To remain the most popular search engine in the world, Google has to continuously update its algorithm to continue delivering users useful results.
To this end, Google also makes available Google Search Essentials, so everyone from web developers to SEO professionals knows the rules of the game.
Of course, there are plenty of people who want to win the game without following its rules.
The tactics they use are known as black hat SEO.
Black hat SEO gets its name from old cowboy movies where the bad guys wear a black hat.
Black hat SEO practitioners know the rules of search engine optimization and use that understanding to take shortcuts that aren’t exactly laid out in Google’s best practices.
This is in juxtaposition to white hat SEO practitioners who promote high-value content, and engage in deep keyword research to win in the SERPs.
Google is good at identifying and penalizing black hat SEO techniques, but that doesn’t stop people from trying them anyway. As technology develops, new techniques are invented, which push Google to intensify the fight against them.
Here are 13 black hat practices to avoid because they can land you an algorithmic or manual penalty.
Some of these you may do without intending to, so it’s good to familiarize yourself with black hat SEO to make sure you’re in the clear.
Black Hat Link Techniques
1. Buying Links
A high-quality, relevant link can drive traffic to your domain while telling Google’s algorithm that you’re a trustworthy source.
A good backlink can also help Google map your website so that it has a better idea of what you’re all about, making it easier to serve you up as a search result.
Buying a link, however, is against Google’s Search Essentials, and – according to Google – it doesn’t work.
If you’re caught, you could get an automatic and manual penalty that affects specific pages or, worse, the entire site.
Google tracks links that are likely to have been bought and those that have been earned.
Additionally, the sort of website that sells you a link is the sort of website you wouldn’t want to buy a link from because it is easier than you think for Google to identify unnatural patterns – even for Google’s own properties.
For this reason, Google created a form to help you disavow links.
This way, when you go through your backlinks, you can disentangle yourself from any undesirable domains.
2. PBNs
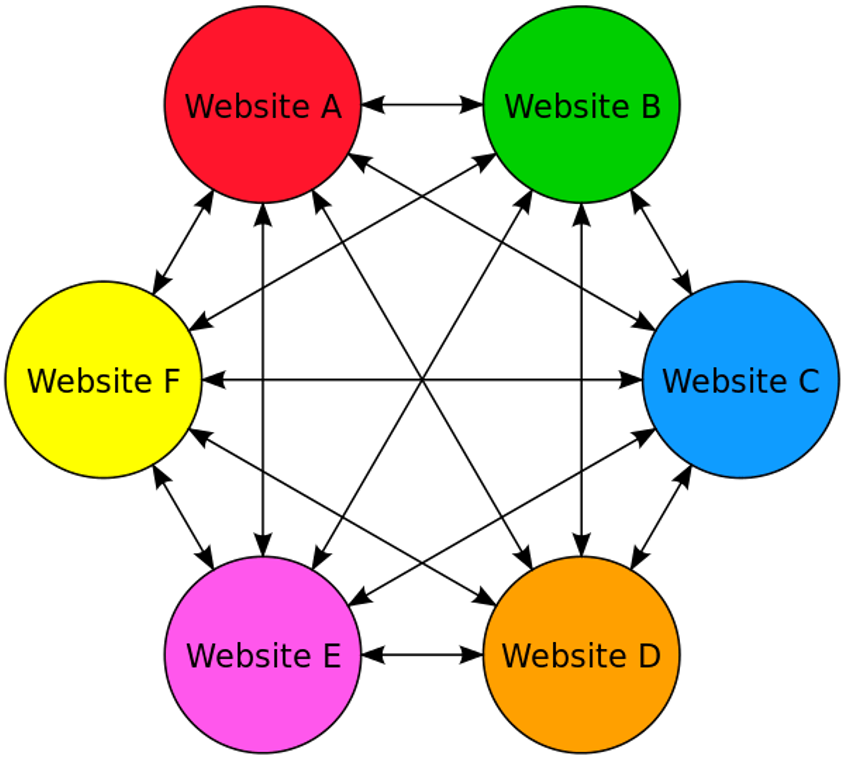 Image from author, November 2024
Image from author, November 2024PBNs are websites that link to each other.
They used to be much more prevalent in the 1990s and early 2000s, particularly among fan pages for TV shows, movies, musicians, etc.
It is considered a link scheme when it is designed to manipulate algorithms, and with current AI advancements, search engines are perfect for catching such patterns.
