Picture this scenario: you wake up one morning. You grab your cup of coffee and head to your desk.
You check your Google Search Console and Google Analytics for your first ten minutes in the morning.
And gasp.
You find that your traffic has dropped over 75% overnight.
You could be wondering what you did to deserve this?
Most likely, you have been hit by a Penguin penalty.
Penguin is Google’s algorithm meant to target toxic links that harm your backlink profile.
This can result in an algorithmic demotion or full-out manual penalty if your links are severe enough.
What, exactly, are toxic links?
These are any links that go against Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. My other Search Engine Journal post on the topic is available here.
While Google is on record as saying that they are good at ignoring links, negative SEO still exists.
If someone begins a negative SEO attack on your site, and they reach enough of a link velocity and saturation that causes your site to tank, then you have experienced a negative SEO attack.
The basics of link remediation cover the nuts and bolts of what you should do and when in order to help yourself recover from a Penguin penalty.
How to Discover an Algorithmic Devaluation
We have just gone over the beginning of when a link penalty usually shows up.
Did you know that they can be extremely granular?
Down to the folder or page, even.
The penalty does not have to be sitewide. Google mentioned this in Penguin update 4.0:
“In the official announcement of the Google Penguin 4.0 rollout, Google pointed out what’s different about this Penguin update. Apart from the real-time aspect, Google Penguin is also more granular.
“Penguin is now more granular. Penguin now devalues spam by adjusting ranking based on spam signals, rather than affecting the ranking of the whole site. “
Many webmasters ask themselves what does “granularity” mean? The fact that Google Penguin will be more granular means that now Google will not necessarily penalize a website as a whole, but it can also penalize only parts of it. Google can penalize a domain, a sub-directory, a group of keywords or just a page. So anything that goes into the organic rankings will now be affected by the Penguin algorithm on a fine level. You can have a penalty only for a part of your website, while before a Google Penguin filter affected the entire domain. We expect to see a lot of negative SEO attacks directed to single directories.” – How does the Real Time Google Penguin work?, Christoph C. Cemper, LinkResearchTools
What exactly does this mean?
Say that you have a page on your site that’s sending a ton of traffic to your site as a whole.
If you see an algorithmic drop, while there are several reasons, you must first check to see if a page on your site has somehow been penalized and is no longer delivering that traffic.
In addition, if you have removed that page, that could also be a reason.
This is also why a drop may not be an algorithmic devaluation – it could simply be that you removed a page that was sending a lot of traffic to your site, without checking for that beforehand.
Is It an Algorithmic Devaluation or a Manual Penalty?
There are several ways to figure out whether you are experiencing an algorithmic devaluation or a manual link penalty:
- Google Analytics
- Google Search Console
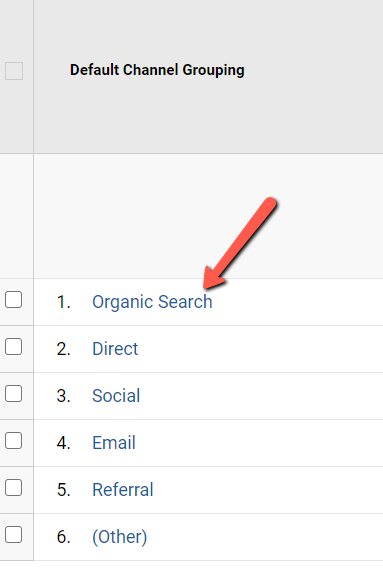
In Google Analytics, click on Acquisition > All Traffic > Channels.

Then, click on Organic Search.
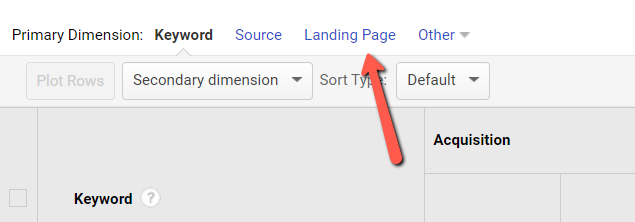
Next, click on Landing Page as the primary dimension:
If you wanted to get really granular you could go for keyword, then landing page as the secondary dimension by clicking on Secondary dimension, searching for “landing page”, then clicking on Landing Page.
