Google CEO Sundar Pichai finally took action and made significant leadership changes.
Prabhakar Raghavan, who ran Google Search, Ads, Commerce, Geo, Assistant, and Payments, now reports to Pichai as Chief Technologist and hands the Search reins over to Nick Fox.
Pichai announced, “He’ll return to his computer science roots and take on the role of Chief Technologist,” which is Latin for “He messed up, so we’re giving him a role that saves face but has no direct impact on our core business.”
This move is a demotion for Raghavan, most likely as the result of a long series of fumbles across Search and AI.
Unless for personal reasons, who would voluntarily step away from Google’s most important position to “go back to their roots”? It doesn’t track.
The Raghavan era marks one of the hardest periods for Google, leaving behind five areas of struggle:
Monopoly
Google’s stock dropped 14% since its all-time high on July 10, in large part because the DOJ revealed that it would take aggressive action against Google.
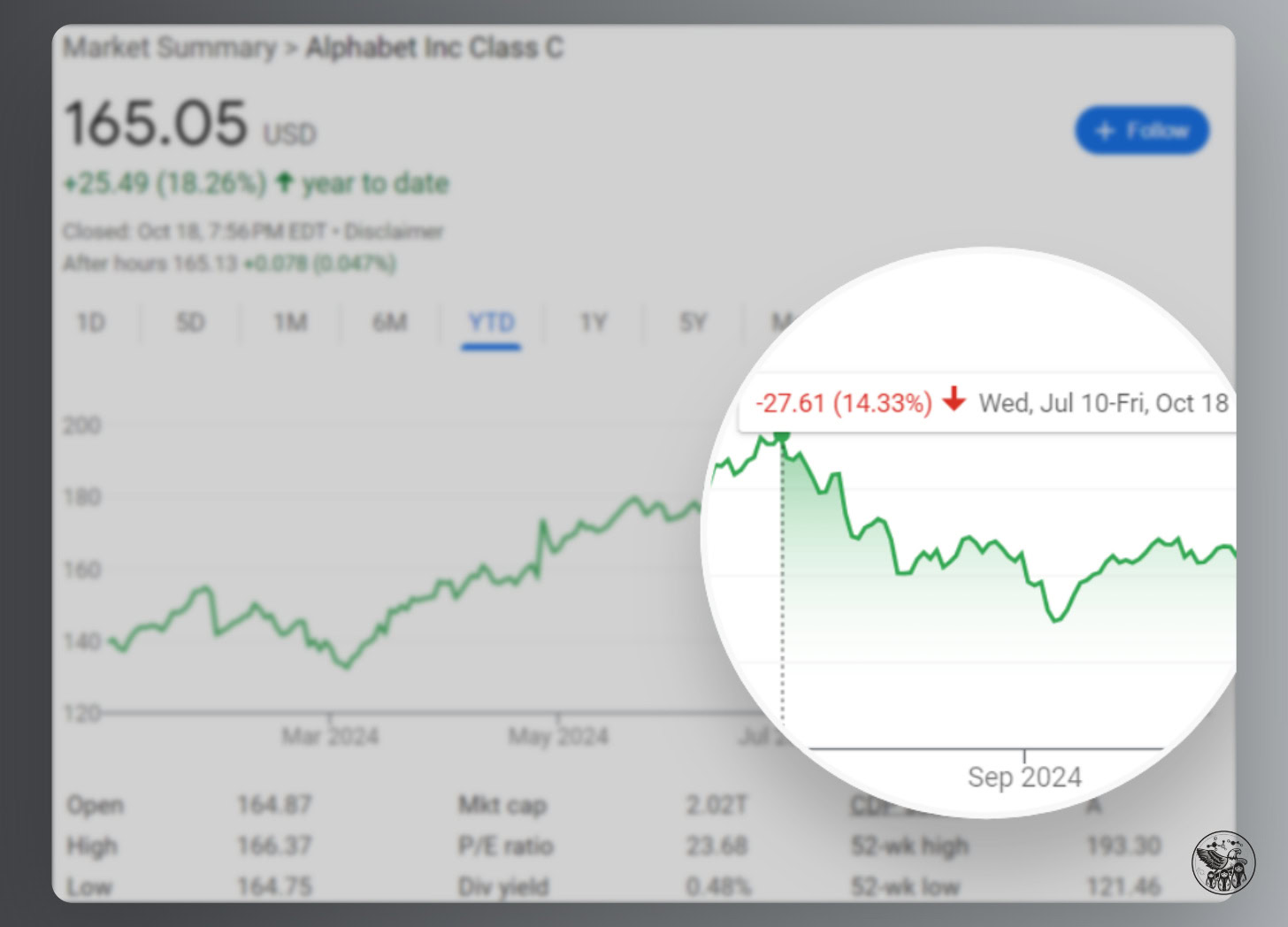 Image Credit: Kevin Indig
Image Credit: Kevin IndigAfter it was originally assumed that the DOJ sought to prevent Google from making exclusive deals with distributors like Apple, a new possible outcome floating around is to break Google up by detaching Chrome, the Play Store, and Android:
Behavioral and structural remedies that would prevent Google from using products such as Chrome, Play, and Android to advantage Google search and Google search-related products and features.1
The DOJ even considers forcing Google to share rank data with competitors:
Barring Google from collecting sensitive user data, requiring it to make search results and indexes available to rivals, letting websites opt out of their content being used to train AI products and making Google report to a “court-appointed technical committee” are also on the table.2
Realistically, the chances of these remedies actually coming into effect are low:
- It will take years for the court and Google to go through several hoops of appeal.