3. Comment Spam
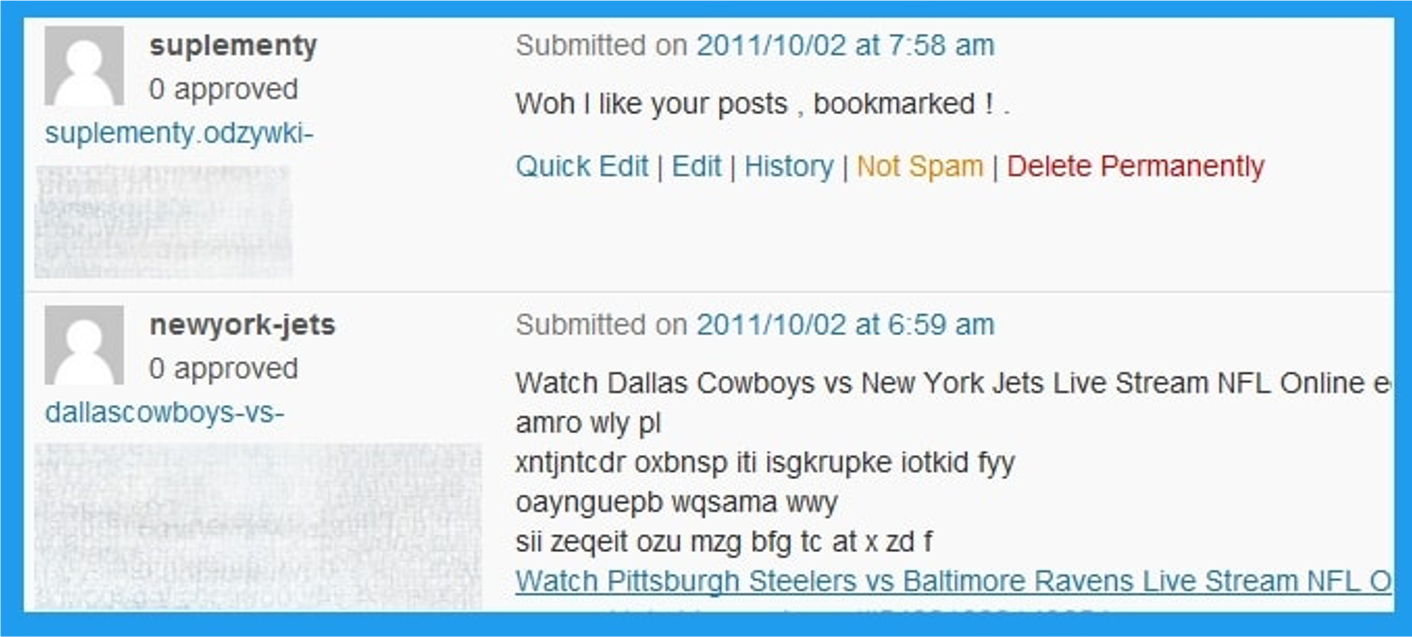 Image from author, November 2024
Image from author, November 2024You may be able to share a link to your website in the comments section of a website, but you should avoid doing so unless it’s relevant.
Otherwise, you risk being penalized for being a spammer, as using comments to build links is essentially not effective.
4. Footer Links
 Image from author, November 2024
Image from author, November 2024The footer is prime real estate for a link because footers appear on every website page.
If you’ve been adding footer links with commercial anchor text at scale to manipulate results, Google will likely be able to identify those and penalize you for it.