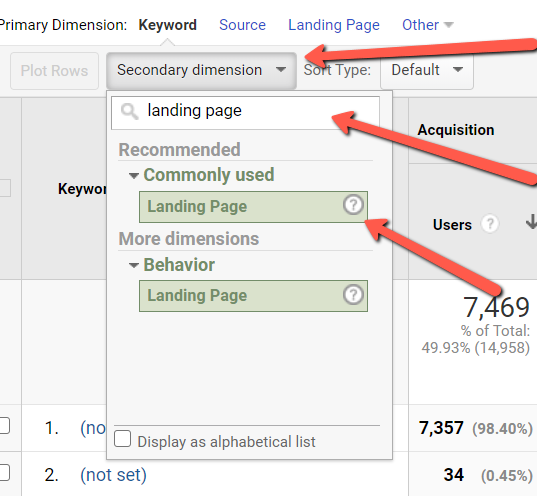
This will give you both keyword and landing page as specific traffic drivers on your site.
Because of Google’s (not provided), you won’t be able to attribute keywords by default, but you can see what pages could have likely dropped in traffic as a result.
Doing these steps can help you figure out exactly what page has lost traffic, and you should be able to take steps from here to correct the problem.
Google Search Console
In Google Search Console, you can do more granular traffic analysis based on the search queries that are driving traffic to your site.
Here, we’re going to click on the Performance button:
Next, click on + New:
Then click on Page…
Click on URLs Containing then type in the name of the page you want to search for:
The next section below will show you any pages that you have that may (or may not) have lost traffic.
If you have suspicions regarding pages that you found through the Google Analytics analysis earlier, you can figure out more detail here in Google Search Console.

By doing your analysis in this way, you can discover pages that may have been driving traffic before but no longer are.
At this point, you have discovered a single answer to one of the many problems that could be causing your link profile to become compromised.
If you have a manual penalty, it will appear here in this section of Google Search Console:
Next, we’re going to discuss how to tackle link remediation.
When should you put all your effort into analyzing your entire link profile?
If you find that you have a number of toxic links pointing back to your site, then you should definitely perform a link analysis.
What Is a Link Analysis?
A link analysis is, quite simply, a comprehensive, in-depth review of the links pointing back to your site, or your link profile.
This profile is the total accumulation of all links, good and bad. This analysis can help you recover from a penalty when it’s done right.
You’ve Been Hit with a Manual Penalty – Now What?
If you have been hit with a manual penalty, you will receive a notification in Google Search Console.
This will tell you about any manual actions you may have levied against your site.
All you have to do is follow the instructions within Google Search Console, work with the spam team on removing the links they have called out, and you will (usually) be able to recover.
If your site has a decent quantity of links, you could be in for a long haul of removing links before you end up ever beginning to get back into Google’s good graces.
One site I worked on required over 8 months of manual link removals and 7-8 messages back and forth with the webspam team to remove these toxic links.
Yes, manual penalties are brutal. If you want my honest advice – don’t ever get one.
Make sure you follow Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
Is the slower pace to results less than desirable? Perhaps.
But the long-term rewards are more than worth it – you won’t have to go through this process to reclaim your site’s value in Google’s index.
And following their guidelines.
First, Gather All Your Links
You want to gather all of the links in your link profile.
To do this effectively, you need to pull them together from multiple sources.
What these multiple sources will do is give you the ability to see your profile as a whole.
While it’s impossible to gather all 100% of your links, this is the next best thing and will help you get a good cross-section of your links across the web.
Sadly, Google Search Console is not the be-all, end-all source for finding links in your link profile.
It’s a partial cross-section, and even Google doesn’t crawl all your links.
Therefore, it’s necessary to do combine links from multiple sources.
I recommend using the following sources to combine your links:
- Google Search Console
- SEMrush
- Ahrefs
- Majestic
- Raven Tools
- Moz Open Site Explorer
Here, you will find that different software gives you different links.
And the only way to get all of your links is to use a combination of all the software that’s available.
This ensures that you get the most possible links that you can from the most sources that you can.
Perform Link Remediation
What is link remediation?
This is the process of link pruning, just under a different name.
You crawl your links, put them all together in a spread sheet, and then you have to go through them manually, one by one.
Marking them as spam or not spam, and depending on how you do it, defining what type of link they are.
It’s tedious. And yes, it’s a lot of hard, manual work. But getting back into Google’s good graces is worth it.
