Google Analytics, now GA4, is a powerful tool that lets website owners learn how users interact with their webpages.
The amount of information we can get from Google Analytics is so in-depth that a theory has been circulating, for over a decade, that GA data is a ranking factor.
Is Google Analytics really powerful enough to influence Google search results?
Let’s take a closer look.
[Recommended Read] → Ranking Factors: Systems, Signals, and Page Experience
The Claim: Google Analytics As A Ranking Factor
In Google’s How Search Works documentation, we can see that a webpage’s relevance is one of the many factors used to rank webpages.
-
 Screenshot from Google’s How Search Works, June 2022
Screenshot from Google’s How Search Works, June 2022
The most basic relevancy signal is that the content contains the same words as the search query.
Additional information about how Google determines a page’s relevance is provided.
Beyond simple keyword matching, Google says,
“We also use aggregated and anonymized interaction data to assess whether search results are relevant to queries. We transform that data into signals that help our machine-learned systems better estimate relevance.”
-
 Screenshot from Google’s How Search Works, June 2022
Screenshot from Google’s How Search Works, June 2022
What is “interaction data,” and where does Google get it?
Some marketers hypothesize that these factors include metrics such as time on page, organic click-through rate, bounce rate, total direct traffic, percentage of repeat visitors, etc.
That makes sense because those are the metrics marketers are familiar with and understand to represent the interactive data Google may be looking for.
Marketers may also notice a correlation between the metrics improving as their position in the SERP improves.
Is it possible that we are somehow improving Google’s understanding of our website’s user experience using Google Analytics? Like some sort of SEO bat signal?
Let’s assume the answer is yes. In that case, Google would have a backdoor where anyone could easily manipulate the ranking of websites.
This is because anyone could send fake data to Google Analytics, which would then be used in search rankings. It’s relatively simple to manipulate Google Analytics using browser DevTools.