- There’s even a chance that a Trump presidency would veto aggressive remedies.
- Precedents like the case against Microsoft show that the actual remedies are not as severe (Microsoft was ruled to split into two companies but found a settlement).
However, the reputation damage from exposed emails and statements during the lawsuits and bad press marks a turnaround from Google’s polished image.
And, there is a chance that the DOJ will follow through, which could weaken Google’s position in Search.
Search
Search has been heading in the wrong direction. Raghavan’s legacy is too many Reddit results, too many ads, unhelpful results, and cluttered SERPs.
![Google search for [is google going downhill]](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/google-search-99.jpg) Image Credit: Kevin Indig
Image Credit: Kevin IndigGoogle’s Helpful Content Update sought to mitigate overoptimized search results but caused so much collateral damage that the industry revolted against Google until it released an update to the algorithm that specifically aimed to reestablish the search visibility for small and independent sites.
However, the effect was much smaller than expected, with many affected sites only regaining a fraction of their lost traffic.3
An underlying problem with search results quality is the unclear direction or algorithm updates and untransparent and fuzzy guidance of “creating helpful content.”
In that same vein, it also became clear in 2024 that Google reacted to bad press and punished sites like Causal or Forbes, which were called out publicly for questionable practices.
Lars Lofgren uncovered a company within Forbes that also seems to create content on other sites and drives millions in revenue.4 Shortly after, Google seems to have taken at least some action against the site.
Google’s reactions show how important reputation is for the company.
Brand might be Google’s biggest moat, maybe even bigger than all the data it captures, as we can see at the fact of Google not losing market share in Europe after smartphone manufacturers were forced to show users choice screens for browsers and search engines.
From 2 Internets:
However, most users still choose Google despite randomized choices for other search engines since the search engine market share distribution in the EU remains unchanged.
AI
Artificial intelligence terraforms the tech world. Despite Google having invented most parts of the engine, it’s not driving the car. OpenAI is.
According to StatCounter, Google’s market share dropped to 90% for the first time since the drop to 88% in 2013. The drop could be the result of many reasons, and it could revert.
However, it could also mark a shift from Search to generative AI. I don’t see Google giving away market share to Bing or DuckDuckGo but ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Microsoft Copilot.