And yes, I know Google says one thing and then they say another.
This is why I think it’s best to go by the official guidelines unless a new announcement is made that further re-affirms what Google can and won’t reward.
Or, they decide to do away with (or “disallow” if you want some cheeky SEO humor) certain link acquisition practices entirely.
Link remediation is meant to be a slower, more tedious process. If it’s not taking you awhile, you’re not doing it right.
Some automation exists, but it’s not always possible to accurately review a site using programs or AI.
Simply because they cannot replace the perception of a real human being. But they’re getting closer.
Remove Toxic Spammy Links
The next critical part of your link cleanup tasks is to remove toxic links.
Google’s official guidelines for link removal state that you must spend as much time removing them as you have spent building them.
They recommend in their webmaster guidelines that you consider removing them. If you can’t get those links removed, then you can disavow them.
Ideally, this means creating and executing a link removal campaign where you are contacting webmasters who have your link on their site, and then you ask them directly (via email) to remove the links.
If you think this is tedious, you’re right. If you think that this takes time, you’re also right.
Again, they want to see you remove as many links as possible.
And, if you have a large site with a large link profile, this can take many more hours.
Remember my honest advice earlier? Never get into a manual action penalty in the first place.
Finally, Create a Disavow File
Your last step in this process is to create a disavow file.
This file serves as notice to Google, letting them know that there are links on your site they should not count when evaluating your site.
But, you must be careful when using this tool.
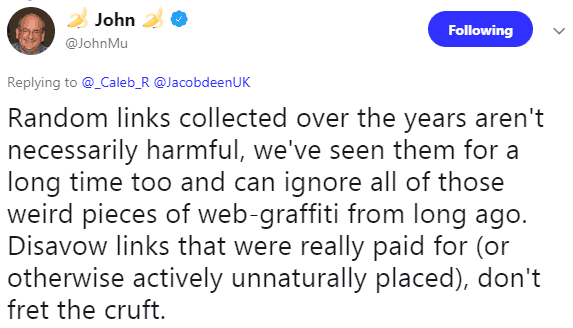
Unless you are 100% confident about the fact that the site is linking to you is a bad site in violation of Google’s guidelines, you may want to hold off. Google’s John Mueller is on record as saying that 95% of sites don’t need to use a disavow file:
Search Engine Journal’s Roger Montti explains:
Google’s John Mueller recently tweeted that publishers should not worry about random low-quality links that websites tend to acquire. Every site that ranks for anything tends to acquire random low-quality links. Below I explain why these links don’t matter.
Here is what Google’s John Mueller tweeted about disavowing links:
“Random links collected over the years aren’t necessarily harmful, we’ve seen them for a long time too and can ignore all of those weird pieces of web-graffiti from long ago. Disavow links that were really paid for (or otherwise actively unnaturally placed), don’t fret the cruft.”
An experienced SEO is needed in order to sift through all the bad links and make sure that you only get rid of those that are harming you, rather than those that are helping you.
Link Remediation Is Critical for the Modern SEO
If your site has suffered significant losses as of late, it could be due to an algorithmic or manual penalty.
The only way to find out is to perform a deep dive into link analysis and disavow those links that are harming you.
You may also find out that you have suffered at the hands of a negative SEO attack by a competitor.
Believe me, this happens more often than you would think in competitive industries.
Remember to keep your head level, and don’t panic if you do. There is a way out of this.
It may be a longer haul than other solutions, but you can get out of this. It just takes time, effort, and removal of toxic links behind your site’s drop in performance.
But, don’t forget about the next phase – you should not remove all links and just stop.
You must re-build the site’s authority, trust, and expertise through new links in order to replace those that were lost through these efforts.
This is why it doesn’t end with just the disavow – you must continue re-acquiring valuable links.
In-depth analysis, remediation, removal, and disavowing of toxic links is a critical part of a modern SEO.
Providing a modern, proactive defense against bad links through the implementation of regular link profile analysis is critical to maintaining on-going success.
If you only do link analysis on a reactive rather than a proactive basis, you may not see the best possible results from your search campaign.
More Resources:
- The Basics of Link Profile Analysis
- 10 Bad Links That Can Get You Penalized by Google
- How to Find Unnatural Links to Your Site & What to Do About Them
Image Credits
Featured Image: Created by author, July 2020
All screenshots taken by author, July 2020