Here’s how someone could manipulate Google Analytics data:
Open the browser DevTools and locate the GA hit URL, which is a request to the GA server that sends data about user interaction on a website. This could include events like scrolling or other forms of engagement.
In our case, it’s a scroll depth event.
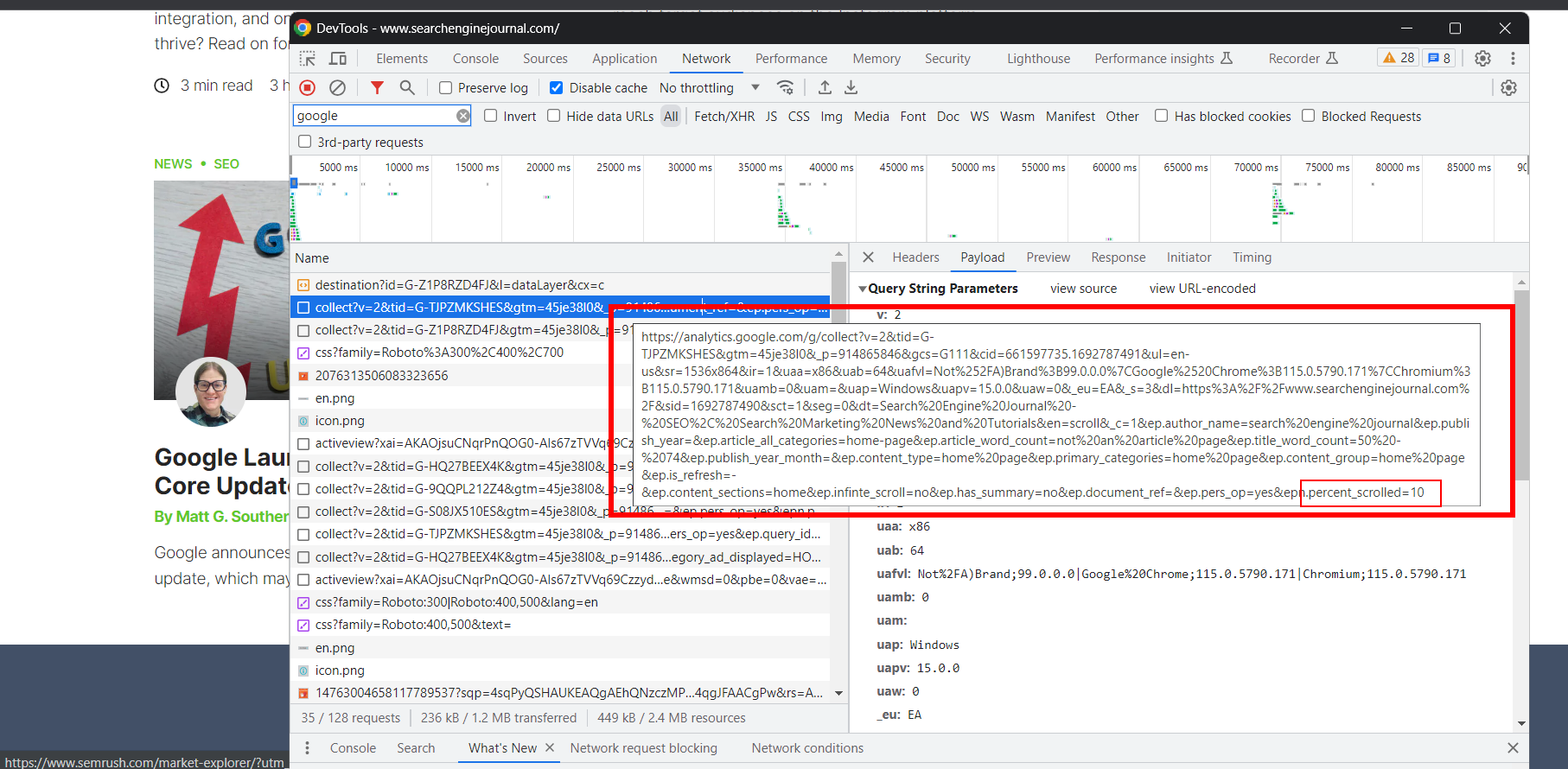
- GA scroll depth tracking hit URL.
Now, I can easily write a few lines of JavaScript code and make requests to that URL thousands of times.
-
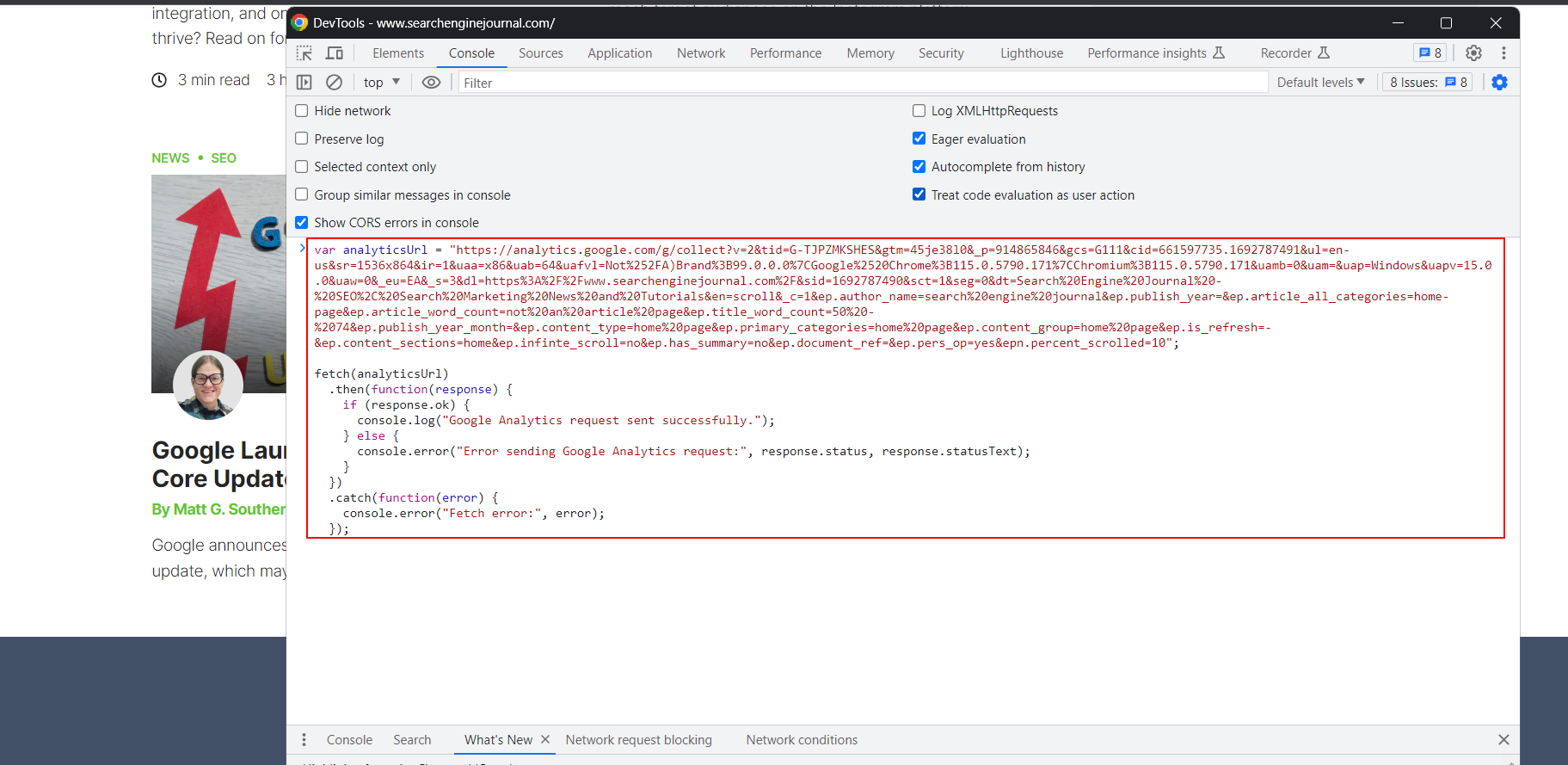 JS code in console of browser which makes a request to GA.
JS code in console of browser which makes a request to GA.
If Google were using the scroll depth metric of Google Analytics as the basis for its interaction data, one could easily manipulate the ranking of any website using this simple trick.
So, if it’s not Google Analytics, then where does Google gather all the interaction data it is referring to? One of the sources: Chrome browsers.
If you read Chrome’s online agreement, it clearly states that it sends data to Google, which is then stored and processed.