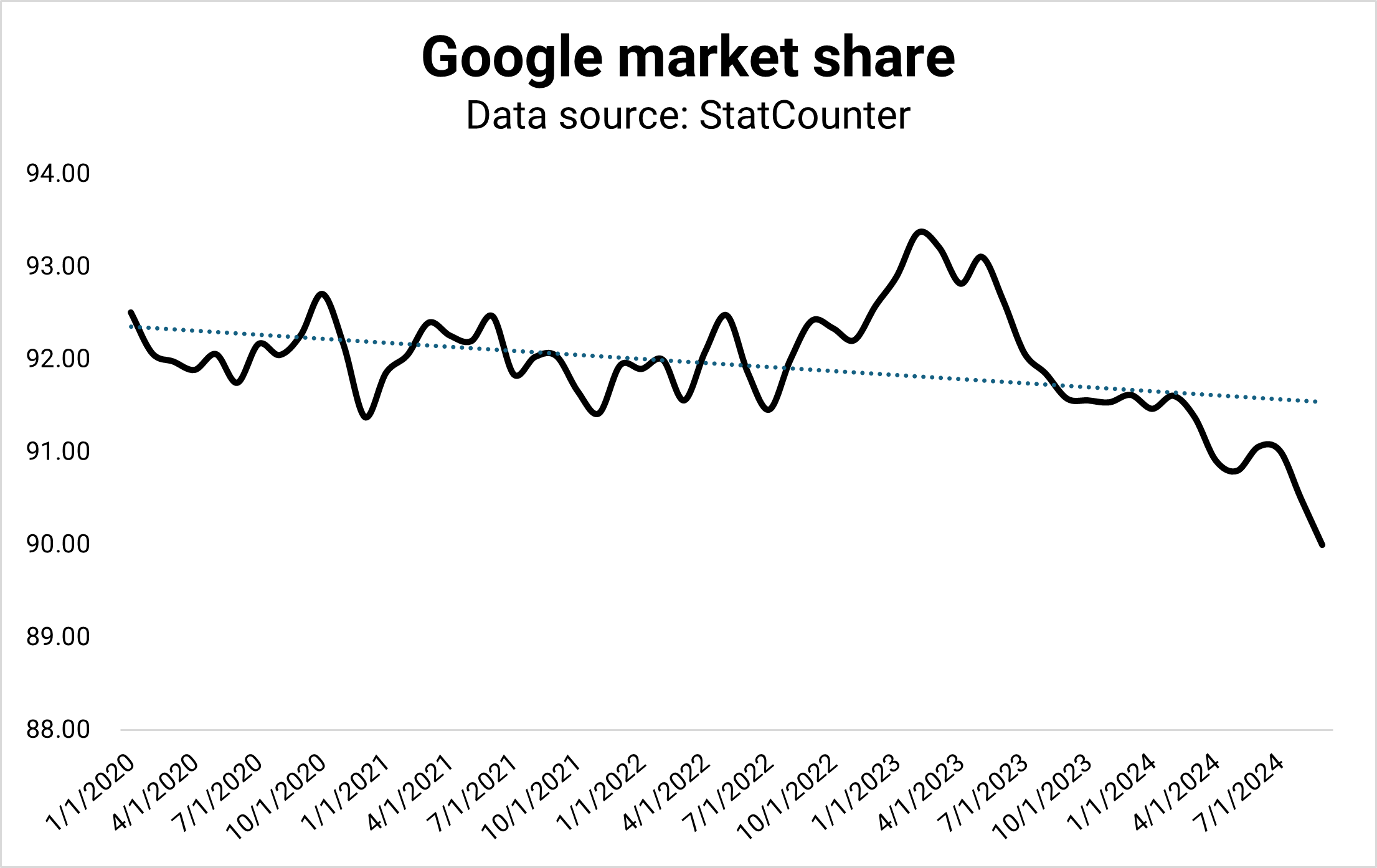 Image Credit: Kevin Indig
Image Credit: Kevin IndigWhile Google maintains a 90% market share in Search, it doesn’t lead in the market of the future: Gen AI.
Gemini was supposed to be Google’s horse in the AI race, but its market share is flattening while Claude and Perplexity are gaining ground – fast.
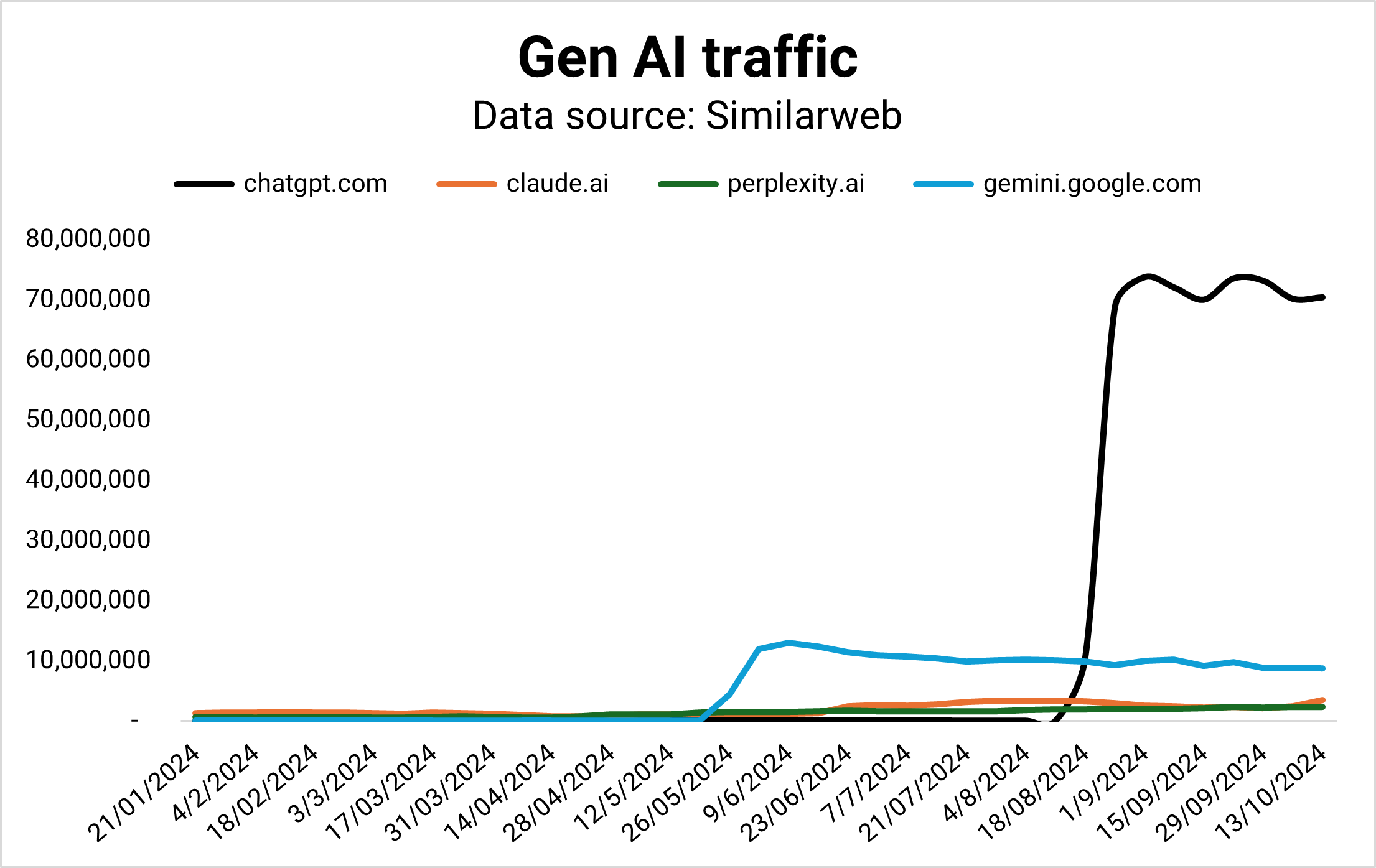 OpenAI is currently winning the Gen AI competition by traffic (Image Credit: Kevin Indig)
OpenAI is currently winning the Gen AI competition by traffic (Image Credit: Kevin Indig)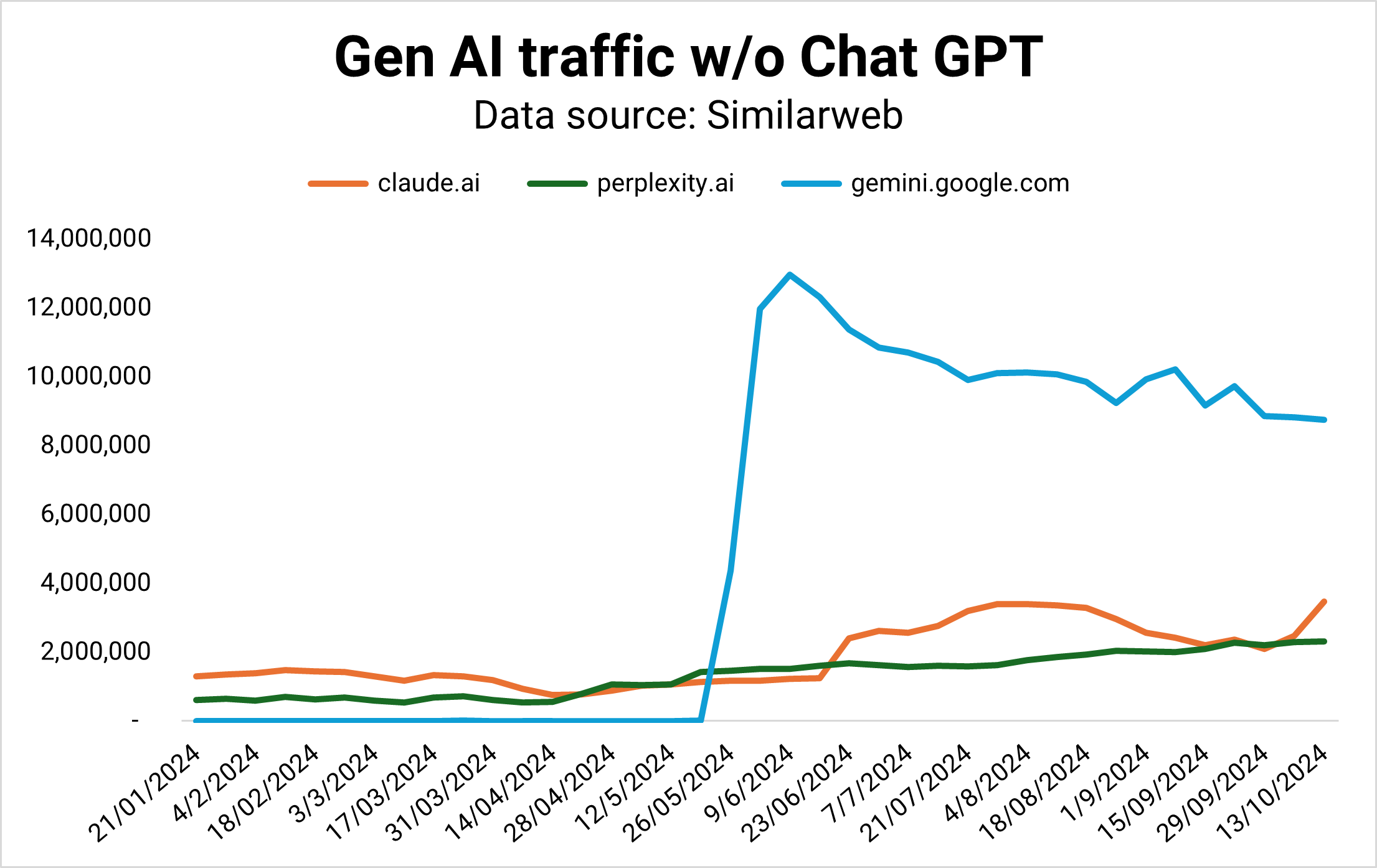 Taking Chat GPT out of the picture, we can see that Gemini is stagnating (Image Credit: Kevin Indig)
Taking Chat GPT out of the picture, we can see that Gemini is stagnating (Image Credit: Kevin Indig)In 2024, Perplexity answered as many queries per month as it did in the whole year of 2023. The number is still small compared to Google, but the trend is growing.
A series of painful fumbles – from diverse Nazi pictures to fake demo videos and misinformation – mark Google’s chase to keep up with the competition.