5. Hidden Links
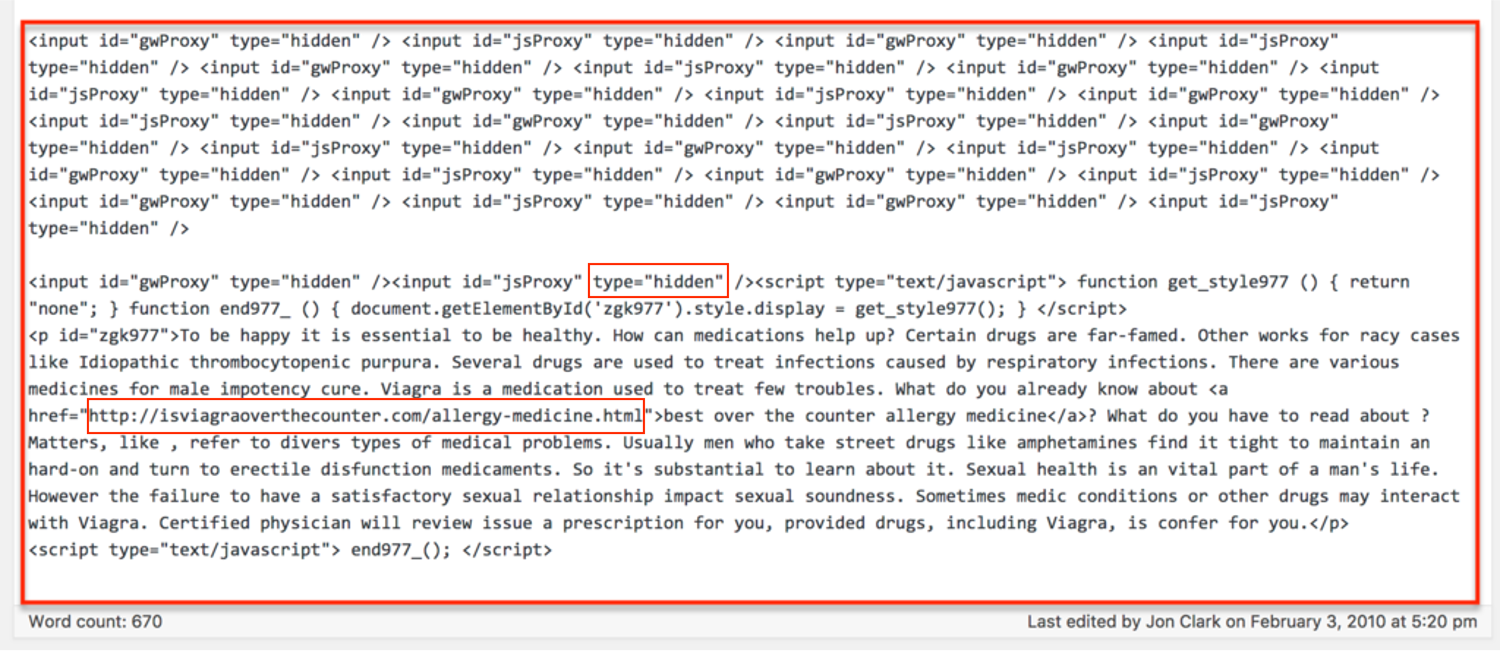 Image from author, November 2024
Image from author, November 2024You may think that you can hide a link in your website’s text or by having the link appear as the same color as the background, but Google will notice and penalize you for trying to game the system.
Additionally, if you include enough irrelevant links, you’ll give Google less reason to direct traffic to your target audience since you’ll be diluting your relevance.
Deceptively hidden links are a violation of Google’s guidelines. That means:
- No hiding text behind an image.
- No keeping text off-screen using CSS or JavaScript.
- No using a font size of 0.
- No making one little character, like a period, a link.
For the full list of unnatural link types, see this article.
Content Black Hat Techniques
6. AI-Generated Content At A Scale
With the rise of AI, chatbots producing large volumes of content has become easier than ever.
Google has updated its guidelines to address the use of AI-generated content at a scale and advises that it should be thoroughly reviewed and fact-checked to ensure accuracy and reliability.
This means the use of AI to mass-generate content without human oversight violates Google’s guidelines.
However, black hat SEO pros in the early days of AI exploited these technologies by creating large volumes of content without proper human supervision.
Consequently, many of these sites were removed from search results when Google updated its algorithm and detected AI-generated spam patterns.
Below is what it looks like to be penalized by Google for AI-generated spam.
