs brand ratios, as well as the anchor text distribution. It may seem an oxymoron, but we work hard at making the profile seem less contrived.
Content Marketing
Keep creating, and socially sharing, excellent content. As the web becomes inundated with short, fluffy articles, make sure your articles really shine. I try to make sure all articles are at least 750 words, with pinnable images, and offering genuine value. These articles become link bait, which generate opportunities for natural links.
Our goal for client sites is to publish at least one high quality article per week on their site, which is a great complement for our link building efforts. Simultaneously, it increases the content update ratio and gives the site more long tail keywords to target.
What if I’m already penalized? Should I still follow these steps? Or should I start over with a new domain?
I still recommend the same process mentioned above:
- Evaluate links
- Link Removal
- Normalize Backlink Ratios
- Link Disavow
- Reconsideration
- Build Positive Signals
Following these steps has helped to recover sites hit by Penguin 1.0. It’s too early in the game with Penguin 2.0 as we typically spend 1 month in the link removal process. The problem with trying to recover a penalized site is that you are not guaranteed an outcome. We follow the same steps for all our clients, but some recover, some don’t, and there’s no way to predict which way a site will go.
Due to this uncertainty, we sometimes recommend sites that are not heavily branded to start fresh or promote two domains simultaneously. The reason is a penguin penalty introduces an element of uncertainty that may result in a waste of resources if the site doesn’t recover. Starting fresh with a new site does guarantee a certain outcome. I know that every domain that I promote and follow my SEO Strategy Blueprint will inevitably rank if the right amount of resources are allocated to it based on the competition level. There’s no element of doubt, it’s only a matter of time.
Every business will have a different situation, so choosing an approach has to be based on the specific needs of that business.
Go forth and Normalize!
As I mentioned above, backlink audits and link profile protection now have to be a fundamental element of your SEO strategy. Negative SEO DOES work. I’ve spent many a sleepless night cleaning up profiles of penalized sites courtesy of competitors. Even if you are doing everything correctly, you could still suffer from a penalty because one of your competitors goes to fiverr and sends you 10,000 wiki do follow not indexed home page links with money anchor text for $5. If you are tracking your backlink profile at least monthly if not more often, you’ll be the first to know something’s wrong, and can disavow the links before they result in penalties.






![[SEO, PPC & Attribution] Unlocking The Power Of Offline Marketing In A Digital World](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/sidebar1x-534.png)