From The Big Disconnect:
Then there are fumbled AI product launches. Google’s first reaction to ChatGPT’s stunning success was a stunning failure. The introduction of Bard in February 2023 cost Alphabet $100 billion in market value due to false facts in the announcement.
In December 2023, an impressive demo of Gemini turned into a PR disaster when it turned out to be fake.
In March 2024, Alphabet’s shares dropped by -5% when it turned out Gemini delivered heavily biased and obscure historical images.
Google wants to get AI right so badly that it’s willing to cut corners. Not something you’d expect from the company that invented the underlying LLM technology (Transformers) in the first place.
Former CEO Eric Schmidt’s opinion about the cause of Google’s struggles didn’t help the situation:
“Google decided that work life balance and going home early and working from home was more important than winning. And the reason startups work is because the people work like hell.”5
Google’s AI Overviews are the antithesis of the classic search model. Early referral traffic data from gen AI like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity shows a tiny amount of users clicking through to sites.
If that’s any indication of what we can expect from AI Overviews, Google is turning from a click distributor to an engagement platform.
Advertising
The big question for Google shareholders is how well the company can navigate advertising in the new LLM search world.
Ads can be complementary to search results. But, when users get the answer directly, sponsored results distract from the experience. The old ad format might not fit the new mold. Google has to figure this out but has not yet delivered an innovative approach.
AI transforms digital advertising across creative + copy, matching/targeting, and spend optimization.
However, with more AI Overviews answering questions in the search results, users might need fewer queries to solve problems overall, shrinking the ad market for Google.
Google is projected to hit an all-time low of less than 50% of available ad dollars next year. Strong challengers like Amazon and TikTok and long-term rivals like Meta are grabbing market share.