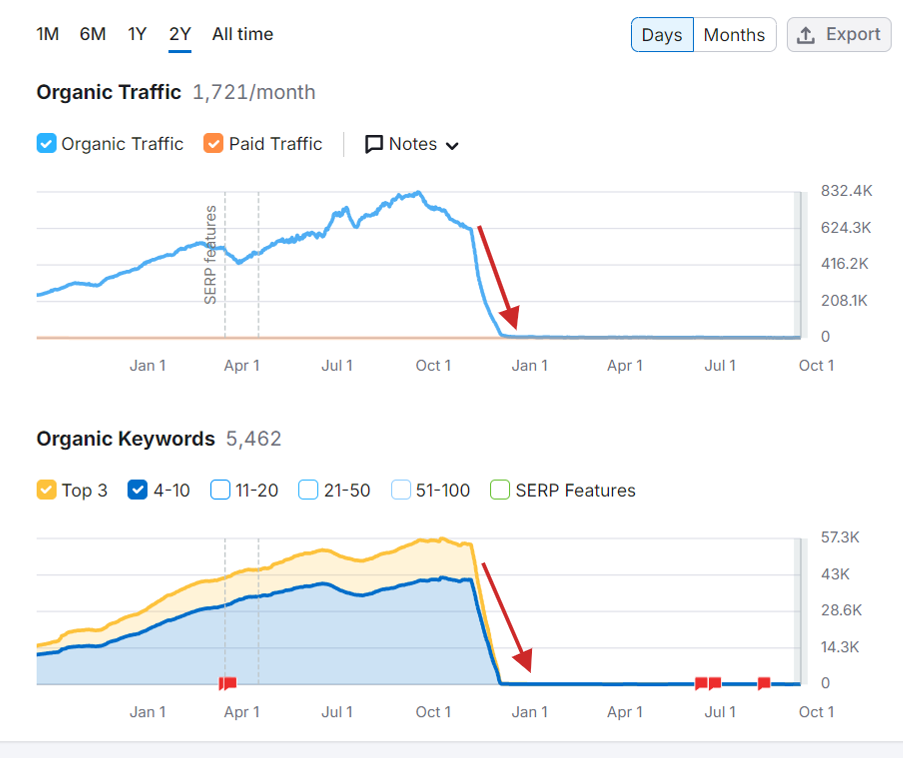 A website that gained 830,000 monthly visits from Google search vanished after the algorithm update.
A website that gained 830,000 monthly visits from Google search vanished after the algorithm update.7. Article Spinning & Scraped Content
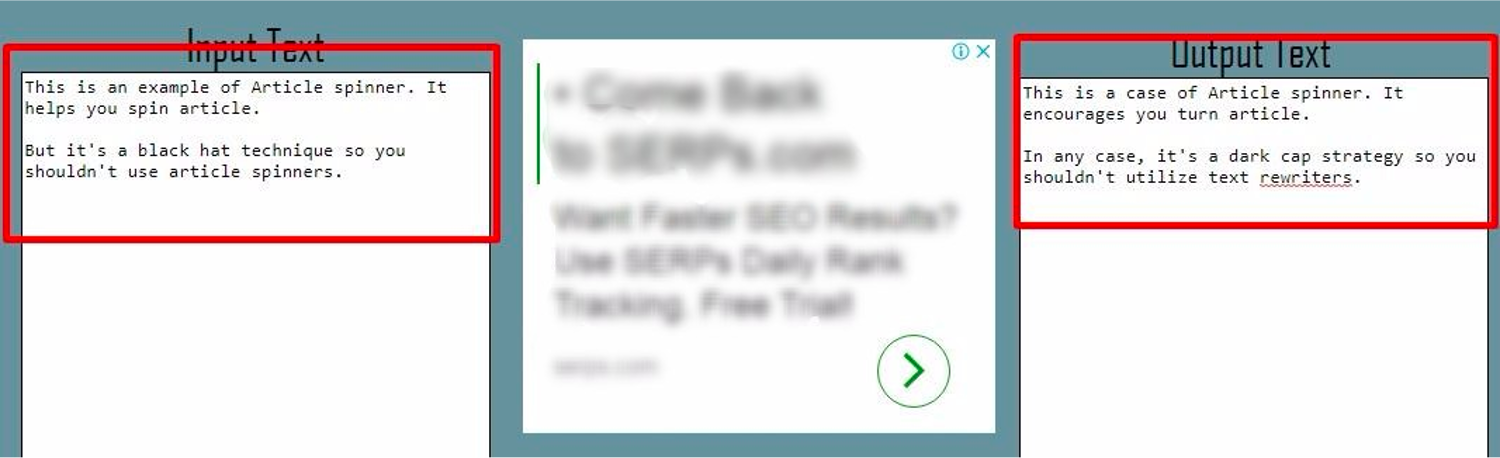 Image from author, November 2024
Image from author, November 2024Article spinning is a technique that involves re-writing content by substituting synonyms, changing sentence structure, or re-writing text entirely while communicating the same information as the source material.
Article spinning or scraping can be done manually, but modern techniques often use AI and sophisticated software, making it harder to detect.
For a good reason, such articles degrade the quality of the internet, which is why Google penalizes you.
8. Cloaking
Cloaking is an old black hat trick that’s still used to this day – use a flash or animated page to conceal information your visitors that only Google can see in the HTML.
It’s very difficult to mislead Google without being detected. Google uses Google Chrome’s data, which means it can see what is rendered on the webpage on the users’ side and compare it to what is crawled.
If Google catches you cloaking, you’ll get a penalty.
9. Doorway Pages
Doorway pages are a form of cloaking.
They’re designed to rank for particular keywords but then redirect visitors to other pages.
They’re also known as:
- Bridge pages.
- Portal pages.
- Jump pages.
- Gateway pages.
- Entry pages.
10. Scraping Search Results And Click Simulation
Scraping search results for rank-checking purposes or using bots to access Google Search is against their spam policies.
This often takes place in conjunction with article scraping, when an automated script scrapes Google Search to find articles ranking in the top 10 positions for automatic spinning.
Another type of spam is to program a bot that accesses Google and clicks on search results to manipulate click-through rates.
They aim to mislead search engines into thinking that certain pages are more popular or relevant than they are. This manipulation can temporarily boost a site’s perceived engagement metrics but harshly violates Google’s guidelines.
11. Hidden Content
Like a hidden link, hidden content is content that’s made the same color as the background or moved away from users’ screen view using CSS techniques.
It’s a tactic that intends to include as many keyword phrases, long-tail keywords, and semantically linked words as possible on a page.
Of course, Google’s algorithm can tell the difference between keywords within the body of a paragraph and keywords hidden in the background.
Hidden content can take several routes to your site beyond being intentionally placed there by the site owner.
- You could publish a guest post from someone who includes hidden content.
- Your commenting system could be insufficiently rigorous and, as a result, fail to pick up on hidden content.
- Your website could get hacked, and the hackers could put up hidden content. This is also known as parasite hosting.
- An authorized user could accidentally put up hidden content because they copied and pasted text with CSS styling from a different source.
Not all hidden content, like accordions or tabs, is forbidden.
The rule of thumb is that content is okay as long as it is visible to both the user and the search engine.
An example may be content that’s only visible to mobile visitors but is hidden to desktop visitors.
12. Keyword Stuffing
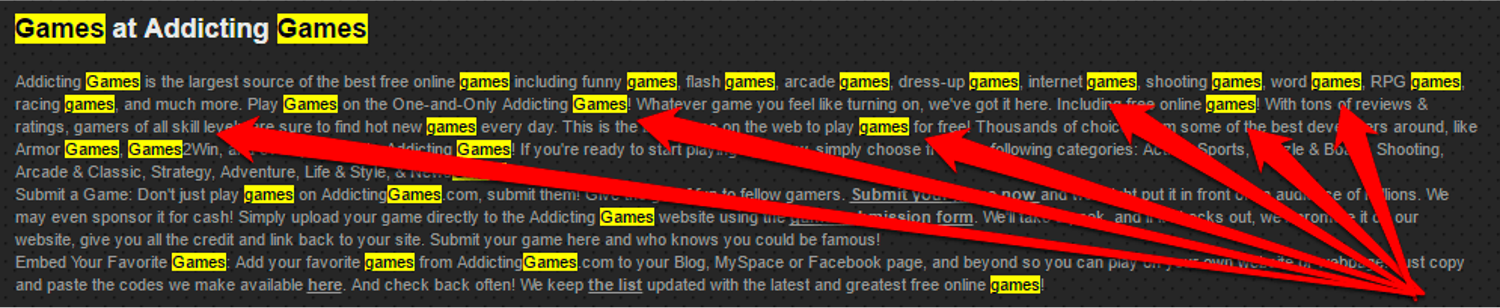 Image from author, November 2024
Image from author, November 2024If SEO were only about using keywords, then a block of keywords would be all it takes to rank as No. 1.
However, since Google wants to deliver high-quality results, it is looking for content-rich in semantically linked keywords.
That way, the algorithm is more likely to provide high-quality content instead of content that simply bears the superficial markings of high-quality content.
13. Rich Snippets Spam
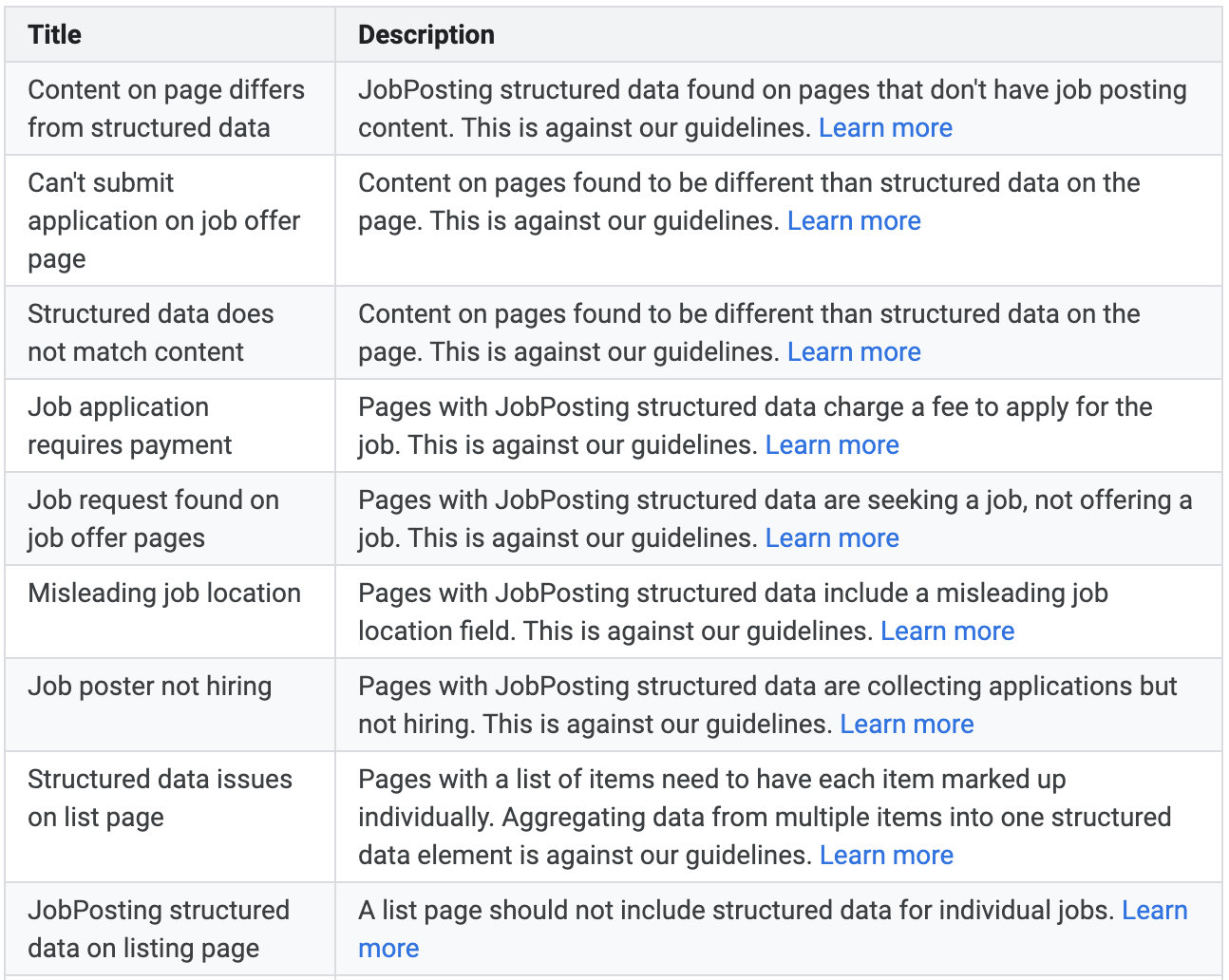 Image from author, November 2024
Image from author, November 2024Rich snippets are snippets with more information on SERP pages. Enhanced visibility can increase CTR to your site from SERPs and drive more traffic.
But there are many ways that the schema used to generate these snippets can be manipulated. In fact, there is an entire Google support page dedicated to it.
However, if you get a manual action because of abusing structured data, it will not affect the rankings of your website. Instead, it will remove all rich snippet appearence from SERP for your website.
Bottom Line
The rewards of the black hat path are short-lived. They’re also unethical because they make the internet worse.
But you can’t do something right without knowing how to do it wrong, which is why every white hat SEO also needs to know about the black hat path.
That way, you know how to steer clear of it.
And if you accidentally get penalized or decide to change your practices, there are ways to recover from Google’s penalties.
More Resources:
- White Hat Vs. Black Hat Vs. Gray Hat SEO: What’s The Difference?
- Why It’s Time to Retire Black, White & Gray Hats in SEO
- SEO For Beginners: An Introduction To SEO Basics
Featured Image: PeopleImages.com – Yuri A/Shutterstock






![10 Top Converting Landing Pages That Boost Your ROI [With Examples]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/sidebar1x-599.png)