-
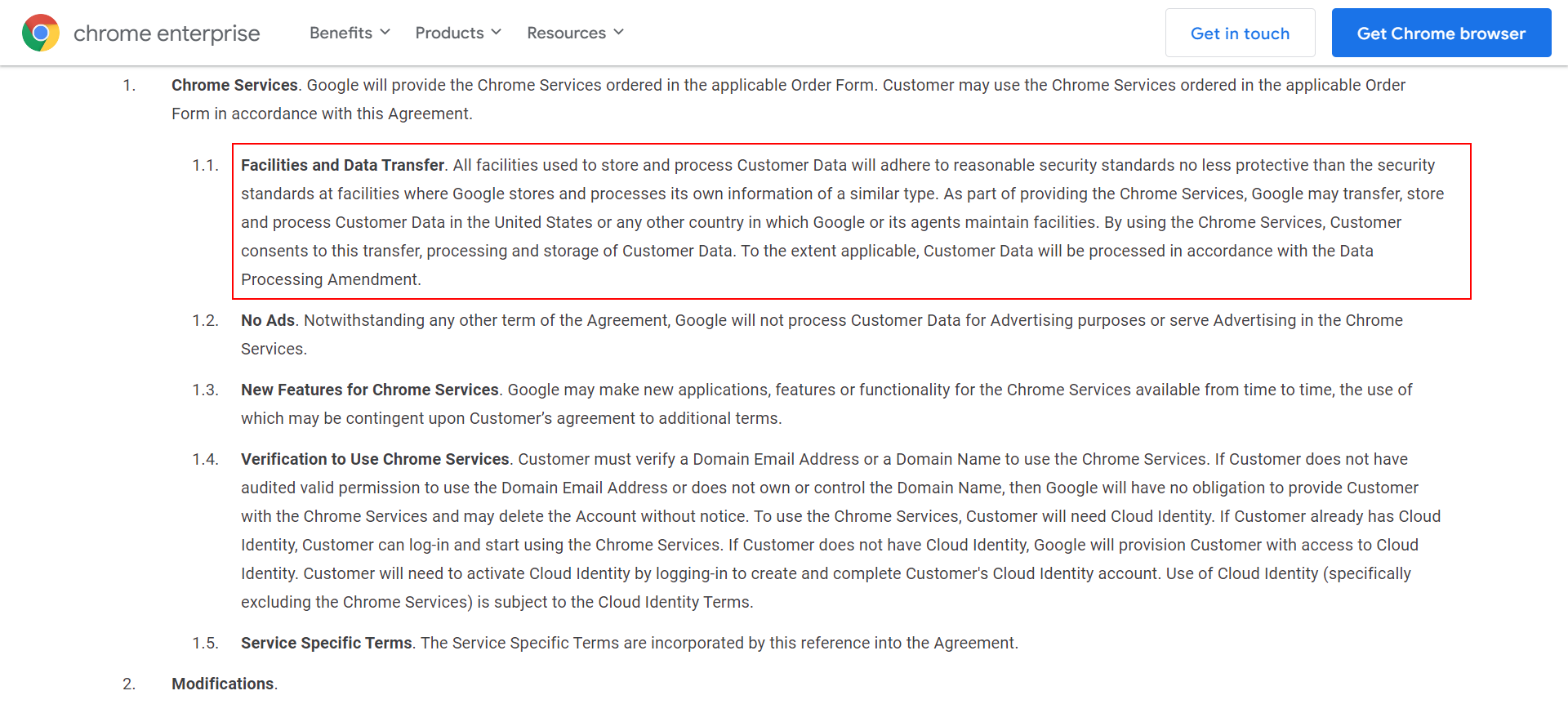 Screenshot from Chrome Online Agreement, August 2023
Screenshot from Chrome Online Agreement, August 2023
Since the Chrome browser has a 63.5% market share with billions of installations, Google has more than enough data about any website and how users interact with it.
[Free Ebook] Get The Complete Google Ranking Factors Guide →
The Evidence Against Google Analytics As A Ranking Factor
While we don’t have direct access to Google’s algorithm, evidence shows Google Analytics as a ranking factor is not a plausible theory.
First, Google representatives have been clear and consistent in saying that they don’t use Google Analytics data as a ranking factor.
As recently as March 16, 2022, John Mueller has responded to tweets about Google Analytics impacting rank.
-
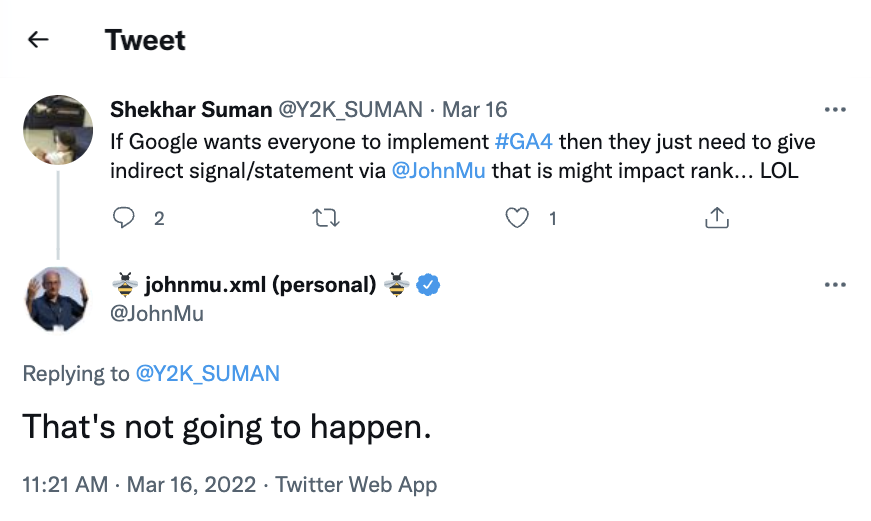 Screenshot from Twitter, June 2022
Screenshot from Twitter, June 2022
In jest, a marketer suggested that if Google wanted people to use GA4, the company could just say it would improve ranking. John Mueller replied, “That’s not going to happen.”
