You may have read that as of Friday, September 23, Penguin is now part of Google’s core algorithm. But what does that mean, exactly? In this article, I’ll talk about the key differences between Penguin 4.0 and previous updates, how those changes impact your website, and how to see if you’ve been impacted (for better or for worse) by Penguin’s most recent update.
Editor Note: to learn more about Google’s Penguin update and disavow links, check out this Marketing Nerds episode with Jim Boykin and Loren Baker:
What Is Google Penguin?
Google Penguin is an algorithm designed to penalize and prevent link spamming. Google introduced Penguin back in April 2012 to combat web spam and to penalize websites whose SERPs relied on exploiting “black hat” SEO tactics (e.g. keyword stuffing, link schemes, cloaking, duplicate content, etc.).
What’s Changed in Penguin 4.0?
Over the years, Penguin has undergone a number of updates, all intended to promote quality content and hamper anyone practicing unethical link building. To that end, Penguin 4.0 has made two major changes that come as a welcome relief to many SEO specialists:
1. Penguin now runs in real-time.
2. Penguin is no longer a site-wide negative ranking factor.
Penguin used to run intermittently (i.e. Google would only run its algorithm once every few months) and usually you could only incur a penalty or get a penalty lifted whenever this algorithm was refreshed. As a result, even if a penalized website removed the offending links the day after they received a penalty, they might have to wait months to get that penalty lifted.
Additionally, before the update, Penguin didn’t penalize just one page when it detected spam signals — it buried your entire website. Your domain would plummet through the SERPs even if most of your website was spam-free. Worse still, this penalty would stick until the next time Penguin refreshed — which sometimes took months — even if you proactively corrected the problem immediately after receiving your penalty.
Penguin 4.0 has changed all of this. Now, Penguin refreshes in real-time, which means that site penalties are incurred or lifted whenever Google crawls and reindexes a page. In other words, building spammy links could burn your SERPs tomorrow, but you no longer have to wait for ages for a penalty to be lifted.
The latest Penguin update is also more granular, which means Google will penalize individual pages as opposed to your entire website. If Penguin detects web spam on your website, it might bury the offending page in the SERPs, but the rest of your domain still has the potential to rank well.
How Will Penguin 4.0 Affect My Website?
The effects of a Penguin update are usually felt immediately in the SEO community: “black hat” SEO is penalized, while websites who have had their penalties lifted begin to rise in the ranks again. But the latest Penguin update is a bit of a strange animal — if you’ll pardon the pun — because most SEO specialists and webmasters didn’t feel its effects until a few days after Google began rolling it out.
According to Moz’s co-founder Rand Fishkin, SEOs began to feel a SERP flux approximately three to five days after the update. He polled his followers and found that 24-28% of them were affected by the update, with some feeling the effects later than others. Most of the websites affected — including Moz itself — enjoyed a slight boost in rankings and only a small number of sites experienced penalties.
The takeaway from this is that the latest Penguin update won’t hurt websites that don’t spam. In fact, the update is likely to improve the rank of websites who improve their links and focus on quality content.
Marie Haynes’ excellent case studies are testaments to this. She lists many examples of websites that have been suppressed for years (some since Penguin first launched in 2012) that are finally escaping the yoke of their penalties. In one striking example, a previously penalized e-commerce store is now ranking 10th for a keyword they were ranking 95th for only two short months ago.
So will the Penguin update affect your rankings? Hopefully only positively. As Rand puts it, “Penguin 4.0 is a good time to cheer for Google. It’s brought a lot of traffic to a lot of good websites and pushed a lot of sketchy links down. We will see [what] happens as far as disavows and reconsideration requests for the future.”
How to See If You Were Affected by Penguin 4.0
To see if Penguin’s latest update affected your SERPs (positively or negatively) you’ll need an anti-Penguin tool. I used my tool — SEO PowerSuite’s Rank Tracker — to measure organic traffic against Penguin updates:
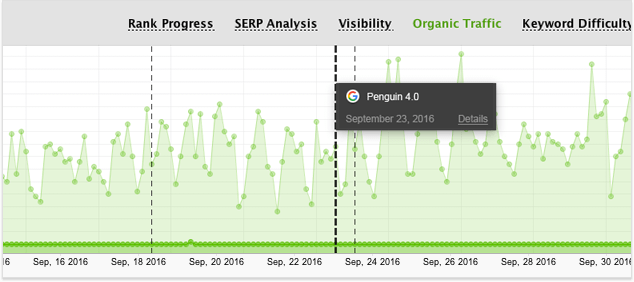
Hopefully, you’ll see the same healthy spike in traffic that I did following Penguin’s latest update.
If for some reason you instead see decreased traffic, you’ve probably had some pages penalized. You may be suffering from some of the common Penguin hazards, such as:
- Disreputable links from low quality (“spammy”) websites
- Links from PBNs or other websites created for link building
- Too many links from off-topic sources
- Link schemes or paid links
- Keyword over-optimization
- Deceptive on-page SEO such as automatic redirects or hidden text
- Thin or duplicate content
All of these issues could result in a Penguin penalty. If you’ve fallen afoul of an ill-advised link-building campaign or if you’ve accidentally posted some duplicate content since the last Penguin update, your website may have taken a hit.
How to Resolve Penguin Penalties
Thankfully, as I stated above, the beauty of Penguin 4.0 is that if you have received a penalty after the recent update, you won’t have to wait forever to see that penalty lifted. First things first, however, because your penalty won’t be lifted so long as issues remain. Here’s what you should do:
1. Remove Harmful Links
Whenever possible, petition webmasters to remove spammy links from the offending sites. If they refuse, or if you can’t contact these webmasters, disavow these links using Google Disavow tool.
2. Steer Clear of Common Hazards
This Penguin update hasn’t drastically changed what Penguin penalizes so much as what and how it deals with web spam. To that end use your preferred penalty risk assessment software to get a list of all of your website’s backlinks and then check them for any potential risks. Riskier sites should be removed or disavowed, as specified above.
3. Focus on Quality Content
The best way to earn links is to beef up your content with regular, high-quality offerings. Plan out your content in advance so that you have a content calendar for publishing blog posts, ebooks, and other assets. Focus your content on important topics that will earn you attention and help you rank for your targeted keywords.
4. Diversify Your Link Building
Finally, when you have your quality content locked and loaded, you just need to spread the word. Reach out to any industry authorities you reference in your content and see if you can win links from multiple high-profile experts who will help spread the word organically. This shouldn’t be too hard if your content satisfies a need you see in your audience.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Penguin
I think it’s safe to say that Penguin 4.0 is the update many of us have wanted for a while now. Previously, Penguin left all SEOs a little paralyzed at the thought of incurring a penalty and suffering under it for months on end. Now that Penguin is running in real-time, it feels like we’ll be better able to correct potential mistakes and reap the rewards a whole lot sooner.
Image credits
The featured image and the in-post image are by author.