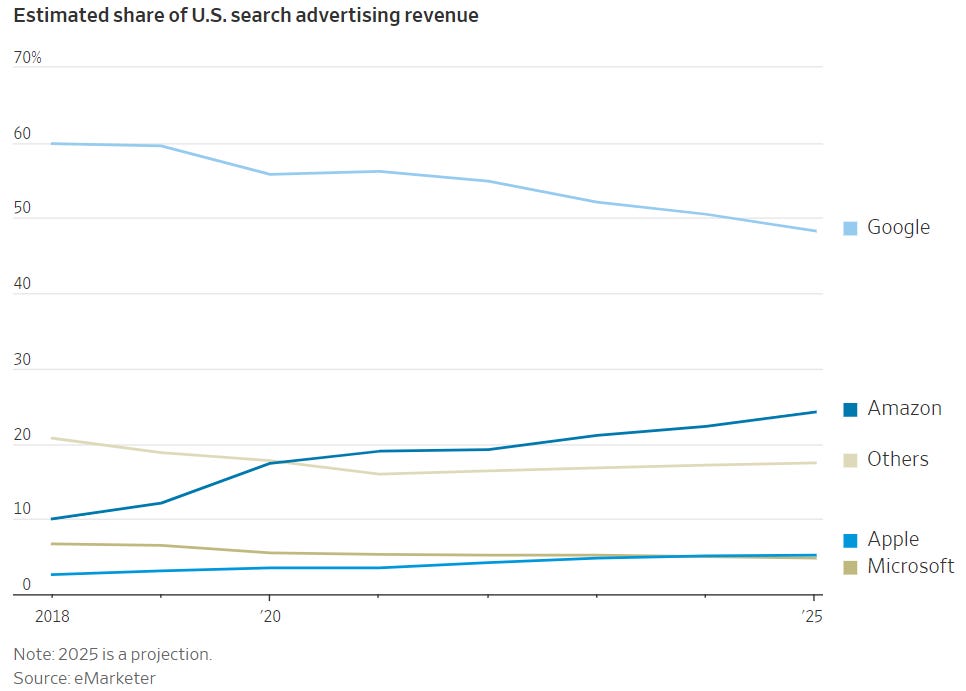 Google is projected to hit less than 50% ad revenue market share in 2025 (source) (Image Credit: Kevin Indig)
Google is projected to hit less than 50% ad revenue market share in 2025 (source) (Image Credit: Kevin Indig)Ecommerce
Google announced a new shopping experience with little to do with a classic search engine.
The reimagined ecommerce experience shows how hard Google wants to compete with Amazon, which faces more competition from TikTok.
As a result, TikTok is competing not only with Google in search but also with ecommerce.6
The focus on ecommerce indicates the opportunity for Google to make money from high-intent searches when users don’t need to click through to sites anymore for answers.
But Google wasn’t able to ever kick Amazon off the throne, leaving it exposed for commercial queries.
Conclusion
We can only hope that Prabhakar’s departure leads to a better Google Search. Nick Fox, who will succeed Raghavan, might not be the change agent we seek.
In an email thread with then Head of Search Ben Gomes from 2019, Fox seems open to taking on revenue goals but also not an advocate for it.7
To Ben Gomes’ concern:
“…I think we are getting too involved with ads for the good of the product and company…”
Fox responds:
“Given that (a) we’re responsible for Search, (b) Search is the revenue engine of the company, and (c) revenue is weak, it seems like this is our new reality of our jobs?”8
However, I question how important Fox is for the future of search anyway. The more important person is Demis Hassabis, founder and CEO of Deep Mind.
Every leadership change brings with it an opportunity to move to a better formation.
With Raghavan’s “promotion” come two important shifts: Gemini moving under Deep Mind, and Assistant moving to the devices team.
Hassabis is the person we need to watch because he now runs Gemini and with it, the quality and volume of AIO answers.
On the talking track, Hassabis stresses the need for responsible use of AI.
How that manifests remains to be seen.
Boost your skills with Growth Memo’s weekly expert insights. Subscribe for free!
1 US Weighs Google Breakup in Historic Big Tech Antitrust Case
2 US plan to break up Google’s search dominance threatens profit engine, AI growth
3 What to know about our August 2024 core update
4 Forbes Marketplace: The Parasite SEO Company Trying to Devour Its Host
5 Former CEO Eric Schmidt explains why Google fumbled its lead in AI [YouTube Video]
6 Google Shopping’s getting a big transformation
Featured Image: Paulo Bobita/Search Engine Journal





![[SEO, PPC & Attribution] Unlocking The Power Of Offline Marketing In A Digital World](https://www.searchenginejournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/sidebar1x-534.png)