Google seems to continuously be batting down the idea that its analytics services influence ranking in any way.
Back in 2010, when we were tweeting to snag the top spot in results for a few moments, Matt Cutts said, “Google Analytics is not used in search quality in any way for our rankings.”
-
 “Is Google Analytics data a factor in a page’s ranking?” Google Search Central, June 2022
“Is Google Analytics data a factor in a page’s ranking?” Google Search Central, June 2022
And you don’t have to take Google’s word for it.
Here are 3 websites ranking in the top 10 for highly competitive keywords that do not have the Google Analytics tag on their site.
1. Ahrefs, An SEO Tool, Famously Does Not Use Google Analytics
-
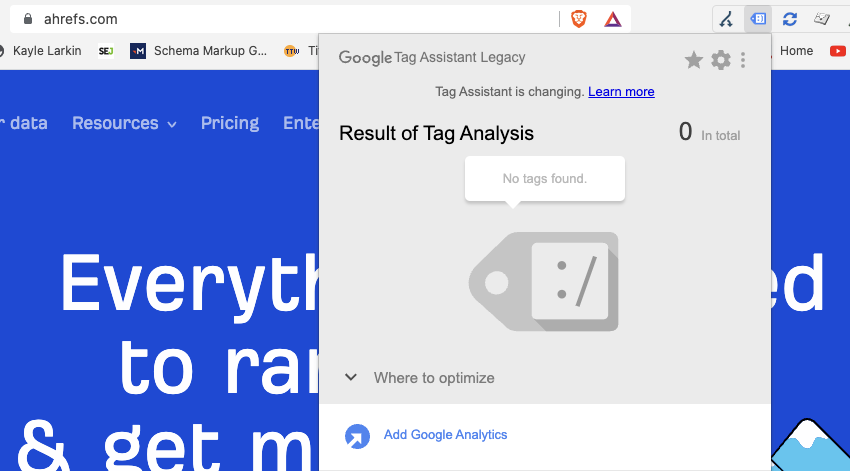 Screenshot from Ahrefs, June 2022
Screenshot from Ahrefs, June 2022
Tim Soulo, CMO at Ahrefs, tweeted in December 2019, “Every time I tell fellow marketers that we don’t have Google Analytics at ahrefs.com, they react with ‘NO WAY!'”
-
 Screenshot from Twitter, June 2022
Screenshot from Twitter, June 2022
And the Ahrefs domain ranks in the top 10 positions for over 12,000 non-branded keywords.
-
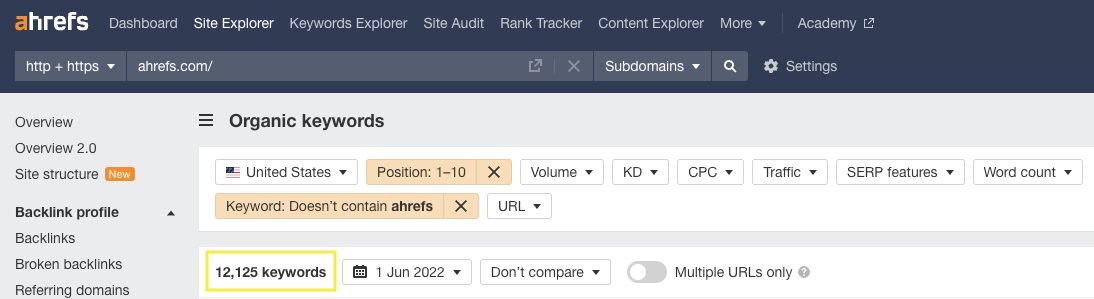 Screenshot from Ahrefs.com, June 2022
Screenshot from Ahrefs.com, June 2022
2. Another Famous Example Is Wikipedia
Wikipedia articles dominate Google search results, ranking very well for definition-type searches such as computer, dog, and even the search query “Google.”
