PHP 5.6 and 7.0, the scripting language that underlies 57.1% of all WordPress sites will stop receiving security updates in December 2018. No security patches will be issued for those versions of PHP after that date, making those sites less secure moving forward.
That could mean a loss of traffic and a ranking nightmare for WordPress websites still using those old versions of PHP in the event of a vulnerability.
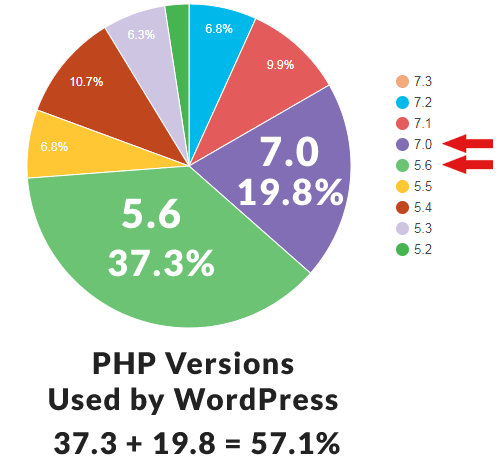 This graph shows the percentage of sites using PHP 5.6 and 7.0. It is somewhat concerning that more than a third of WordPress sites use 5.6.
This graph shows the percentage of sites using PHP 5.6 and 7.0. It is somewhat concerning that more than a third of WordPress sites use 5.6.What is PHP?
PHP is a scripting language that enables the creation of websites. There are different versions. Each version represents an improvement from the previous version. As each version is created, software (like WordPress) are updated to be able to take advantage of the latest performance improvements.
When are Security Updates Ending?
- Security updates for PHP 5.6 is ending on December 31, 2018.
- Security updates and patches for PHP 7.0 are ending on December 3, 2018.
 This table shows when PHP 5.6 and 7.0 will no longer receive security updates.
This table shows when PHP 5.6 and 7.0 will no longer receive security updates.How Many WordPress Sites are at Risk?
According to WordPress’ official published statistics, 57.1% of WordPress sites run these outdated versions of PHP.
Why is Security Support Ending?
Security support for each version is scheduled to last a limited amount of years until it reaches what’s known as End of Life (EOL). At this point there will be no more security improvements created for it, even if a vulnerability is discovered.
According to the official PHP website, this is what EOL means:
“A release that is no longer supported. Users of this release should upgrade as soon as possible, as they may be exposed to unpatched security vulnerabilities.”
All websites are required to upgrade to the latest version or risk becoming vulnerable to hacking events.
What if You Fail to Update PHP?
All websites that fail to upgrade to the latest version of PHP will be insecure and vulnerable to hacking events once versions 5.6 and 7.0 enter their End of Life (EOL) period. This means that even if security vulnerabilities are discovered, nobody will make a patch to fix the vulnerabilties in versions of PHP.
Additionally, many plugins, themes and WordPress itself will eventually stop working with these versions of PHP.
If you run a WordPress website, the most prudent action to take is to upgrade to the latest version of PHP.
How to Identify Which Version of PHP is in Use?
The easiest way to tell is to log into your hosting control panel and find a link to a section focused on PHP. There are online tools that can tell you but it’s best to log in directly to your control panel and check it yourself.
There are also plugins that can tell you which version you’re using. For example, the WordPress phpinfo() plugin is an easy to use plugin that can tell you which version of PHP your WordPress site is using. Once you know which version of PHP you’re site is running on, you can remove the plugin.
Alternatively you can call your hosting provider’s support and ask for help identifying which version your site is using and instructions for how to upgrade.
How to Upgrade PHP From 5.6/7.0 to Latest Version
Step 1 – Backup Your Site
It is important to back up your WordPress site. The easiest way to do this is with the UpDraftPlus plugin.
Step 2 – Check Plugin Compatibility
Make sure all of your plugins have been updated to their latest version. Additionally, the update should have happened within the last few months to no longer than a year.
If the plugin has not been updated in a long time, visit the plugin’s authors web page and verify if the plugin is compatible with the latest version of PHP (PHP 7.2).
If the plugin is not compatible then switch to the most popular and recently updated plugin that does the same thing. You really should not be running any plugin that isn’t compatible with the latest version. Poorly maintained plugins can be security risks.
Step 3 – Upgrade PHP Version
Log in to your web hosting control panel, find the PHP section and upgrade the PHP version for your website. If this is to difficult then contact your web hosting support for help.
Make Security a Part of Your SEO Process
Security issues are not commonly a part of SEO. SEO is largely concerned on improvements that will help ranking.
However, once a site is hacked and the search traffic disappears, security rapidly becomes an SEO nightmare. So why wait until your site is hacked to add security to your SEO toolkit? Add security to your SEO routine and avoid the crisis of losing traffic. SEO is as much about retaining traffic as it is about gaining it.
Read the details of PHP support at the official PHP web page
https://secure.php.net/supported-versions.php
More Resources
- Moving a WordPress Website from HTTP to HTTPS: A Complete Guide
- HTTP to HTTPS Migration: The Ultimate Stress-Free Guide
- Study Shows Web Security Directly Affects SEO
Images by Shutterstock, Modified by Author
Screenshots by Author, Modified by Author





![AI Overviews: We Reverse-Engineered Them So You Don't Have To [+ What You Need To Do Next]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/sidebar1x-455.png)