There’s no denying the importance of search engine optimization.
Fully 68% of all online experiences start with a search engine, and organic searches are responsible for 53.3% of all website traffic.
Google reports that SEO traffic is 10 times greater than social media and 5 times greater than PPC.
But here’s the problem – Google doesn’t completely pull back the curtain to reveal every single factor of their ranking algorithms, leaving SEO experts to make educated guesses.
And the factors we do know about are constantly changing as Google makes updates to improve searches for users.
So, how do you make sure your content is ranking well on Google and landing on page 1 of the SERPs?
The answer – by bringing SEO copywriting into your content strategy.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn the do’s and don’ts of SEO copywriting and a step-by-step process to optimize your content for Google’s ever-evolving search algorithms.
What is SEO Copywriting?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the practice of enhancing a website for the purpose of achieving high rankings with search engines, especially Google.
SEO copywriting follows a similar goal but focuses on the content creation process, ensuring it offers maximum value and readability for both Google as well as regular users looking for information.
Google’s primary focus with each round of updates has always been to make search results more relevant for its users.
This is good news for content creators because if your focus is on building the best possible website for your audience, you’re already optimizing for high Google rankings. Still, there are additional steps to maximizing those rankings.
SEO copywriting is the creation of content that:
- Google can understand and index.
- Provides answers or relevant information for search queries.
- People find engaging enough to read and share.
- Is organized in a way that viewers and search engines can both easily read.
- Targets keywords and phrases that users are searching for on Google.
SEO copywriting usually has additional goals that encourage readers to take a specific action – for example, to buy a product, subscribe to a newsletter, etc.
But the primary focus is on quality content. Any additional calls to action come second.
How to Plan, Create & Format SEO Content That Ranks in Google
If you’re going to produce high-quality SEO copywriting, you need to do some prep work before you jump into the writing process.
There’s a delicate balance between writing for Google and writing for humans.
If you write specifically for Google, your writing will be stiff and repetitive as you slip your keywords in word-for-word at every opportunity. That’s not how humans naturally speak.
If you write specifically for your audience without any consideration for Google, your content probably won’t rank well because you aren’t drawing enough attention to your targeted keywords.
But if you write with both Google and your human audience in mind, you’ll achieve maximum SEO potential.
Phase 1: Keyword Research
Before you start writing, you need to know your topic.
This is why keyword research is important.
You’ll want to target specific keywords that are relevant to your website’s established niche and have low competition (which gives you a much higher chance of landing on the first SERP).
The example below is from Semrush, which is one of many keyword research tools available to assist you:
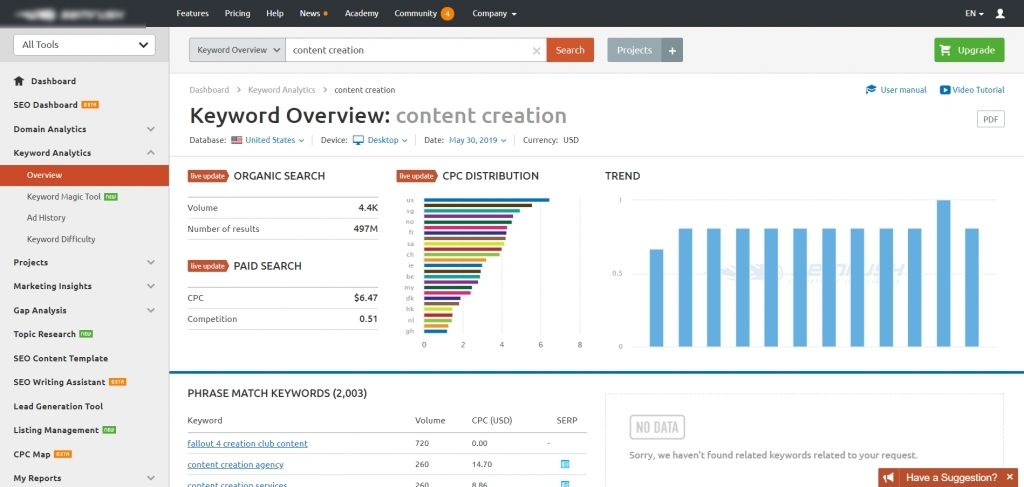
KWFinder is another great tool that can help you find long-tail keywords to target.
These valuable resources can help you pinpoint the best keywords to target and generate ideas for similar keywords and variations you may not have considered.
Phase 2: SERP Intent
SERP (search engine results page) intent – also sometimes referred to as search intent – puts topics and keywords into perspective based on why someone is searching for a particular keyword on Google and how they intend to use the information.
Understanding search intent will allow you to properly target your intended audience based on their motives for using a search engine.
For example, let’s say we’re targeting [best pizza] as a keyword.
What is your audience actually searching for?
- The best local pizza restaurant with outdoor dining?
- The best pizza recipe to make at home?
- The best pizza delivery service?
- The best pizza toppings?
Knowing the search intent behind your keywords is just as important as the keywords themselves so you can tailor your content to the needs and expectations of your audience.
If you’re targeting [best pizza] from the perspective of a local pizzeria offering dine-in, takeout, and delivery, you’ll want your content to be for people in the area searching for places to eat, not people who are looking for online recipes.
Phase 3: Plan and Outline Your Article
Keyword?
Check.
Search intent?
Check.
Time to start writing?
…Not quite yet.
Before you dive right into the content, you need to finalize your plan.
Remember, Google and other search engines reward readability and organization, which means you should spend a little extra time planning out your content to ensure a logical flow and presentation.
Before you begin writing, ask yourself:
- What is the purpose of the article? Are you hoping to inform, educate, promote a product or service, solve a problem, or answer a question?
- What do I want to achieve? What’s your end goal? Are you hoping to get more website traffic and ranked keywords? Or do you want readers to take an action?
- Who is my target audience? Knowing who will be searching for and reading your content is just as important as knowing what you’ll be writing about. If you’re talking to a Gen Z audience, your tone and language isn’t going to be the same as it would be if you were addressing a 65+ audience.
- How will I order the information I present? What are the logical steps you need to include? For example, many articles present a problem and then propose a list of solutions to address the said problem.
- What structure will best frame my content? A listicle, for example, will be laid out differently than a how-to article.
At a minimum, you should outline your headings and subheadings so you have a logical plan when you start writing.
Phase 4: Structure Your Article
As you build up your outline, pay attention to the structure of your article.
Readability is key, not just for Google, but also for readers who will likely be skimming through your article on a mobile device.
Be on the lookout for opportunities like these.
Visual media. Long blocks of text are difficult to read, especially on mobile devices. If your human audience struggles to read your article, Google isn’t going to be favorable toward it, either. Break up text with images, videos, and white space.
Subheadings. Make it easy for skimmers to scroll through your content and find the most valuable sections based on their needs and interests.
Lists. Break up important points into bulleted or numbered lists whenever possible. Lists are easy to read for humans, but they’re also a favorite for Google to easily generate information in a featured snippet.
For example:
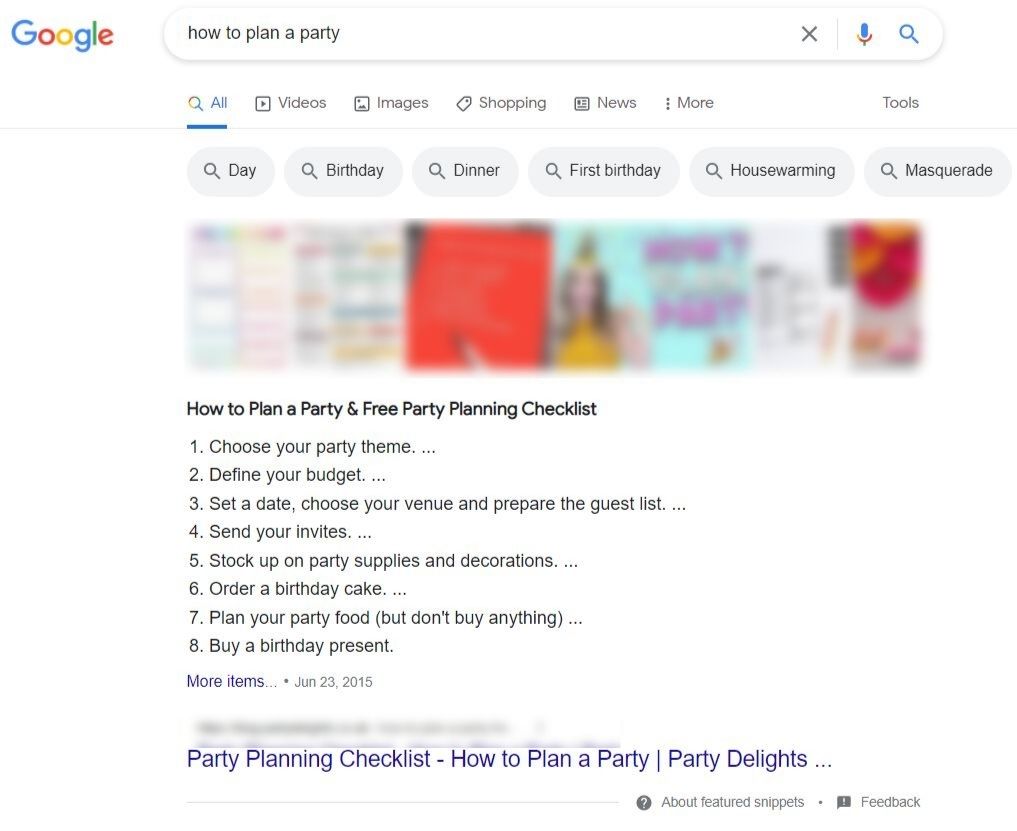
Clicking into the featured article reveals an insightful look at the article structure.
Each point that Google listed in the featured snippet is a separate numbered subheading in the article.
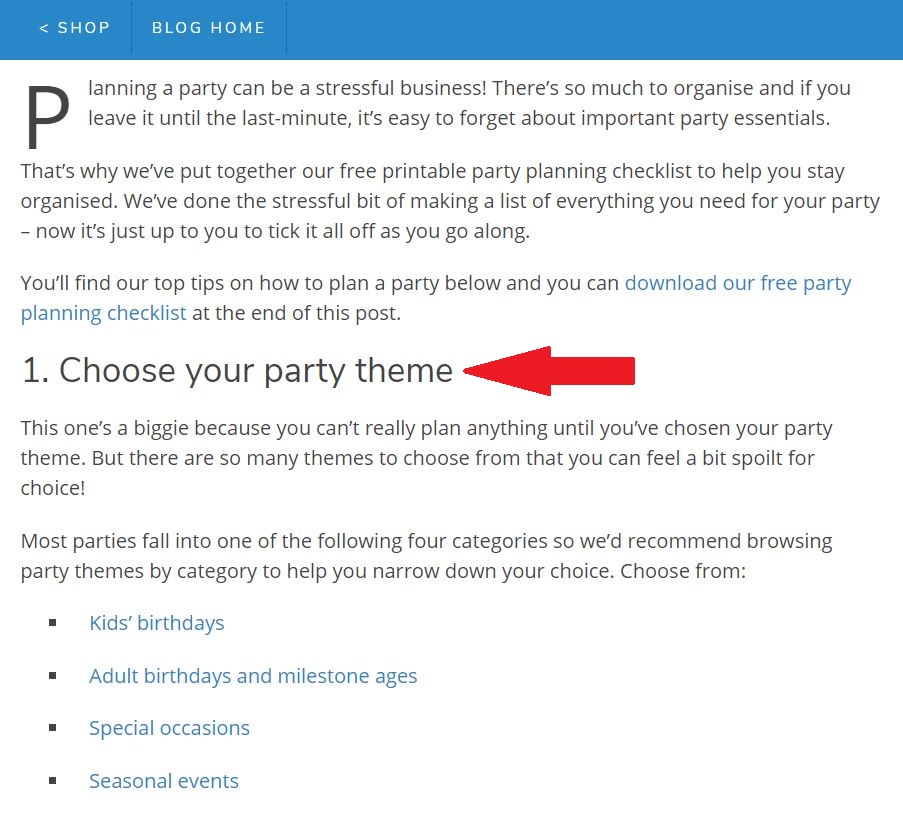
See why lists and subheadings are so crucial?
One of the most common writing structures used in journalism is the inverted pyramid. This technique organizes an article with the most important information at the beginning.
Within the first paragraph, a reader should have all of the necessary details. Later paragraphs are used to elaborate and provide examples.
This tried-and-true writing technique works well for many types of content, especially if the article’s primary purpose is to answer a question.
Make your article structure part of your outlining process so you’re ready to hit the ground running with the next step.
Phase 5: Content Creation
Finally, it’s time to write.
It seems like a lot of prep work to reach this stage. But all of that time, research, and planning is what separates successful SEO copywriting from run-of-the-mill blog posts cranked out with minimal effort.
As you write, keep your keyword and audience in mind, but remember to let the writing flow naturally.
Don’t stuff your keyword into every other sentence. If you’re staying focused on your topic, the keywords and phrases will fit seamlessly into your writing as you go.
Be sure to include your keyword in at least the first subheading, preferably more than one.
Yes, you want to make it easy for Google to catalog the main points of your article. But ultimately, you’re writing for the humans who will be reading it, not the search engines.
Including links in your content is important for SEO. Be conscious of the websites you’re referencing so you can ensure you have high-quality links. Alexa is a great resource to check a website’s authority.
Phase 6: Edit
Do not hit publish on a rough draft without editing first!
SEO copywriting is all about producing high-quality content.
That means poor research, typos, disorganization, and other errors will take a serious hit on your credibility. Your content needs to showcase your expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-A-T).
Ideally, you should have a content calendar so you can stay on track and let your articles sit for a day or two before you return to them for a final proofread.
At the very least, read through your article a few times before you hit publish. Reading out loud can help you to identify areas that are awkward and lose their flow.
Be sure to check for:
- Spelling.
- Grammar.
- Punctuation.
- Active Voice.
- Transition Words.
- Tone.
- Readability.
- Sentence Structure.
- Sentence Length.
- Paragraph Length.
When necessary, break long paragraphs into smaller ones for better readability.
Be critical of your own work. Does the article convey the point you wanted to make? Does it have a clear call-to-action for the reader? Does it stay on topic?
Don’t be afraid to ask for feedback from others or enlist professional help to make sure you’re publishing the highest quality article possible.
The Secret to SEO Copywriting Success
The most important lesson to remember is that SEO copywriting is a process.
If you’re whipping out articles on a whim with no research or planning, you’re not going to see the same level of success that you would if you slowed down and approached content creation with a step-by-step approach.
Not everyone has a natural-born talent for writing.
And that’s okay.
You don’t need to have that talent in order to be successful at SEO copywriting.
If you’re willing to do the work, your SEO copywriting skills will improve over time.
As they say, practice makes perfect.
More Resources:
- SEO Content Writing vs. SEO Copywriting: What’s the Difference?
- 10 Elements of Good SEO Copy
- 7 Effective Productivity Hacks to Combat Crappy Copywriting
- Content Marketing: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
Image Credits
All screenshots taken by author, July 16, 2021.





![AI Overviews: We Reverse-Engineered Them So You Don't Have To [+ What You Need To Do Next]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/sidebar1x-455.png)