And it ranks for all this with no Google Analytics code on the site.
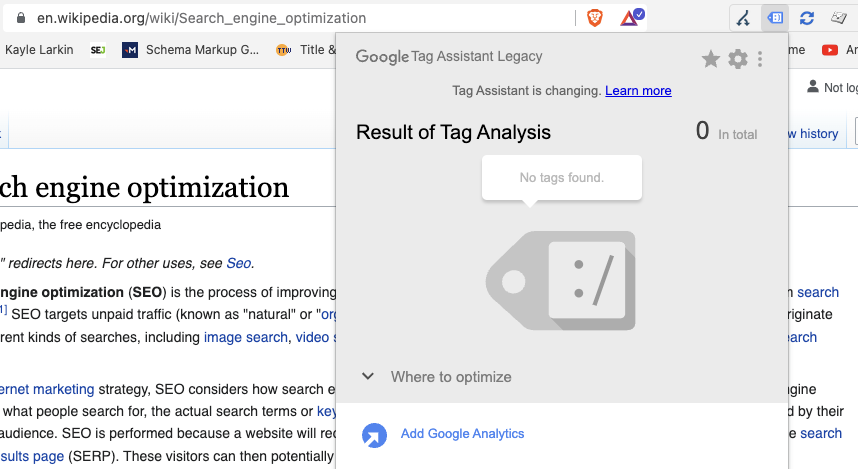
- Screenshot by author, June 2022
3. One More Example Is Ethereum
Ethereum is ranking in the top 10 for [nft]. NFT is an enterprise-level keyword with over one million monthly searches in the United States alone.
Ethereum’s website does not have Google Analytics installed.
-
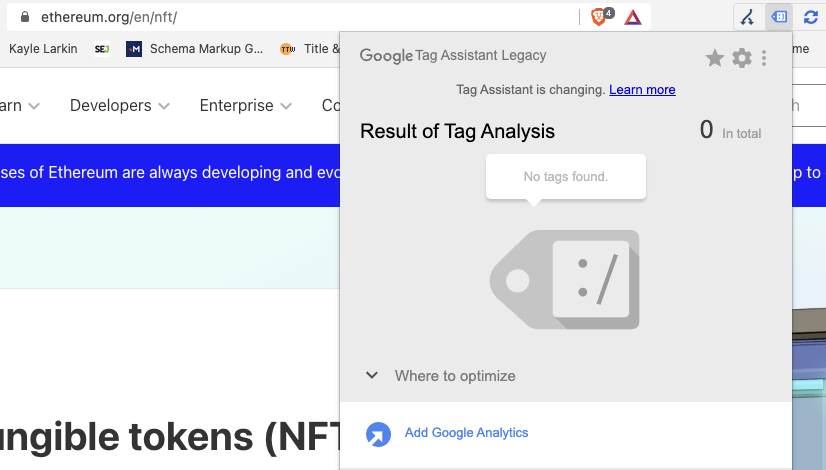 Screenshot from Ethereum, June 2022
Screenshot from Ethereum, June 2022
[Ranking Factors 2023] Download the free ebook + cheat sheet →
Our Verdict: Google Analytics Is Not A Ranking Factor

Google Analytics is a powerful tool to help you understand how people find your website and what they do once there.
And when you make adjustments to your website – by making it easier to navigate or improving the content – you can see GA metrics improve.
However, the GA code on your site does not send up an SEO bat signal.
The GA code is not a signal to Google, and it does not make it easier for Google to assess relevance (whether your webpage fulfills the user’s search query.)
The “bat signal” is for you.
Google Analytics is not a ranking factor, but it can help you understand whether you’re heading in the right or wrong direction.
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal





